Accounting Applications
Banana Accounting Plus offers various easy to use and professional applications, inspired by Excel, that allow for instant results.
The accounting Apps use an accounting calculation, planning and reporting engine, based on the Double-entry accounting method and offer several common features.
Income & Expense accounting
- Cash Manager (previously Cash Book)
For management of a single account, with the possibility of classifying income and expenses by category. - Income & Expense accounting.
To manage comprehensive accounting with various balance sheet accounts and categories, to which income and expenses are attributed.
This is a simplified mode of use, that doesn't require knowledge about Debit and Credit. There are also Balance Sheet and Income statement reports.
Double-entry accounting
- Double-entry accounting with or without VAT options
Comprehensive accounting solution, according to the Double-entry method. Transactions are classified by indicating the Debit and Credit account. The financial statements are complete with Balance Sheet, Income statement, Journal and Account cards. - Multi-currency accounting with or without VAT options
Double-entry accounting offering the possibility to manage accounts in different currencies:- Accounts for customers and suppliers, in various currencies.
- Transaction with current, historical or freely set exchange rate.
- Invoices in the currency of the customer's account.
- Balance sheet and account movement in base currency or that of the account in foreign currency.
- Calculation of unrealized exchange gains and losses (exchange rate differences).

Invoicing integrated in accounting
- Invoice entry as normal transaction rows.
- Columns for different contents, related to invoices.
- With or without VAT.
- Ability to edit and correct.
- Printing of a single invoice or bundling of several invoices via a simple command.
- Choice of different print print formats available. and customizable.
- Exports in digital format via Extensions.
- Customizable recalls and account statements.
VAT management
Any national specifications supported:
- VAT code table to indicate the different VAT rates and case studies. Any VAT transaction supported.
- Automated VAT calculation, net or gross..
- VAT control reports.
- Electronic transmission of VAT data on the VAT platform of the Swiss Confederation.
- National extensions for VAT reporting based on the requirements of tax authorities.
Financial Planning
- For existing companies or startups.
- Inclusion of budget by means of transactions in budget.
- Automatic assumption of repetitive expenses or income (rent, wages, bank charges, etc.).
- Possibility to indicate item code, quantity and price.
- Javascript calculation formulas to automate the dependent values (calculation of interest on the actual use of a loan).
- The program automatically sets up financial plans, complete with liquidity planning, balance forecasts, balance sheet and provisional income statement and movements on an account.
- Automatic financial projections for several years.
- Choice of display per period.
- Comparison between Budget and Finalized Balance Sheet.
Features for accounting applications
The various accounting applications provide different functionalities.
These features can be activated or added as per your requirements.
The program is easily applied because, if a feature is not used, it is not activated.
Accounting setup
- Works in any currency. The currency symbol is chosen from the list or freely set.
- Possibility to alter the number of decimals (generally 2), from 0 to 12 decimals to manage crypto-currencies.
- Accounting period is set freely, either as a calendar year or with a start and end date different from the calendar year.
- Choice of accounting language.
Files and data saving (similar to Excel)
Applicable to all Banana applications:
- Create new file starting from preset templates or from own files.
- The data for an accounting year are saved in one single file.
- The file can be located on any media, computer, network, cloud or sent by email.
- Possibility to manage unlimited number of accounting files, of any kind.
- Data is accessible to multiple users simultaneously, but to one person only when in edit mode.
Chart of Accounts
- Plan and structure of accounts are fully customizable.
- Numeric or alpha-numeric account and group number.
- Possibility to add notes or further columns.
- Grouping and totals are adaptable and according to any nationally required grouping scheme.
- Balance, account movement and totals are displayed and updated in real time.
- Cost and profit centres, for detailed control of costs and revenues of specific activities or projects.
- Segments for reporting by sector (branch), thanks to Segments.
- Customer details with monitoring of pending invoices, reminders and account statements.
- Supplier statements with monitoring of paid and pending invoices.
- Management of customers and suppliers, also as non-Balance Sheet accounts (with cost centre) for accounting managed with the cash method.
- Off-Balance sheet accounts.
Transactions
- Single or collective transactions (on multiple rows).
- Accrual or cash method.
- Use of Excel type interface, select, copy and paste, add lines, search and replace.
- Suggestions, auto-complete and memorization of repetitive operations for faster input.
- Automatic or customized numbering of documents.
- Ability to edit data entered, organize or add columns and any other information.
- Link to files of receipts in digital format (pdf, images) and opening of documents by a click.
- Import of data from bank statements:
- Several formats are supported.
- Possibility to complete or remove imported operations.
- Row colouring.
- Possibility to have different displays of columns.
- Contextual information concerning account balance, differences or errors.
Blockchain for data protection
- Protection of movements entered with digital data certification technology (similar to Bitcoin).
- Compliance with legal requirements.
- Transfer of data to auditor with the certainty of impossibility of tampering.
Standard and customized reports:
- Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Journal, Account cards.
- Customization and saving of print settings.
- Export and link data to Excel.
Charts
- Overview of account evolution.
- Comparison of Budget and Final Accounts.
- Real time display while entering.
Check Accounting
- Check accounting command. In one click, the accounting is recalculated as if all transactions were inserted again.
- Any erroneous settings, differences or errors will be reported.
- Each report is linked to a help page that explains the causes and provides the solutions.
- Possibility to correct anytime.
Year-end closing and Creation of New Year
- Automatic process for creating new year files, with report of balances and profit or loss.
- You may start working on the new year, even if you have not closed the previous one.
- Command to report the final balances when the previous year has been closed.
- Possibility to add and print year-end notes.
- Command for archiving all data and printouts in pdf format.
Various
- Creating new files starting from an existing file.
- Converting from one accounting type to another, in order to grow and add functionalities.
- Adding other tables:
- Items Table
- Serves to indicate items to be included in invoicing.
May serve as a small inventory or securities management.
- Serves to indicate items to be included in invoicing.
- Documents Table:
- To store images (company logo) or text documents (for example Javascript programs).
- Other tables:
You can add tables where you may enter notes or other information. Tables can be customized by adding columns to them.
- Items Table
XBRL Report
Ability to create instances of XBRL files suitable for different countries.
Double-entry accounting
Double-entry accounting is an application of Banana Accounting Plus, to manage your accounts with great professionalism. It is free up to 70 transactions, in the Free plan of Banana Accounting Plus. In the Professional and Advanced plans it is instead unlimited.
Ideal for SMEs, experienced accountants and frequent bookkeepers. Work fast and get the Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss statement, Financial Planning, Budget and many other reports in no time.
Many complex operations, such as VAT management, multi-currency, budgeting and profit and loss accounts have been made very simple because they are all automated.
- ▶ Video: How to start double-entry Accounting
- Discover all the double-entry Accounting characteristics

Many functions, more automation
- Start Immediately: Choose one of many templates for diversified needs.
- Quick entries: Import from ebanking, store repetitive transactions with Auto-completion rules.
- Immediate checks: With the Balance column you can quickly see if there are any imbalances between the Debit and Credit columns and from which line the differences start.
- Balances updated after each entry, with an indication of the result for the year.
- Attach documents quickly: link each transaction to its digital document.
- Data import and export
- Balance sheet and Profit and Loss statement, Account cards (ledger), Journal in one click
- Analytical accounting for projects, sectors or particular activities thanks to Cost/Profit Centres and Segments
- Automated account cards (ledger). The carry forward of amounts is automatic after posting in the journal (Transactions table).
- The Balance Sheet and the Income statement can be displayed instantly with a click and you can choose either a simple structure with the grand totals or a more detailed structure, with intermediate totals for the subgroups .
- To register VAT, you do not need to enter an additional transaction, but simply enter a code that allows to calculate the VAT amount and to record it simultaneously in the VAT account.
- Automated VAT statements with data in Xml for online submission to tax authorities.
- Create budgets for financial and income planning and ensure an uncertainty-free future.
Learn more
- Organizing your accounting documents
- Accounting with accrual or cash method
- VAT management
- Multi-currency accounting
Starting a Double-entry accounting
▶ Video: How to start a Double-entry accounting file. Find out how to easily set up a Double-entry accounting, adapt the Plan of Accounts, import bank transactions easily or insert transactions manually, set up a Budget, enter the Transactions and Print reports.
Creating an accounting file, starting from a template
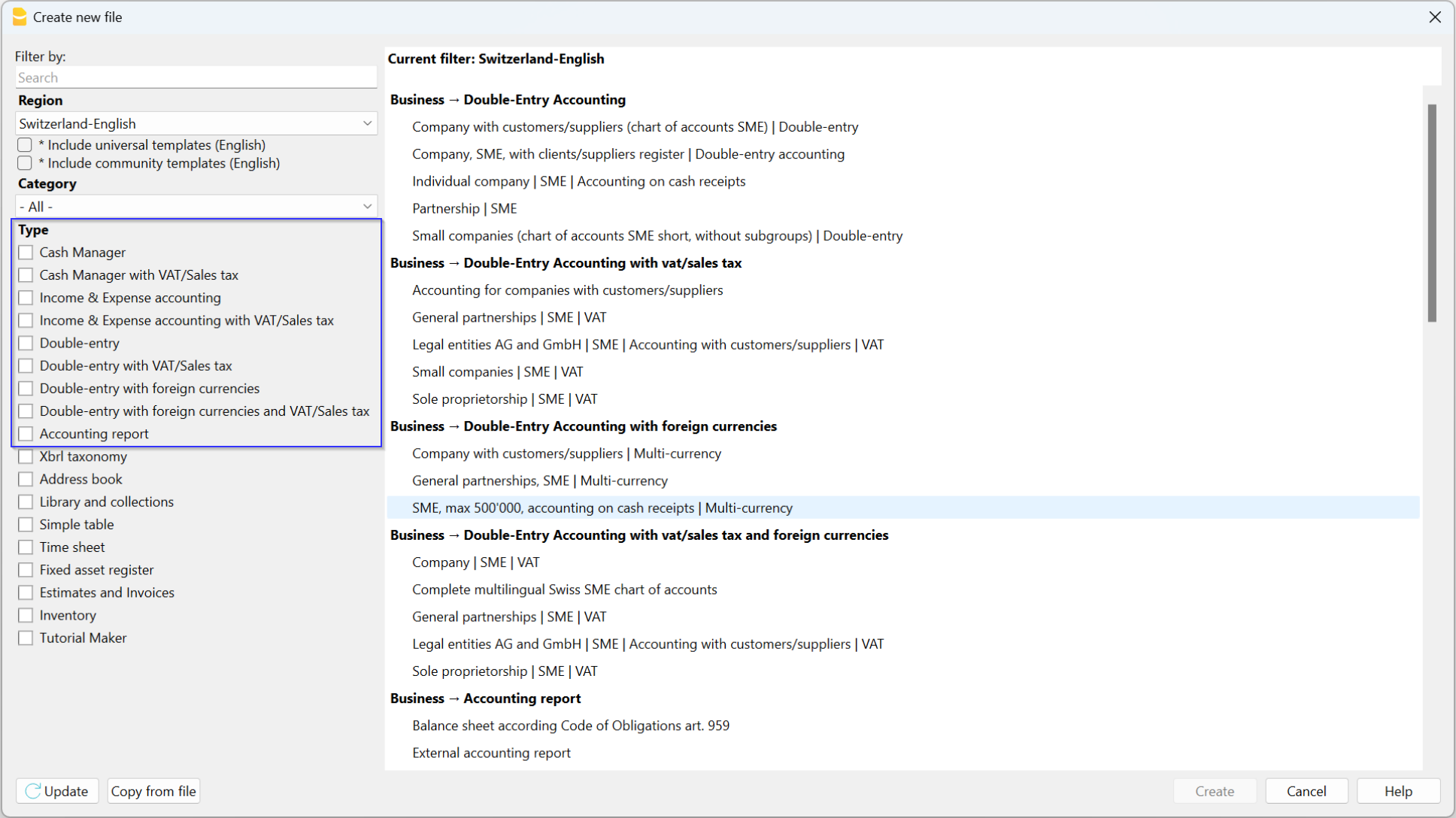
Banana Accounting Plus includes templates for all legal forms, divided by country and by category. They can be opened directly in the program, from the File menu, New... command, or they can be downloaded from our Templates page.
Here is how to start choosing a template directly from the program:
- File menu, → New...
- Select the region, the language, the category and the accounting type.
- From the list of the templates that appears, select the template that is closest to your own needs.
- Click on the Create Button.
In the Search area, when entering a key word, the program will display the templates that contain the entered key word.
It is equally possible to set out from a blank file, by activating the Create Empty file option. However, in order to facilitate the start and avoid grouping errors, we recommend that you always start with an existing template.
More information on the Create New File page.
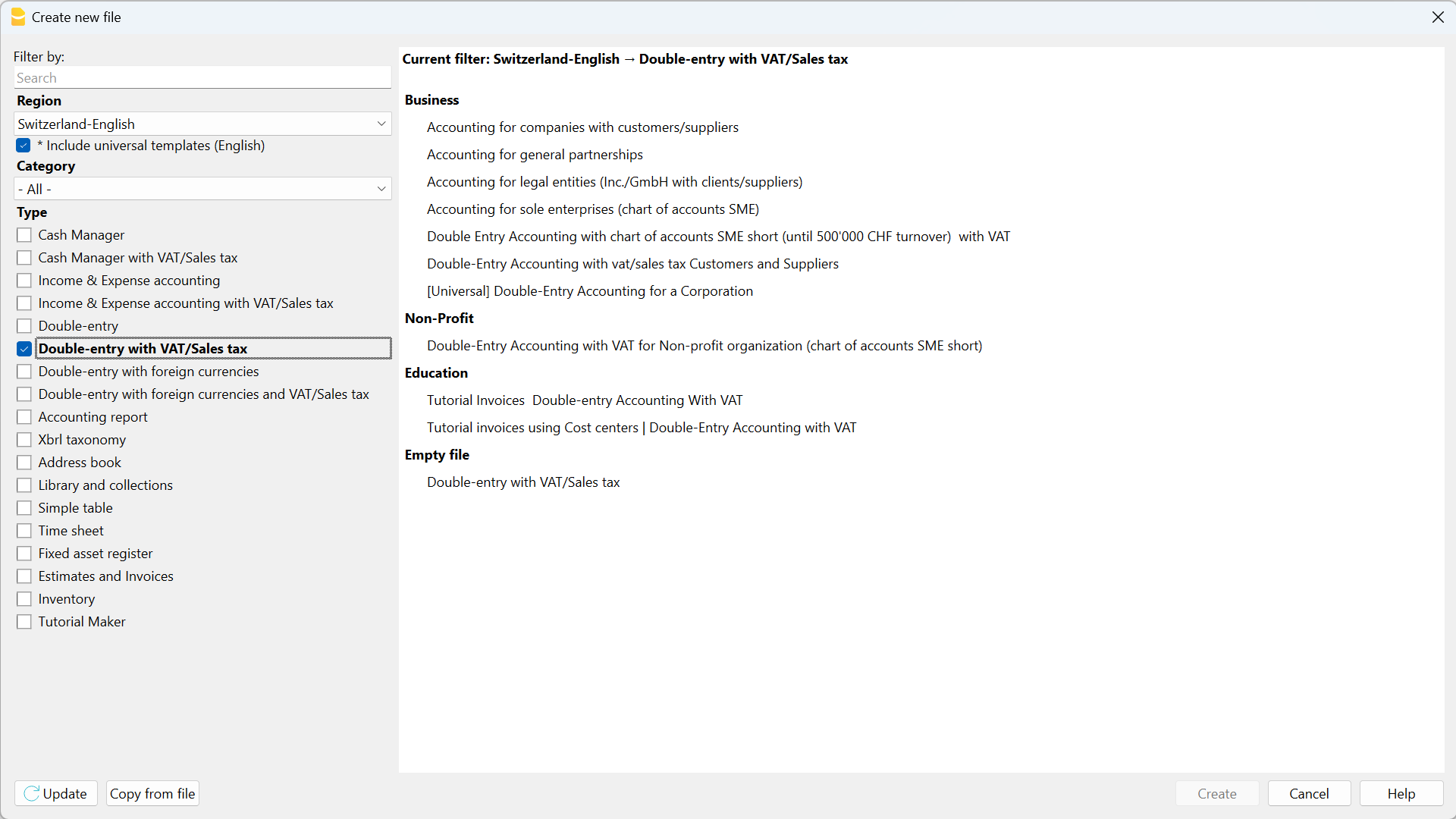
Setting up the file properties (basic data)
- Via the File → File and accounting properties command, indicate the company name that will appear in the headers of the printouts and on other data.
- Select the base currency, in which the accounting will be kept.
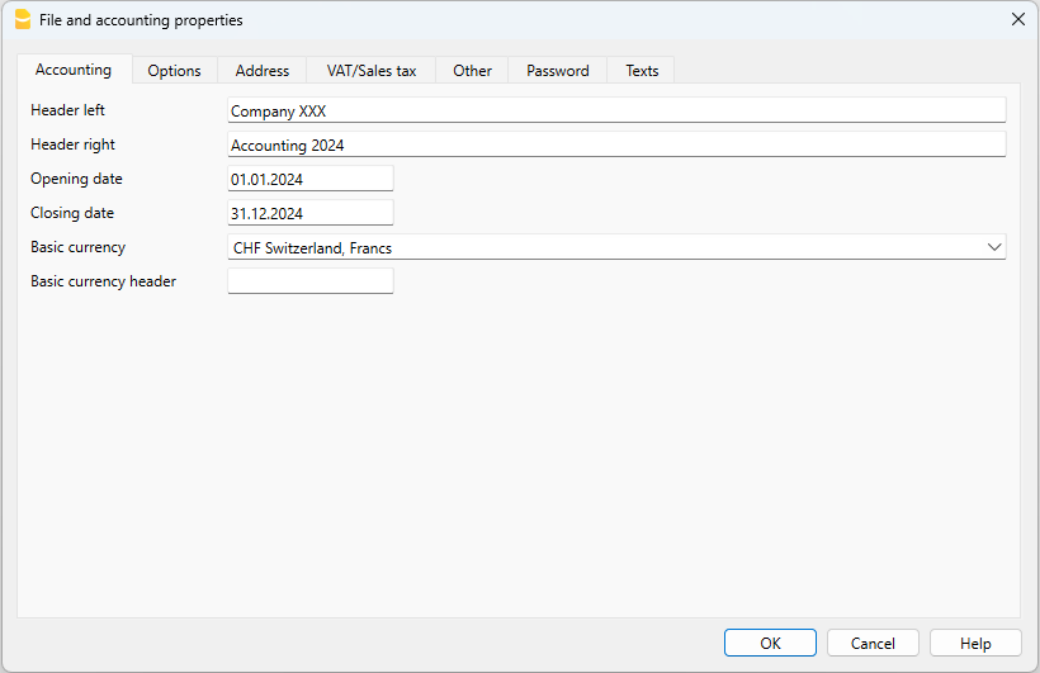
Save to disk
With the File → Save As command, save the data and also assign a name to the file. The typical save dialog of your operating system will be displayed.
- It is advisable to use the name of the company followed by the year "ie. Company-2020.ac2." to distinguish it from other accounting files.
- You can keep as many accounting files as you need, each will have its own name.
- You can select the path you want, (save to disk, usb key or cloud).
If you plan to have documents linked to the accounting of the current year as well, we recommend creating a separate folder for each accounting year in which to group all the files. Please also visit the Organizing your files page
General use of the program
Banana Accounting Plus is Excel-inspired. User commands are kept as similar as possible to the ones of Microsoft Office.
For more information on the general use of the program, please visit our Program interface page.
Customizing the Chart of accounts
In the Accounts table, customize the Chart of Accounts and adapt it to your own requirements.
It is possible to:
- Add new accounts and /or delete existing ones (see Adding new rows)
- Modify the account numbers, the description (fe. enter the name of your own Bank account), enter other groups, etc.
- Create subgroups, please consult our Groups page.
- Define Cost centers or Segments that are used to catalogue the amounts in a more detailed and specific way.
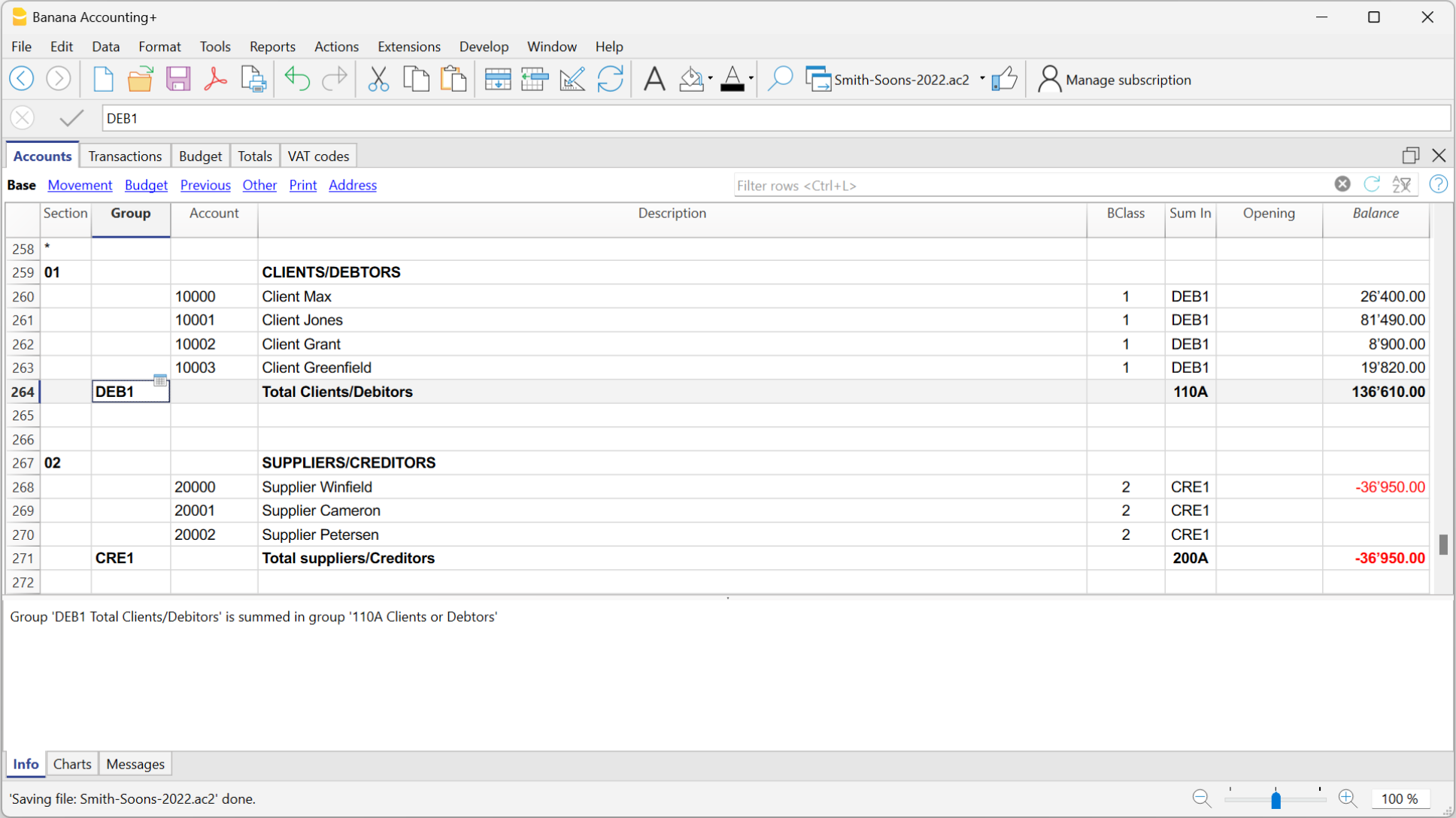
The Transactions
Transactions must be entered into the Transactions table and they compose the Journal.
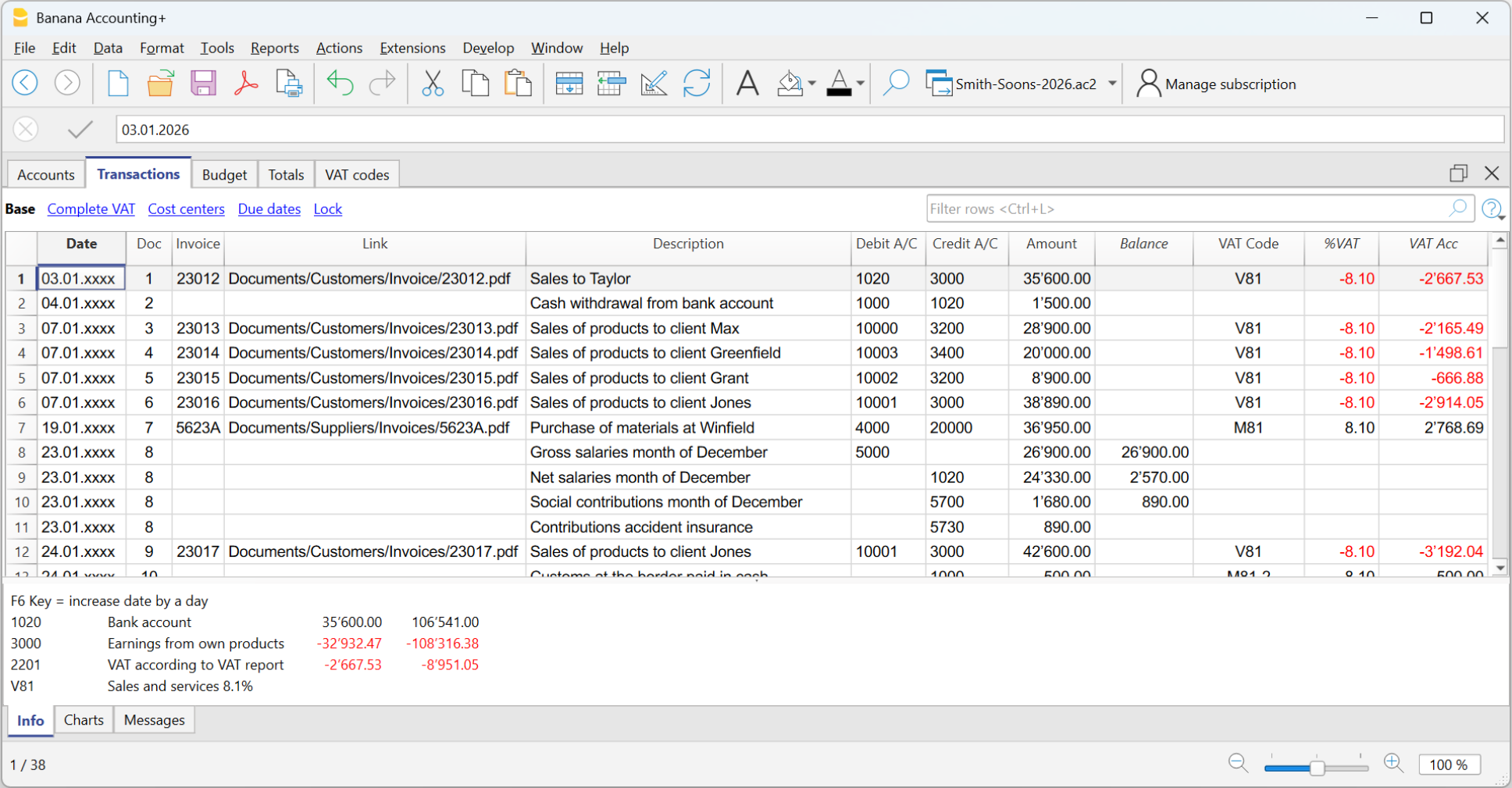
In the specific columns :
- Enter the Date
- Enter the Document number, manually assigned to the paper document. This allows for easy location of the documents once the accounting transaction has been entered.
- Enter the Description
- Into the Debit account column, enter the destination account.
- Into the Credit account column, enter the account of origin.
- Enter the Amount.
- In the accounting with VAT, enter the gross amount and VAT code. The program will separate the VAT, splitting the net cost or net income.
Make visible the Balance column in the Transactions table
The new Balance column is a very useful feature: it allows you to immediately spot possible differences.
The Balance column is not visible by default: you can make it visible via the Data → Columns setup menu.
Speeding up the recording of the transactions
In order to accelerate the recording of the transactions, you can use:
- Smart fill - allows for auto-complete of data that has already been entered previously.
- Recurring transactions - memorizes repetitive movements in a table and can be called up when necessary.
- Import transactions from bank or postal statement - imports all transactions from the bank, postal or credit card statement into the accounting file.
Transactions with VAT
In order to enter transactions with VAT please proceed as follows:
- Select Double-entry accounting with VAT/Sales tax in the File → New... menu.
- Choose one of the existing accounting templates with existing VAT Codes table, containing all prevailing VAT codes.
In order to enter transactions with VAT, please visit the Transactions page.
Transactions on multiple rows
Compound transactions, those that concern debits and / or credits to multiple accounts (e.g. when paying different invoices from the bank account) must be recorded on several rows:
- One row for each debit and / or credit account.
- When all the debits and credits have been entered there must be no differences.
For more details, consult the page Composed transactions.
Checking customer and supplier invoices
Banana Accounting allows you to keep track of invoices to be collected from customers and paid to suppliers. Further details are available on the following web pages:
The Account cards
The account cards automatically display all the transactions that have been recorded on the same account (e.g., cash, bank, clients, etc).
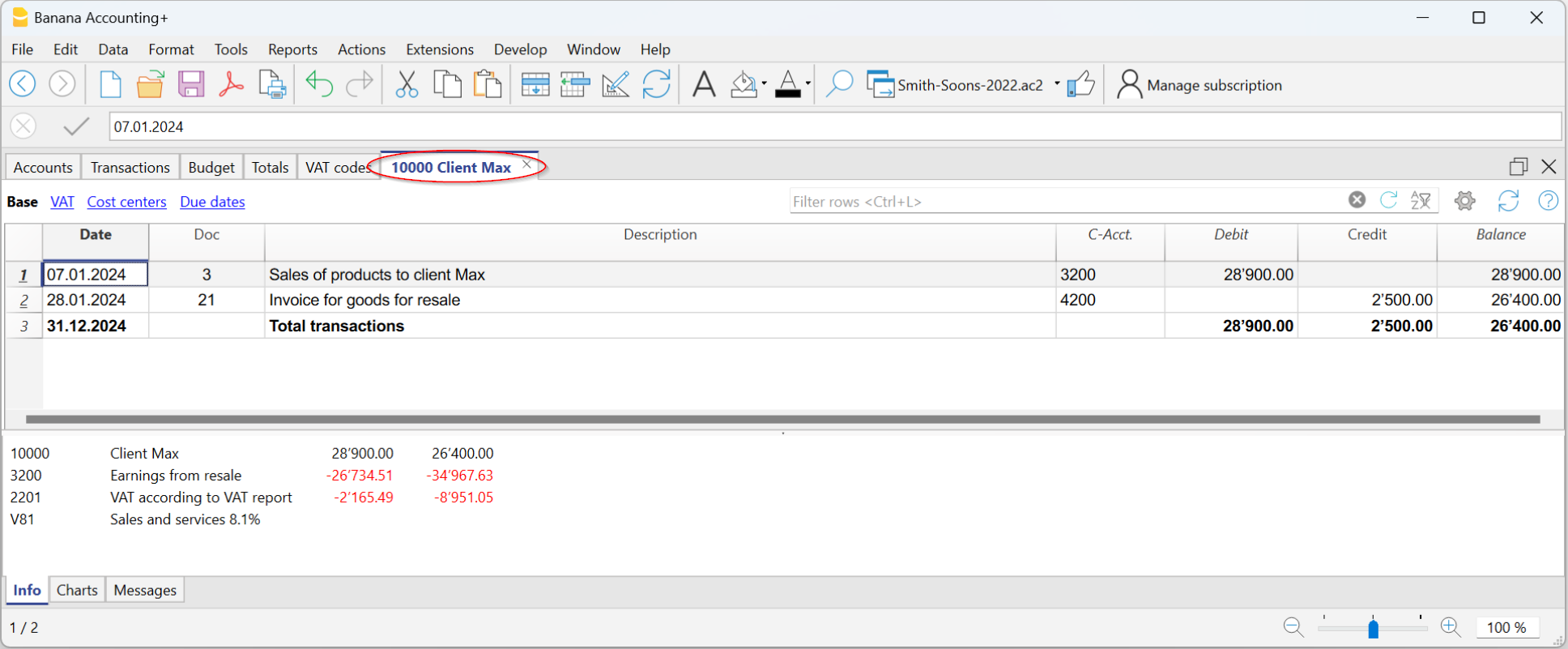
To display a single account card, just position yourself with the mouse on the account number and click on the small blue icon that appears in the cell.
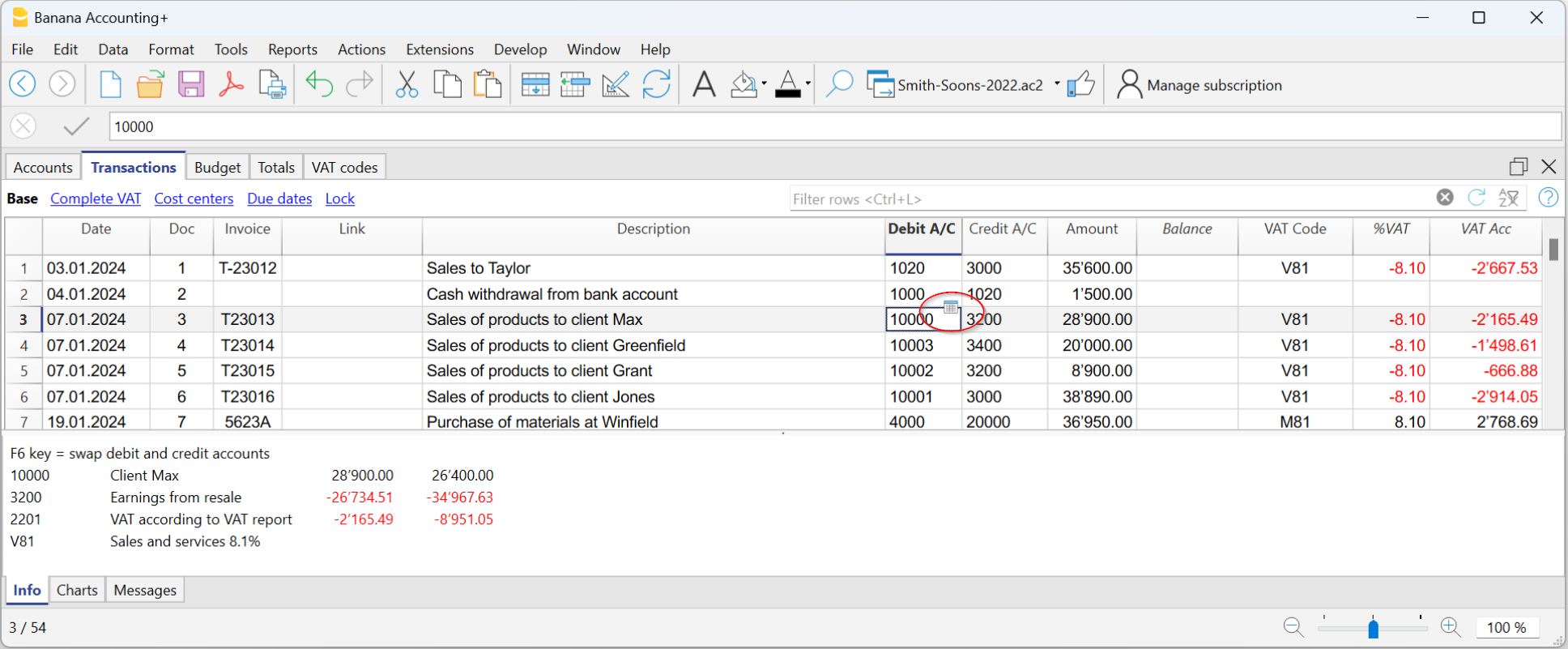
Account card by period
To display the account card with the balances referring to a specific period, proceed as follows:
- Menu Reports → Account Cards.
- In the Period section, activate Period selected, by entering the start and end date of the period.
For more details, consult the Period page.
Printing one Account card
In order to print a single account card, just display the card from any table (Accounts or Transactions) and launch the print from on the File menu.
Print all or some account cards
To print all or some account cards, proceed as follows:
- Menu Reports → Account Cards,
- Select the account cards to print:
Using the filter in the window, you can automatically select all accounts, cost centers, segments, groups or you can simply select the desired accounts only.
For more details, consult the Account Cards page.
The Balance Sheet
The Balance sheet displays the balances of all the Assets & Liabilities accounts and determines the Equity capital.
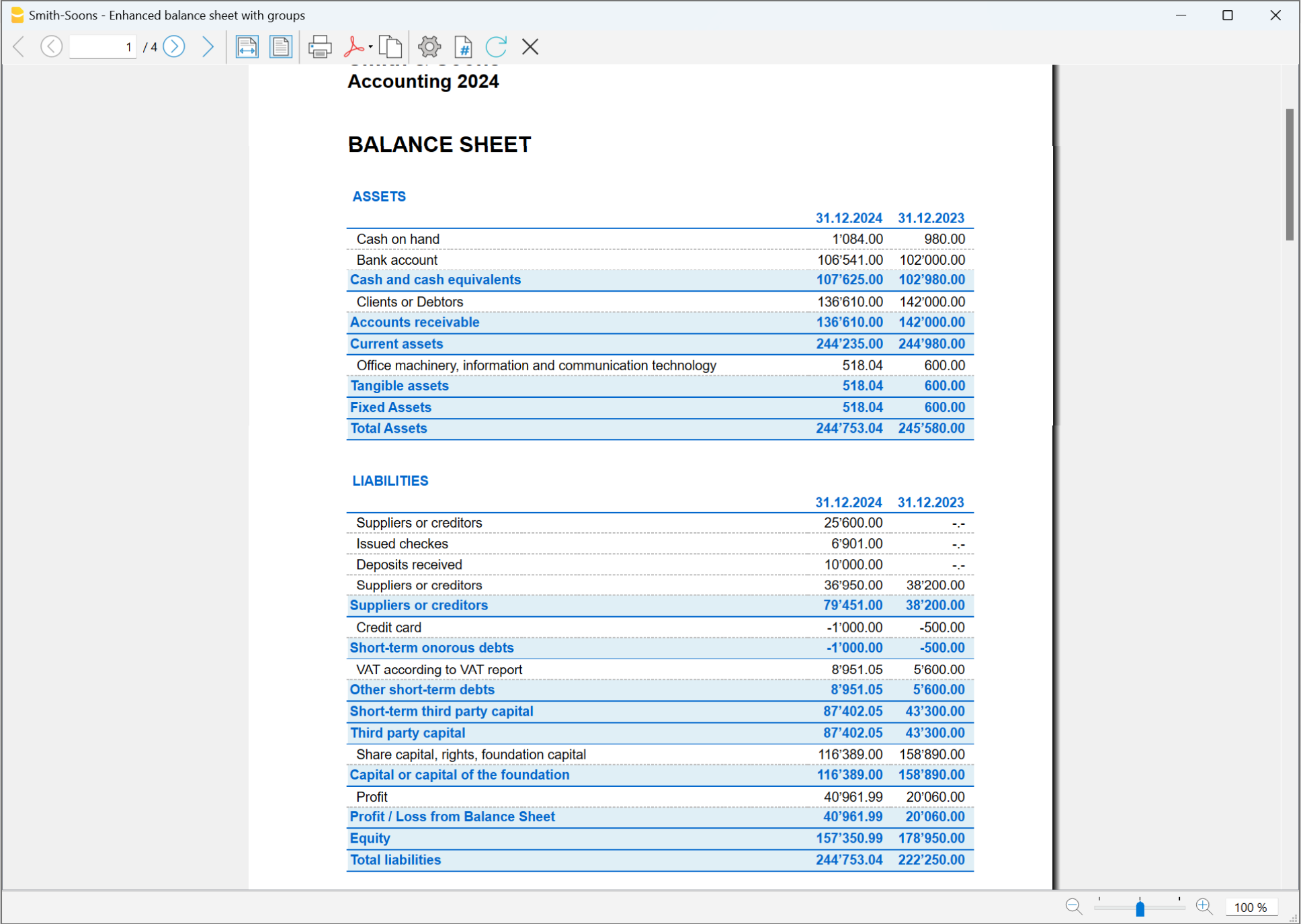
The Profit and Loss Statement
The Profit & Loss statement displays all the Expenses and Income accounts indicating the Profit or Loss of the Accounting year.
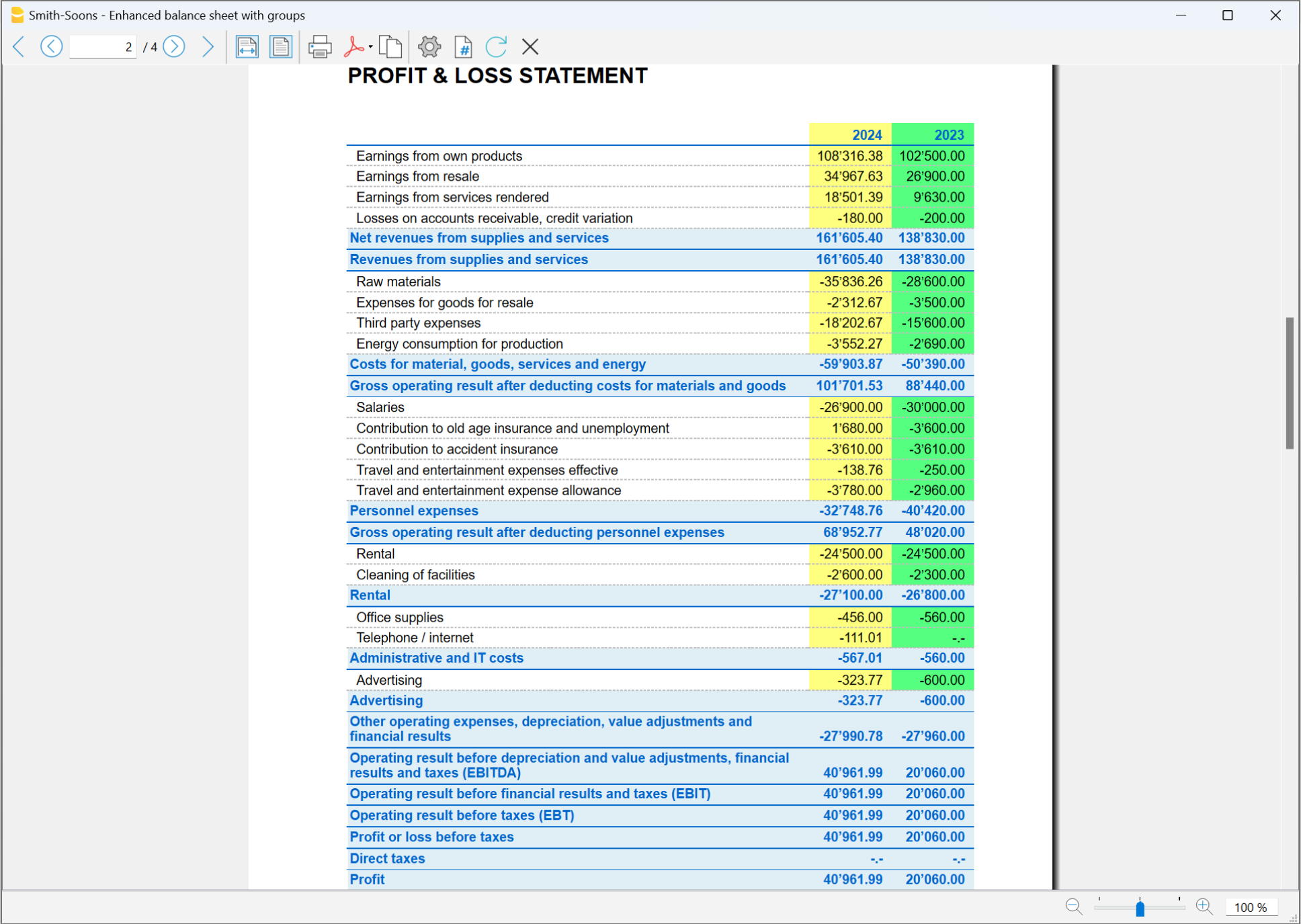
Printing of the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement
In Banana Accounting, the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement can be printed and viewed in two different ways:
- In Enhanced Balance Sheet mode, a balance sheet with a simple listing of all accounts is displayed, without distinction of Groups and Subgroups.
- In Enhanced Balance Sheet mode with groups, the balance is displayed with the accounts divided into groups and subgroups; in addition there are many features to customize the presentation that are not included in the Enhanced Balance sheet.
To print the Financial Statements and the Income Statement in the two modes:
Data archiving in PDF format
All the accounting data can be archived at the end of the year, when the entire accounting has been completed, corrected and audited, :

The Budget
- Annual budget is set in the Accounts table, Budget column. The annual budget amount is indicated for each account. In this case, when the Budget is elaborated via the menu Report → Enhanced statement with groups, the budget column displays the amounts that refer to the entire year.
- Budget is set in the Budget Table. The Budget table is activated via the Tools → Add/Remove functionalities menu.
This table records all the movements referring to expenses and income, as if the movements were to be recorded in the Transactions table. When this table is switched on, the Budget column of the Accounts table is automatically deactivated.
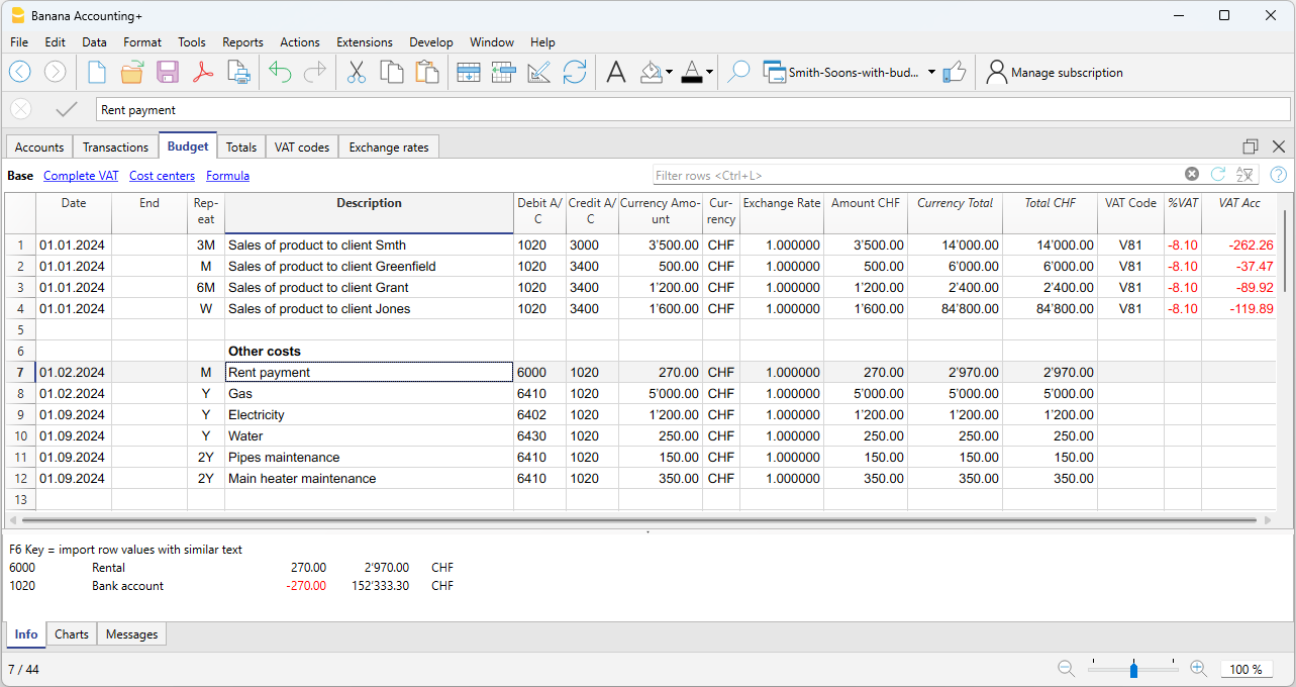
For more details, consult the Budget page.
Characteristics of the Double-entry accounting method
The double-entry bookkeeping application meets the professional criteria for companies and entities of any kind, where accounting is required by law.
- It is a very powerful tool, but is very flexible and easy to use at the same time, as the different features can be activated or deactivated. This allows you to manage both the main accounting as well as structured Chart of Accounts on several levels: with VAT, customer and supplier management, invoicing, cost centers and segments.
- It can be edited at any time, offering everyone perfect results. It is ideal for the experienced accountant who wants to work quickly as well as for beginners. For this reason it is used for teaching accounting in many schools.
▶ Video: How to start a Double-entry accounting
Similar to Excel
Excel-like features and commands
- All the data you enter in the tables are always on display and close at hand.
- You work quickly because you can select, copy and paste recurring transactions on multiple cells and multiple rows.
- If you make a mistake, you can correct it by canceling or restoring operations.
- Add as many rows as you want without limits, or delete the lines you don't need.
- If you have made a mistake on a a value, an account, a VAT code, a description, you are able to correct it in an instant with the Find and Replace function.
- You don't need to enter formulas because the calculations are updated instantly and you have a contextual view (like in spreadsheets).
- Everything you see can be printed or exported to pdf or other formats.
- You can set your company logo to customize the printout headers.
- The columns are customizable, you can move them to position, add new ones and change their width.
- Work with the format that suits you best.
- Colour the lines to immediately identify the transactions that you need to review or show to the accountant or that need to be completed.
Spreadsheet-based
Accounting management is concentrated in three tables, which are used in a similar way to the Excel spreadsheets, but that are already completely set up and programmed with everything needed to keep your accounting quickly and safely.
- Accounts table.
Set up all liquidity accounts, customers, suppliers, etc. and enter the opening balances without having to enter them manually in the Transactions table. You can aggregate multiple accounts, such as the cash accounts, bank or post in the liquidity group, so as to have the updated balances and they can be checked immediately. - Transactions table.
The centre of keeping accounts, where the transactions are entered or imported. The debit and credit transactions can be completed with additional information to manage customers and suppliers, issue invoices, manage cost / profit centers, segments, quantities and prices and anything else you need. Scrolling through the table you will have a comprehensive view of all the events. It can be modified in order to always keep accounting in perfect order. - Totals table.
This displays the totals by Group and is used to check the accounting balances.
Further tables can be added to support additional functionalities.
- Budget table.
Prepare financial forecasts, with the double-entry method. Complete with liquidity planning, budget and forecast income statement, customer, supplier, investment, project, segments for one or several years. - VAT codes table.
Set the required rates and parameters to be used in the Transactions table for the automatic calculation of VAT and the reports to be presented to the tax authorities. - Items table.
To set up a list of items to be used for billing. The program keeps track of your income and expenses. - Free tables.
To meet further needs.
Quick start
Templates
Accounting management focuses mainly on three tables, which are used in a similar way to Excel spreadsheets, but which are already fully set up and programmed with everything needed to keep accounting quickly and safely:
- Easy and immediate start, creating your accounting file starting with a template.
- If you already have your own template in Banana Accounting you can upload it with all the settings and use it for a different accounting.
- Over 1000 templates subdivided by country and type of user, customizable and with user documentation.
- Easy search and use of templates directly in the program.
Accounting setup
- Freely set the currency for your accounting, you can choose it from a list of world currencies or set it freely (cryptocurrencies).
- Freely set an accounting period, even over several years if required and not linked to the classic 1st January to 31st December period.
- Headings and accounting data set in a single dialog box, easy to display.
- Enter as many decimals as you want, from 0 to 27 (selected when the accounting) is created.
- You can change the number of accounting decimals during the year without problems.
Multi-lingual
- You are free to choose the language for your accounting when you create your file.
- Customize the column headers as you wish.
- You can run accounting in multiple languages simultaneously.
- Prints are also customizable in multiple languages.
File and data saving
- All the data is saved in a single file, where you can easily retrieve everything without wasting time.
- A separate file is created for each year. All data refer to the year so there is no confusion.
- Assign the file the name you want.
- With a single license you can manage an unlimited number of accounts.
- Data remains in your full possession.
- Data saved to any media, computer, network, cloud or can be emailed. You can access it wherever you are.
- Simultaneous access by multiple users, but only one person can open the file when in Edit mode.
- Make your accounting more secure by using password protection.
Plan-Execute-Control
In the same file and always with the double-entry method, you can keep the accounting, or your budget or both. The powerful Plan-Execute-Control approach is very intuitively used.
Double-entry accounting method
- Banana Accounting allows you to keep accounting with the international double-entry method and is compliant with international standards.
- Meets the criteria for keeping any accounting.
- Usable in any country.
- Transactions with debit and credit columns.
- Should there be imbalances in the transactions, a related notification will be generated.
Amounts are displayed in the columns in the format used by your computer, without you having to get used to other formats that you are not familiar with.- Debit amounts are indicated in positive and in credit in negative.
- Calculation is done according to the Debit - Credit = 0 equation.
- Balance sheet, Income Statement and all typical accounting printouts.
- All printouts are customizable.
- Choice of display format.
- Transactions according to the cash or accrual principle.
- Protect your data with cutting-edge blockchain technology (patented method).
- The double-entry method is used by many schools around the world to teach accounting.
Chart of Accounts
- Fully customizable Chart of Accounts to better meet your needs.
- The same Chart of Accounts is used for accounting and for financial, asset and income forecasts.
- Balance Sheet and Income statement are adaptable according to the structure and content of your requirements.
- Any national, international or free grouping scheme us supported.
- Off-balance sheet accounts for the management of items that should not be included in the budget, but that you need to mark down.
- Choose your account ID freely (numeric or alpha-numeric account, up to 256 characters).
- You can freely enter the description of the text for up to 256 characters.
- It is no longer necessary to insert the initial and final balances via accounting transactions
Enter the balances directly in the Opening column of the Accounts table and only when you use Banana Accounting the first time. In the following years the carryover will be automatic. - Balance, account movement and totals displayed contextually and always updated.
- For each customer, supplier, partner account you have the columns to enter the addresses and other useful data you need.
- Adding other columns for notes, grouping or amounts.
- If you add amount columns, they are automatically totaled.
You thus have the possibility to create columns with your own data and have very selected details.
Transactions
- You can insert single or compound transactions.
Single ones are registered in a single row, while the compound ones allow you to easily record transactions that will affect multiple accounts. - You can enter with either the cash or the competence method.
- When you enter data, already existing texts are suggested. With one click the transaction will be filled (auto-completion).
- Immediate reporting of errors and differences, with the possibility of completing them later.
- Store recurring transactions to resume them when they reappear without having to rewrite them.
- Predefined columns columns are available in all the tables and can be displayed at your choice.
- Quantity and price columns, for billing or cost control.
- Auto-numbering of documents with different numbers simultaneously.
- Documents are always at hand, by connecting the digital accounting vouchers (pdf, images) to the files, and open them with a click.
- Enter free texts of up to 256 characters as well as on multiple rows.
- Colour the lines to instantly search for the transactions you need to check or correct later, or to report them to the auditor.
- Adding columns to insert any further information.
- Recordings on Cost and Profit Centers.
- Recordings on segments.
- Save the arrangement of the columns (views) to display the content that is most important to you.
- Contextual information about account balance, differences or errors.
- Before the periodic or year-end closings you can use the Check Accounting functions.You will be able to identify errors between the actual balances (e.g. bank balances provided by the statement, and those of the accounting). You will immediately notice the errors and you can correct so as to have everything matched.
- Movements import:
- Speeds up entry of transactions by importing data from digital bank statements.
- You can import transactions in different formats provided by banks.
- Imported rows can be edited, completed or removed.
- It also imports invoice data or from other software.
Financial forecasting
- If you need to create a Budget, you can activate the function by adding the Budget table.
- Work without difficulty with the same methodology you are already used to, based on the double-entry method.
- Financial forecasts complete with liquidity plan.
- Balance Sheet forecasts.
- Income Statement forecasts.
- Automatic projections over several years.
- Entering the transactions through budget postings.
- Recurring income and expenses set with one transaction.
- All the features of accounting available:
- Calculation formulas in Javascript with access to the values of the current forecast:
- Forecast values available in accounting printouts:
- Account card with forecast movements by account or group.
Balance Sheet and Income statement
- Reports with final or Budget data or both, with indication of variations.
- Free arrangement with groups and subgroups.
- Updated results visible directly in the Accounts table.
- Customizable prints:
Watch the video tutorial that shows how to create and print the Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups.- Adding your own logo.
- Choice of columns to include.
- Choice of sections to include.
- Detailed or printout per groups
- Printouts per single period.
- Columns divided by period (month, quarter, semester, year).
- Values from previous year.
- Comparison prediction value.
- Columns with subdivision by segment.
- Added attached notes.
- Grouping as in the Chart of Accounts or according to your own scheme.
- Saving composition.
- Tabular report (similar to customizable printouts, but with the data in the table).
- Export to pdf for data conservation and export to other formats for data processing.
Other accounting prints
- Fully printable content tables or by for selection only.
- Adding your own logo to personalizing documents and prints.
- Journal.
- Account cards with account movements and groups:
- With accounting or forecast movements.
- By period.
- By Account, Group, Cost Center or Segment.
- Accounting or forecasting data.
- Customizable column arrangements.
- Export to pdf or other formats.
Charts
- Contextual, at the foot of the table.
- Different layouts.
- Evolution per accounts and groups.
- Accounting values.
- Forecasting.
- Preceding year.
- Choice of chart type.
Further management
The program also allows you to add additional information to the transaction, allowing you to use the same data needed for VAT management, for tracking customers and suppliers, issuing invoices, generating reports for projects or business sectors and to face the various corporate and tax obligations.
VAT management
- The function can be activated at choice (when creating an accounting).
- VAT code table to indicate the different VAT rates and cases.
- All national specifications supported.
- It can also be used to manage other types of sales taxes (eg American sales tax).
- Entering the VAT code.
- VAT reversal functionality (using the VAT code preceded by the minus sign).
- VAT calculation as per net or gross.
- Automatic breakdown and registration on the indicated VAT accounts.
- VAT control reports:
- By period or complete.
- With or without movements.
- Optionally, with totals per rate, VAT code, account.
- National extensions for VAT reporting based on the requirements of the relative tax authorities.
Customer management and control
- Function activated at choice (adding accounts in the Chart of Accounts).
- Checking invoices and customer payments.
- Customer master data set in the Chart of Accounts.
- Create groups and totals for customers in different groups.
- Open invoices per customer or global overview.
- Customer movement account statement and open invoices.
- Automatic reconciliation, open invoices.
- Customer management also available as cost centers (on a cash basis).
Invoices to customers
- Function can be activated at choice (using the invoice number column in the Transaction table)
- Entering invoices directly into the Transactions table.
- Requires setting up the customer database.
- Entering invoice data as normal row of transactions.
- See issue and print invoices to customers.
- Column to indicate quantities and prices.
- With or without VAT.
- Possibility of modification, correction.
- Print a single invoice with a click or several invoices combined.
- Choice of different print layouts.
- Customize the invoice according to your preferences.
- Exports in digital format via extensions.
- Customizable reminders via extensions.
- Customizable customer account statements via extensions.
Supplier management
- Function activated at choice (adding accounts in the Chart of Accounts.
- Supplier database set in the Chart of Accounts.
Possibility to group suppliers into different groups. - Invoice and payment to suppliers control .
- Open invoices per supplier or full report.
Supplier movement account statement and invoices still open. - Automatic reconciliation, open invoices.
Cost and profit centers
- Function can be activated at choice (adding the cost and profit centers accounts).
- For projects, cost accounting or profitability.
- Setting up cost centers directly in the Chart of Accounts.
- Multi-level grouping.
- Three levels of cost and profit centers.
- Unlimited number of cost centers per level.
- Negative registration (with minus sign).
- Reports such as Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss accounts:
- Balance constantly updated.
- Customizable reports.
- Card of all movements with progressive balance.
- Contextual chart.
Segments
- Function activated at choice (by adding segment accounts).
- Segment column
- The Balance Sheet and Income statement of one or more business sectors.
- Setting up segments directly in the Chart of Accounts.
- Multi-level grouping.
- Up to 10 segment levels.
- Unlimited number of segments per level.
- Balance constantly updated.
- Reports such as Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss accounts:
- Balance Sheet and Income statement for each segment.
Items table
- For invoices and with integrated warehouse or securities management.
- Linking of the articles to the movements of the Transactions table.
- Automatic update of incoming and outgoing movements.
- Initial and final value.
- Adding additional columns.
Control and closure
Error reports and accounting control
- Command to check the accounts.
The accounting is recalculated instantly, as if all operations were entered again. - Reports any wrong settings, differences or errors.
- Each report is linked to a help page that explains the causes and suggests the solution.
- Checks if the account balance matches the real one (cash, bank, VAT).
- Ability to correct.
Transaction protection
- Rows protection.
- Locking of movements entered with digital data certification technology (Bitcoin type).
- Password protection.
- Compliant with legal requirements.
- Sending data to the auditor with the certainty of the impossibility of tampering.
- Unlock movements with date.
Closing and new year
- Automatic procedure to create the new year file.
- Carryover of balances and allocation of profit.
- Work can begin on the new year, even if the previous one has not been closed.
- Command to carry over the closing balances of the previous year.
Exporting and storing data
- Copy and paste directly to and from Excel.
- Export tables to pdf and various other formats.
- Archiving of printouts and accounting data in pdf or other formats.
- Saving the accounting file on any backup device.
Extensions and other features
Added functionalities
- Adding new features.
- Removing features that are no longer needed.
- Conversion from one accounting type to another:
- Accounting with or without VAT.
- Multi-currency accounting or vice versa.
- From Income/Expense accounting to double-entry or vice versa.
Documents Table
Other additional tables
- Addition of other tables where notes or other information can be entered.
- Tables can be customized by adding columns to them.
Extensions
- Default extensions for various prints and other features.
- Quick search and installation.
- Customizable extensions.
- Automatic update.
- Ability to create and install your own local extensions.
Comprehensive documentation
- Each dialogue and error has its own documentation page accessible in a click.
- Constantly updated documentation.
- FAQ.
- Documentation also available in Pdf format.
File and accounting properties
This is where the main data of the accounting file are entered, such as the printout heading, the opening and closing dates, the base currency, the company address, the VAT account, the password, etc
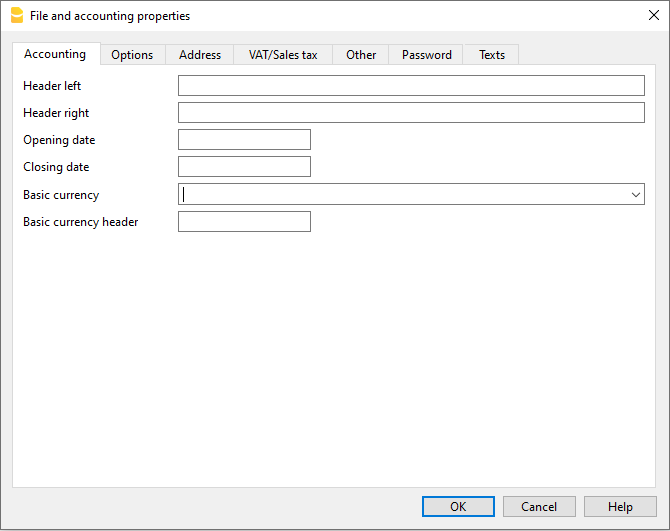
The File and accounting properties window has the following tabs:
Chart of accounts | Double-entry accounting
The Accounts table is the control room of your accounting. It's use is similar to that of an Excel spreadsheet.
In the Accounts table you set up everything you need to manage the accounting and have a quick updated overview of the financial and economic situation of your company.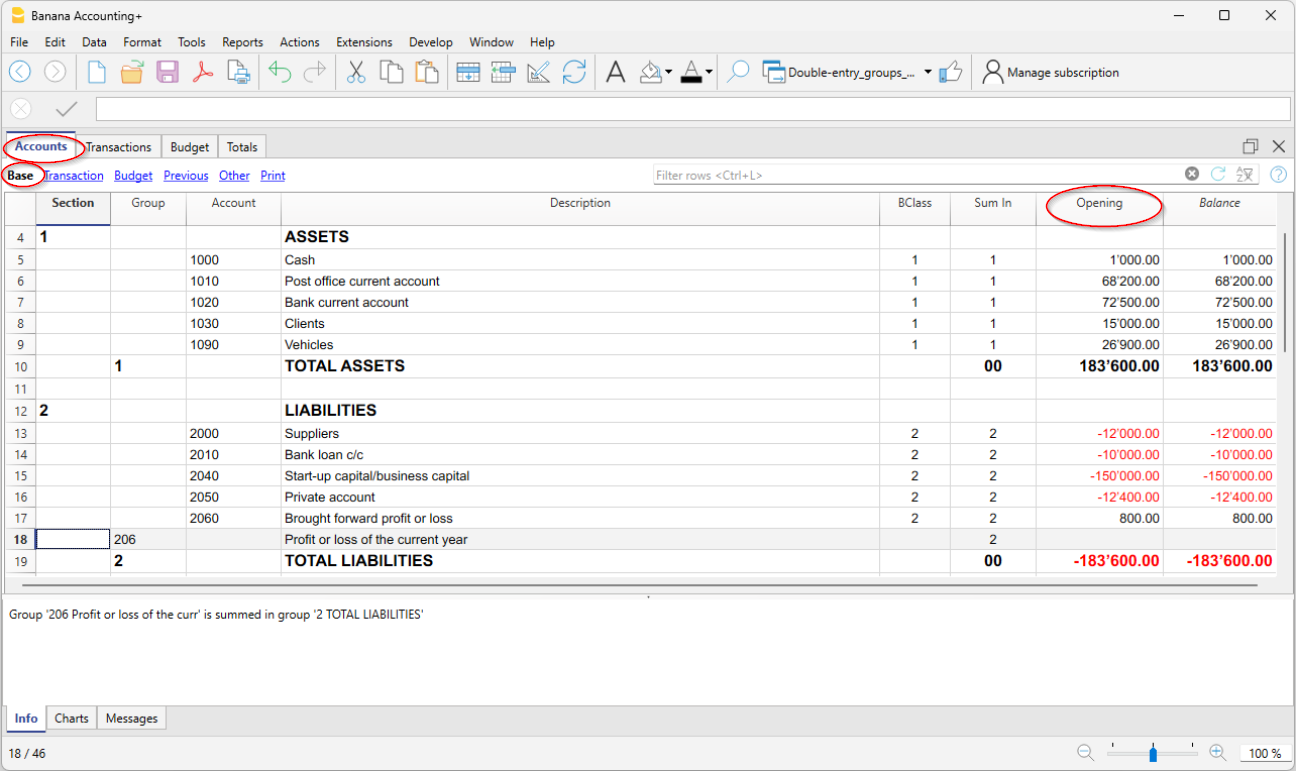
Ready-to-Use Chart of Accounts
Each accounting application by Banana offers a wide variety of chart of accounts templates, already prepared for immediate use. Simply select the file whose template meets your needs, and you'll have the chart of accounts already set up. File templates can be chosen based on the type of business activity and legal regulations.
They have the following characteristics:
- Fully customizable chart and account structure.
- Account and group numbers can be numerical or alphanumeric.
- Ability to add notes or additional columns.
- Grouping and totals adaptable to any national grouping scheme.
- Balances, account movements, and totals displayed and always up to date.
- Cost and profit centers for detailed control of costs and revenues for specific activities or projects.
- Segments for sector reporting (branch).
- Customer database, with control over outstanding invoices, reminders, and statements.
- Supplier database, control over paid and outstanding invoices.
- Management of off-budget customers and suppliers (with cost center) for cash-based accounting.
- Off-balance sheet accounts.
Entering and editing data is simple
- Add and edit accounts quickly and easily by simply inserting or deleting the row.
- There is no limit on the number of accounts to be added in the Chart of Accounts.
- Each account can be set up using numbers or texts.
- The description can also be very long.
- The Groups and Subgroups can be freely arranged to compose the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement.
- The opening balances are immediately entered in the opening column.
- Columns can be added to enter additional information.
- Accounts can be renamed and replaced automatically in the Transactions table as well.
- The columns of the amounts are updated instantly, at glance you know the status of liquidity, capital, sales, profit.
- Then, set the budget and have the comparison with the final balance.
Flexible grouping system
The grouping system is highly flexible and powerful:
- It allows to set up the Chart of Accounts according to any national scheme and to adapt exactly to the needs of the company.
- If you are not satisfied with the arrangement or numbering of accounts and groups, these can easily be changed.
The structure present in the Accounts table is also maintained in the presentation of the Balance Sheet and Income Statement.
Main elements
- Sections
They are used to indicate the subdivisions of the chart of accounts for printing the balance sheet, income statement, etc. - Groups
They allow you to create items that total the accounts and subgroups at multiple levels. - Accounts
These are the elements of accounting where the movements are recorded. They can be indicated in Debit or Credit depending on the nature of the movement, destination or origin.
Each account has a number or abbreviation (account number), a description, the B class and group to which it belongs, the opening balance, current balance, estimate, etc.
Customer and supplier data
You can have specific accounts for issuing invoices and checking payments. They are usually set at the end of the chart of accounts. They can be set up as register with the totals linked to the balance sheet, or as cost and profit centers, with all the details but without links to the balance sheet.
Cost and profit centers
Great to manage projects or have precise details of a specific event, or to manage customers and suppliers on the Cash principle (collected).
- Costs and Profits centers
They are special accounts whose number is preceded by a full stop ".", a comma "," or by a semi-colon ";". Their purpose is to be able to assign some amounts to special accounts other than the general accounting accounts.
Segments
Used to generate financial statements also for different sectors or activities in which the company operates.
- Segments
They are a sort of sub-accounts who's number is preceded by a ":". Their purpose is to be able to assign some transactions to subcategories of the chart of accounts.
Advanced printouts
- Accounting report
It is possible to select just the accounts with transactions, to obtain temporary groupings or accounts grouped according to the BClass or an external grouping scheme. - Enhanced Balance sheet
Prints all the accounts of the accounting divided by Assets, Liabilities, Expenses and Revenue - Enhanced Balance sheet with groups
Allows the user to obtain customized printouts with groups - Specific advanced printouts are available using the Banana Extensions
The columns of the double-entry Accounts Table
The Accounts table is made up of several columns. Depending on the Views, columns are displayed simultaneously. Each column has its own purpose.
The data to be entered in the following columns are explained below:
- Section
Codes are being entered that allow the user to print determined parts of the Chart of accounts only, when printing the Enhanced Balance sheet by groups.
- Group
Contains the code that defines that this is a group row. The group code is then used in the GR column to indicate the total of an account or group.
- Account
The account number, cost center or segment is being entered.
- Description
A text to indicate the name of the account, group, or section.
- Disable (only visible in the Other view)
By entering 1, the account does not appear in the auto-complete list, but can be used in the Transactions table;
By entering 2, the account is disabled and can not be used.
- BClass
It indicates whether the account is 1 = Assets, 2 = Liabilities, 3 = Expenses, 4 = Revenue, see Accounts page
- Sum in (Gr)
The code of a group is indicated so that the programme totals the amount of the line in the group.
The heading 'Sum in' has been adopted with the Banana Plus version.
The column name has remained Gr, to maintain compatibility with earlier versions of the programme.
- Gr1 and Gr2
- Opening balance
- The account balance is entered at the beginning of the year.
- Credit amounts must be entered with a minus sign in front
- The sum of all the amounts, those in debit (positive) and credit (negative) of the accounts belonging to classes 1,2,3 and 4 must result as zero. If the opening balances do not balance, a difference is indicated in the information window.
If accounts have been added and the difference is not exact, Recalculate the accounting. - The opening balance, in the balance sheet accounts, is used to calculate the current balance.
- If values have been entered in the Budget table, the opening balance is used by the program for opening financial planning.
- For further information, see the Double Entry Opening Balances page.
- Debit and Credit movements (Protected columns)
The total of the debit and credit movements included in the Transactions table.
- If there are no errors, the totals of the two columns are balanced, otherwise a difference is displayed in the Balance column which must be checked and corrected.
- In line called Difference must be zero, regarding these two columns, it is correct that there are amounts. The important thing is that their values are equal. See also Mathematical Basis of Accounting.
- Balance (Protected column)
The balance of the account includes the opening balance and the movements in debit and credit.The balance in debit is positive, while a credit balance is negative (minus sign).
- Budget
You enter the budget amount for the current period.- The budgeted amount for costs (debit) must be entered in positive, for revenue in negative (credit).
- If the Budget table has been activated, the Budget column in the Accounts table is protected and the amounts are those calculated on the basis of the budget postings.
-
Difference Budget (Protected column)
The difference between Balance and Budget amount.
- Previous
The balance of the account at the end of the preceding year.
With the command Create new year or Update opening balances the values in the Balance column of the file of the preceding year are being carried forward.
When a new accounting is being created and the user wants to obtain printouts with the amounts of the preceding year, the values of that year have to be entered manually.
- Difference Prev. year (Protected column)
The difference between the Balance and the amount of last year.
- VATNumber
The VAT number in case this account is linked to a client or a supplier.
- VATCode
The VAT code that needs to be applied automatically, when this account is being entered in the debit A/c or credit A/c column of the Transactions.
- Address columns
These columns are used to enter the addresses of the customer and supplier accounts. If the columns are not present, they can be added by activating them via the Tools → Add new features → Add address columns menu in the Accounts table.
Adding or moving columns
- When an Amount column is being added in the Chart of accounts, the program will calculate the total of the amounts according to the selected grouping scheme
-
Columns added of the number type, on the contrary, are not being totaled.
- With the Columns setup command, the columns can be displayed, the sequences can be altered and it is equally possible to add other columns.
- With the Page setup command one can also define the layout of the print (portrait or landscape) and the zoom.
Accounts list sorted by description or other criteria
To obtain lists of accounts sorted in different ways, use the Extract and sort rows command from the Data menu. We recommend you to be very careful when sorting the rows with different criteria in order not to create confusion in the groupings and totals.
Views
- Base The principal columns, the grouping columns and the balances are displayed.
- Transaction The columns with the Debit and Credit transactions are displayed.
- Budget The Budget column and the Difference Budget column are displayed.
- Previous The Previous column and the Difference Prior columns regarding the previous year are displayed.
- Other The Disable column, the VAT number and the Fiscal number column are being displayed.
- Print Only the Account column, the Description and the Balance are being displayed.
The views can be customized and others can be added with the Views setup command.
Accounts | Double-entry book-keeping
Accounts constitute the main structure on which all accounting is created. If you open one of the templates included in Banana Accounting, the accounts are already present in the Accounts table and contain all the settings needed to instantly record the transactions in the Transactions table.
The accounts in the Accounts table are divided as follows:
- Balance Sheet Accounts - Assets and Liabilities.
- Profit and Loss Accounts - Expenses and Income.
- Customer and Supplier master Data
- Account Cost and Profit centers - for managing projects or keeping the Customers / Suppliers register
- Segment Accounts - for managing business segments or branches.
The BClass
The BClass is essential for the correct total of amounts and balances. In the BClass column, each account must be assigned one of the following values, regardless of the account number or group to which it belongs:
- 1 - for Assets
- 2 - for Liabilities
- 3 - for Expenses
- 4 - for Income
Groups and subgroups do not have BClass, so the cell of the relevant column remains empty.
BClass of off-balance sheet accounts
Off-balance sheet accounts are those whose amounts and balances do not fall within the totals of the balance sheet and income statement accounts. They are accounts that are entered in the chart of accounts to view guarantees and conditional commitments.
Off-balance sheet accounts must have the following BClass:
- 5 for Off Balance Sheet Assets
- 6 for Off Balance Sheet Liabilities
- 7 - 10 - for other Off Balance Sheet accounts
Add a new account or category
In the Accounts table, Base view, you can add new accounts (or new categories in the Income / Expense accounting).
Before adding an account or a category it is important to know:
- The account or category number can consist of numbers, letters and separator characters.
- There cannot be multiple accounts or categories with the same number.
- Each account must have a grouping (Gr) and a class (BClass).
To add an account or a category proceed as follows:
- Go to the row preceding the one where the new account or category will be inserted.
- Add a row with the Edit → Insert row command
- Fill in the respective columns the account or category number, the description, the BClass (1 for assets, 2 for liabilities, 3 for costs and 4 for revenues - only for double-entry accounting), the number of Gr which must be the same as the one entered for the accounts belonging to the same Group.
Warning: if you enter a transaction with an account that does not exist in the chart of accounts and only after creating the new account, you will initially receive an error message; to eliminate it, it is necessary to recalculate the accounting with the command Shift + F9 or through the menu Actions → Recalculate totals.
Rename an account
This is a very useful function because it allows you to change an account and simultaneously have it replaced in the Transactions table. It avoids having to change the account for each transaction that contained the previous account. In addition, it also allows you to rename a group or a VAT code.
- In the Accounts table go to the Account / Category or Group column, or to the VAT Code column of the VAT Codes table.
- Use the Data → Rename command.
- Indicate the new account number, group, category or VAT code.
The program automatically updates the Transactions table with the new VAT number or code.
Delete an account
If an accounting is already started, before deleting an account, make sure that it has not been used in the Transactions table or that it does not have an opening balance.
- Locate the row of the account that is to be deleted.
- Use the command Edit → Delete rows command.
After deleting an account or a category it is advisable to use the Actions → Recalculate totals command. If the deleted account or category is in use in transactions, the program reports an error message.
Opening balances of the accounts
The opening balance of an account is shown in the Opening column.
- Debit (Asset) balances are shown normally.
- Credit (Liabilities) balances are indicated with a minus sign (in negative) in front of the amount
- Typically, only the opening balances of the Asset and Liabilities accounts are indicated.
To carry over the opening balances automatically to the following year, see the Create New Year lesson.
Further details on opening balances are available on the Opening balances page.
Differences in opening balances
To have correct accounting, the total of the opening debit balances must match the total of the opening credit balances, so that there are no differences.
If the total does not correspond there will be a notification of the difference between the initial balances in the Info window.
If any account numbers have been changed and there are differences, perform the Full Accounting Recalculation.
When using Banana Accounting for the first time, to create the opening balance, it is necessary to manually enter the opening balances (Opening column), making sure to enter the balances of the Liabilities with the minus sign (-) in front of the amount.
Further details on opening balances are available on the:
- Differences in opening balances (Double-entry accounting).
- Differences in opening balances (Multi-currency accounting).
Customer and Supplier accounts
Customer and supplier accounts can be entered directly in the Balance Sheet sections, listing the accounts for each customer and supplier and creating two distinct totaling groups, one in the Assets for customers, the other in the Liabilities for suppliers. If the list of customers and suppliers is very extensive, it is possible to create a customers / suppliers ledger at the end of the chart of accounts.
There are several setting options:
- Setting up directly in the Financial Statements, listing customers and suppliers, respectively in the Assets and Liabilities.
- Setting up with the customers / suppliers register, at the end of the accounting plan, with the totalization reported in the financial statements. This setting is ideal for those who manage VAT with the accrual method.
- Setting up with cost and profit centers, at the end of the chart of accounts, without totaling in the balance sheet.
This setting is ideal for those who manage VAT with the cash method.
Accounts with addresses
In the Accounts table, Address view, there are columns to enter the addresses of customers, suppliers or members. If the columns of the address view are missing, you can add them:
The address columns are essential to be able to manage billing, reminders and the control of payments and collections.
More details are available on the Address page.

The Cost and Profit Centers accounts
They are ideal for project management, have precise details on a specific event or for any other need.
- Cost and profit centers
They are accounts that have the number preceded by a period ".", by a comma "," or by a semicolon ";" and are used to attribute the transaction amounts to additional accounts as well, with respect to the basic accounting ones.
All the amounts attributed to the cost and profit centers are separate from the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement and are entirely for information purposes.
The Segment Accounts
To have financial statements also of different sectors or activities in which the company operates.
- Segments
They are similar to sub-accounts that have the number preceded by a colon ":" and are used to attribute the accounting operations to sub-categories of accounts.
Customize accounts and categories
Adding a new account or category
With Banana Accounting it is possible to customize the chart of accounts by adding or deleting accounts and categories.
To add a new account or category, proceed as follows:
- Position yourself in the row above the one where you want to add the new account or category.
- Add a new empty row with the command Edit → Add rows.
- Enter in the respective columns:
- The Account number
- The Description,
- The BClass (1 for the Assets, 2 for the Liabilities, 3 for the Expenses and 4 for the Revenue)
- Grouping number (Sum in column) which must be the same as that entered for accounts or categories belonging to the same Totalization Group.
If in the Transactions table you enter a transaction with a non-existing account, the program gives you an error message; to take it away you have to create the new account in the chart of accounts and recheck the accounting with the Shift + F9 key, or with the menu Actions → Recheck accounting command.
Adding a new group
If you want new totalization groups, proceed as follows:
- Position yourself in the row above the one where you want to add the new group
- Add a new empty row with the command command Edit → Add rows.
- Enter in the respective columns:
- The Group number
- The Group Description,
- Grouping number (Sum in column) in which you wish this group to be totalized.
Renaming an account, a group, a category or a VAT Code
This is a very practical function that allows you to rename an account, a category, a group or a VAT code and to have the replacement automatically in the Transactions and Budget table without having to enter them manually.
To rename one of the elements proceed as follows:
- Position yourself in cell where the account or group (Accounts table) or the category (Categories table), that needs to be renamed, is present.
- If it is necessary to rename a VAT code, it is necessary to position yourself in the VAT Codes table, on the cell of the code to be substituted.
- Choose the Data menu → Rename command
- Indicate the new account, group, category or VAT code number.
Removing an account, a group, a category or a VAT Code
- Position yourself on the row number that contains the element that is to be deleted
- Click on the Edit menu → Delete rows.
- Enter the number of rows that you wish to delete
After deleting an account, a group, a category or a VAT code, it is necessary to use the Recheck accounting command. The program will give you a warning message if the deleted element was used in the transactions.
When deleting a group and not all accounts belonging to the deleted group are deleted, you must change the grouping number in the Sum in column for the remaining accounts, otherwise errors will be reported.
Groups
Banana has developed a very practical and immediate grouping system, which allows you to set in the Accounts table all the information necessary to define the structure of the Balance sheet, Profit & loss statement and of other sections of the accounting.
The grouping system is flexible; it allows you to implement any national chart of accounts and at the same time to adapt it to the specific needs of your business. Both very simple and very complex plans and presentations can be created, with multiple levels of totalling, for any type of accounting.
With grouping, the totals of balances, movements and the group budget are displayed immediately.
How it works
To understand how the Banana grouping system works, please refer to our documentation page:
Grouping and totalling system
The Banana grouping and totaling system is based on two columns of the Accounts and Categories table:
- Group (Total row)
- When, in a row, a group identifier is being entered, the row becomes a total row.
- In this row the amounts of the Sum in column, that contain the same identifier, are being totaled.
- In a row, when a group is present, there cannot be an account.
- Sum in
- Sums the row amounts in the indicated group.
- For each account or group row, you indicate the group in which the line is to be totaled.
- The number here must be one of the numbers defined in the Group column.

Main groups in double-entry accounting
Every accounting file template uses its own totaling system. Hereunder explanation of the main groups of double-entry accounting .
In double-entry accounting, the total of the Debit balances (positive) together with the Credit balances (negative) have to result in 0 (zero). In the case of differences, the group line 00 has a non-zero amount.
The calculation sequence to achieve 00 is therefore as follows:
- The 1000 accounts > group 1 (Total Assets) > Group 00
- The 2000 accounts > group 2 (Total Liabilities) > Group 00
- The 4000 accounts > group 4 (Total Expenses) > Group 02 (result Profit & Loss Statement) > Group 206 (Profit/Loss of the current year in the Balance Sheet) > Group 2 (Total Liabilities) > Group 00.
- The 3000 accounts > group 3 (Total Revenue) > Group 02 (result Profit & Loss Statement) > Group 206 (Profit/Loss of the current year in the Balance Sheet) > Group 2 (Total Liabilities) > Group 00.
- The 00 group is the control row where all the amounts are being added together.
- It is the "Grand total" of all the Debit & Credit balances as a result of the transactions entered in the Transactions table.
- If the line in the 00 group shows a difference (non-zero amount), this means that there are mistakes:
- If the difference is shown in the Accounts table, Opening column (all views) there are differences in the opening balances
- If the difference is shown in the Accounts table, Balance column (all views) there are differences in the Transactions table. In the Debit and Credit columns of the movement view, the totals are not balanced.
In cases where the difference is indicated issue the command Check and recalculate accounting. This command suggests any errors that need to be checked and corrected.
- In the Debit and Credit columns of the Movement view (Accounts table), the totals of the balances are always reported. If the totals in the two columns are equal, there are no errors.
The result of Profit & loss statement is added in equity capital
As you can see in the example, the Group 02 (Profit /Loss from Profit & Loss statement) is totalized in the 206 liabilities group (current year result).
With this group organization, we have several advantages:
- The current year operating result is displayed in the balance sheet
- The Total Liabilities will match the Total Assets (provided that there is no accounting error).
Set up of the Chart of Accounts structure
The chart of accounts in Banana Accounting can be set mainly in two different ways:
1. Structure without subgroups (or subtotals).
In this case, the structure is very simple. You list all accounts without subgroups, and total all accounts or categories in the main groups:
For Double-entry Accounting:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Expenses
- Revenue
For Income/Expense Accounting or Cash Manager (Categories table):
- Income
- Expenses
2. Structure with subgroups
The structure is more complex. The accounts or categories of the main groups are divided into several subgroups, which in turn are totaled into the corresponding main groups.
Here we present a structure of the chart of accounts with an example of Subdivision with subgroups in Double-entry Accounting. Each subgroup can be in turn :
Assets
- Current Assets
- Cash and Cash equivalents
- Customers
- Inventory
- Fixed Assets
- Furniture
- Machinery and equipment
- Computers, software.
- Current Assets
Liabilities
- Third-party capital
- Suppliers
- Bank loans
- Other short-term debts
- Long-term debts
- Equity
- Equity
- Reserve funds
- Profit and loss carried forward
- Profit for the year
- Third-party capital
From the Accounts table, at any time, through the menu File > Print or Print Preview you can print the chart of accounts or part of it.
Always starting from the Accounts table, by selecting the Movement view, you have the printing of the verification balance.
Adding a new group
- Position yourself in the row preceding the one where the new group will be entered
- Add a row with the command Edit > Add Row
- Type in the group column the group number, description, and the number of the column Sum in where you want this group to be totaled.
Adding a totaling level
With this system it is easy to add totaling levels.
When we want to create a subgroup for the Cash & Cash equivalents accounts:
- Enter an empty row after the bank account
- Enter the value 10 into the Group column
- Enter the value 1 into the Sum in column
- Indicate the grouping 10 in columns Sum in the accounts 1000 and 1020
- The sequence for the calculation becomes:
The 1000 account > Group 10 (Cash & Cash equivalents) > Group 1 (Total Assets) > Group 00.
The programme totals the following:
- It totals the accounts in a group row.
For example, the Cash account is totalled in the Liquidity group. - Totallises a group or subgroup in another group, which in turn is totalled in another group, thus building the calculation structure of the Balance Sheet and Income Statement.
For example, the Liquidity group is totalled in Total Assets, which in turn will be totalled in group 00, in the control total row.

In case you want to insert another subgroup, "Current Assets", proceed in the same way.
- Add an empty row above the row of the Total Assets.
- In the new row:
- Indicate the number 11 in the Group column
- Indicate the number 1 in the Sum in column
- In the Clients and Goods for resale (inventory) rows, indicate the grouping 11 in column Sum in.
Title rows (with Sum in)
Also in the title rows it is useful to indicate the grouping Sum in (the group of the total row) to which it belongs.
In this way, in the printouts of the Enhanced Balance Sheet by groups, if the accounts are zero, the title will not be printed.

Deleting subgroups
In case the Chart of accounts shows subgroups that are no longer needed or not wanted, these can be deleted. Just delete the row of the subgroup and modify the grouping Sum in of every account that was part of that subgroup.
Checking of the structure
Once the Chart of accounts has been set up, execute the Actions menu > Check accounting command. In case there are errors, the program issues a warning.
Infinite loop error
This warning appears when a Group is being totaled in a Group of a lower level, reason for which an infinite error loop is being created.
There would be an infinite loop when, in the preceding example, the Assets Group (1) would be totaled in Group 10.
The program, after having calculated the Group 1, would total the amount in Group 10, which in turn would total the amount in Group 1, and then again in 10 without ending.
Profit & Loss Statement with Gross Profit
It is also possible to use a Profit & Loss Statement that starts with the total Business result and that subtracts the costs.
Hereunder the example of the Swiss PME Chart of Accounts is shown.

Related Documents
Sections
In the Section column, there must be an encoding that is used to determine the various settings of the printouts. The various items that make up the financial statements are divided into several sections; each section is as if it were in its own right.
This subdivision into sections allows you to choose whether to print the entire balance sheet and income statement, or choose which sections to print (eg only the balance sheet, or just a group, excluding the other components from printing).
Below we present a table with the coding to be used in the Accounts table, Section column.
| * | Title 1 | the asterisk separates the sections and indicates the main headers |
| ** | Title 2 | to be entered for the secondary headers |
| 1 | Assets | to be entered in the row of the Assets title |
| 2 | Liabilities | to be entered in the row of the Liabilities title |
| 3 | Expenses | to be entered in the row of the Expenses title |
| 4 | Revenue | to be entered in the row of the Revenue title |
| 01 | Client's Register | to be entered in the row of the Client's Register title |
| 02 | Supplier's Register | to be entered in the row of the Supplier's Register title |
| 03 | Cost Centers | to be entered in the row of the Cost Centers title |
| 04 | Profit Centers | to be entered in the row of the Profit Centers title |
| # | Notes | to be entered in the row of the Notes title |
| #X | Hidden data | to be entered in the row from whereon the data have to be hidden |
The type of encoding set in the Section column is used to determine the print settings for Enhanced Balance Sheet with Groups.
Each section is printed as if it were a separate table.
Title section
- *
The asterisk indicates a new section.- * Title 1 generates a level 1 folder.
- This section resets the level type to 1.
- It can contain level 2 sections or folders.
- It will be useful for grouping sections that need to be printed together such as the Balance Sheet, which contains both assets and liabilities.
- **
The double asterisk indicates a level 2 section.- ** Title 2 generates a level 2 folder
When you create a new title section, the numeric section is set to 1.
After a title section, the desired number section must therefore always be reset as well.
Numerical sections
The section number determines:
- How the amounts are printed; the amounts can be displayed as in the chart of accounts or reversed.
The credit amounts (in negative,) if they are inverted, are displayed in positive, while those in positive are displayed in negative. - Which columns are used to display the amounts; either the Balance column or the Period Movement column is used.
- The Balance column indicates the account balance at a certain point in time (balance as of June 30th).
- The Total Period Movement column indicates the amount of the movement in the indicated period; it is used for the income statement and indicates expenses or income for a certain period.
The explanations of the different sections are as follows:
- 1 Assets (amounts as in the chart of accounts, balance column).
- 2 Liabilities (inverted amounts, balance column).
- 3 Costs (amounts as in the chart of accounts, total movement column).
- 4 Revenues (inverted amounts, total movement column).
This section can also be used alone and include both costs and revenues (Income statement). In this case, revenues are shown in positive and costs in negative.
These sections must be unique. There can be only one section, 1 Assets or 2 Liabilities. Similar sections can be used for other sections, ledgers or cost centers.
Derived numerical sections
These are sections that behave like the main sections:
- 01 As Assets (amounts as in the chart of accounts, balance column)
Is used for the customer register. - 02 As Liabilities (inverted amounts, balance column)
Is used for the suppliers register. - 03 As Expenses (amounts as in the chart of accounts, total movement column)
Is used for cost centers. - 04 As Revenue (inverted amounts, total movement column)
Is used for profit centers.
Other Sections
There are other sections types:
- # Used to indicate the notes section (print description only)
To be used for budget annexes. - #X Hidden section. This section is not taken up in the selection of the sections nor in the printout. It is used to indicate a part that you do not want to print.
Disposition and width of columns in print
The disposition and the width of the columns are determined automatically by the program:
- Sections 1, 2, 01, 02 are printed with the balances on the specified date.
- Sections 3, 4, 03, 04 are printed with the movements for the period.
Sections of the Balance sheet report
In order to divide the Financial Statements into the various sections, the code indicated in the Section column must be entered:
- Insert a * on the same row as the Balance sheet title.
- Enter 1 on the same line as the Assets title.
- Enter 2 on the same line as the Liabilities title.

Sections of the Profit & Loss statement
- Enter a * on the same line as the Profit & Loss title.
- Enter 4 on the same line as the Revenue title.
- Enter 3 on the same line as the Expenses title.

Sections of the Profit & Loss statement in a graduated format
In the case of a graduated income statement, the groups of expenses and revenues alternate and consequently there is no clear distinction between the section of costs and revenues, therefore enter only:
- A * on the same row as the Profit & Loss Statement title
- 4 on the blank line below the income statement.

Sections in the customers / suppliers register
The display of the amounts is the same as for assets and liabilities. This coding also applies if customers and suppliers are set up as cost centers.
- Insert a * on the same row as the Customer / Debtors Register title or on a blank row (as in the example).
- Enter 01 on the same row as the Customers Register title
- Enter 02 on the same row as the Suppliers Register title

If there are cost and profit centers, you must enter:
- a * in the same row as the Cost and Profit Centers title or on a blank line
- 03 on the same row as the Cost Centers title or on a blank line (preceding the cost centers).
- 04 on the same row as the Profit Centers title or on a blank line (preceding the Profit Centers).
The cost center amounts will be shown in positive as the costs; profit centers will be displayed in negative as revenue.

Related document:
Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups
Transfer to a new Chart of Accounts
Hereunder we explain how to proceed when:
- passing to a chart of accounts with a different numbering,
- retrieve and convert the data of an existing accounting, including the transactions into the new Chart of Accounts.
Converting to the new year
There are two possibilities if you wish to start a new year with a new chart of accounts,
- Convert the previous year (2022) and then create the new year (2023).
There will be two files for 2022 (the one containing the Accounts column with the old account numbers and the Accounts_1 column with the new account numbers) and the file for 2023 with only the new chart of accounts.
This approach is ideal for having the two-year charts of accounts aligned.
This way you can also continue to make changes in the year 2022 and then resume the initial balances in the year 2023. - Create the new year (2023) and then convert the year 2023 file with the balances carried forward.
The 2022 year file will remain the same. For 2023 there will be an intermediate file, with the old chart of accounts, but the opening balances carried forward.
The conversion of the year 2023 file can be performed immediately or even after transactions have been entered.
Having the old account numbers in the year 2022 file, you will not be able to resume any further changes made in 2022 in 2023.
Step 1: Creating a new accounting file
- Create a new file:
- Adapt the chart of accounting to your own needs.
Step 2: Adding the matching accounts
- In the Accounts table:
- menu Data → Columns setup
- click the Add button
- insert Account_1 description .
- For each new account, enter the corresponding account in the Account_1 column of the old chart of accounts.
Should the account remain the same, you may also choose not to indicate it. - In case where several accounts need to be grouped in one, enter the separated accounts with a semi-colon "1000;1001".
- If one account needs to be subdivided into several accounts, you need to proceed manually, see below.

Step 3: Starting the import operation
- Via Actions →Import to Accounting → Import File.
- Using the Browse button, select the file of your old accounting plan

- Confirm by clicking the OK button and proceed to the next window
- Define the import options
- Enable the Convert account numbers option, indicating that the matches are in the target file.

Repeat the import
If errors are reported, and it is necessary to repeat the import, it is necessary to cancel the import operation, so that the starting file is empty, otherwise the balance amounts will be duplicated, both in the opening balances and in the transactions table.
Subdivision of one account into several accounts
When one transfers to a more detailed chart of accounts, it is probably necessary to subdivide one account into several accounts.
After the import operation, proceed manually in the following way:
- In the Chart of accounts, subdivide the opening amounts, budget amounts and previous amounts of one account into several accounts.
- Go over the transactions, one by one, of the account that needs to be subdivided and assign them to the more specific account, or create extra transactions if it is necessary to subdivide one amount into more detailed amounts.
- Proceed in the same way for the transactions of the Budget table.
Results and possible errors
If the program reports mistakes (absence of accounts or others), the import operation probably needs to be canceled, complete the pairing and then repeat the import operation.
The program, confronted with different charts of accounts, cannot automatically do extensive verifications and guarantee that all the data have been imported and grouped correctly.
It is therefore strongly advised to manually check the result, making sure that the totals of the Balance Sheet and the Profit & Loss Statement are correct.
Opening balances | Double-entry accounting
Opening balances when starting an accounting
When using Banana Accounting for the first time, the opening balances need to be inserted manually in order to create the opening balance sheet.
- Position yourself in the Accounts table, Base view, Opening column.
- Enter the opening balances of the Assets and Liabilities accounts manually. Liabilities are to be entered preceded by the minus sign.
- Check if the total Assets equal the total Liabilities so that your accounting squares. If there are differences in the opening balances you need to check and correct them.

Difference in opening balances
At the opening of the accounting year, the Assets accounts (positive) must balance with the Liabilities accounts (negative). If this is not the case, the accounts do not balance and error messages are displayed in the information window at the bottom; in this case, the reasons must be checked and corrected, until the message Difference in opening balances disappears. For more information and solutions see:
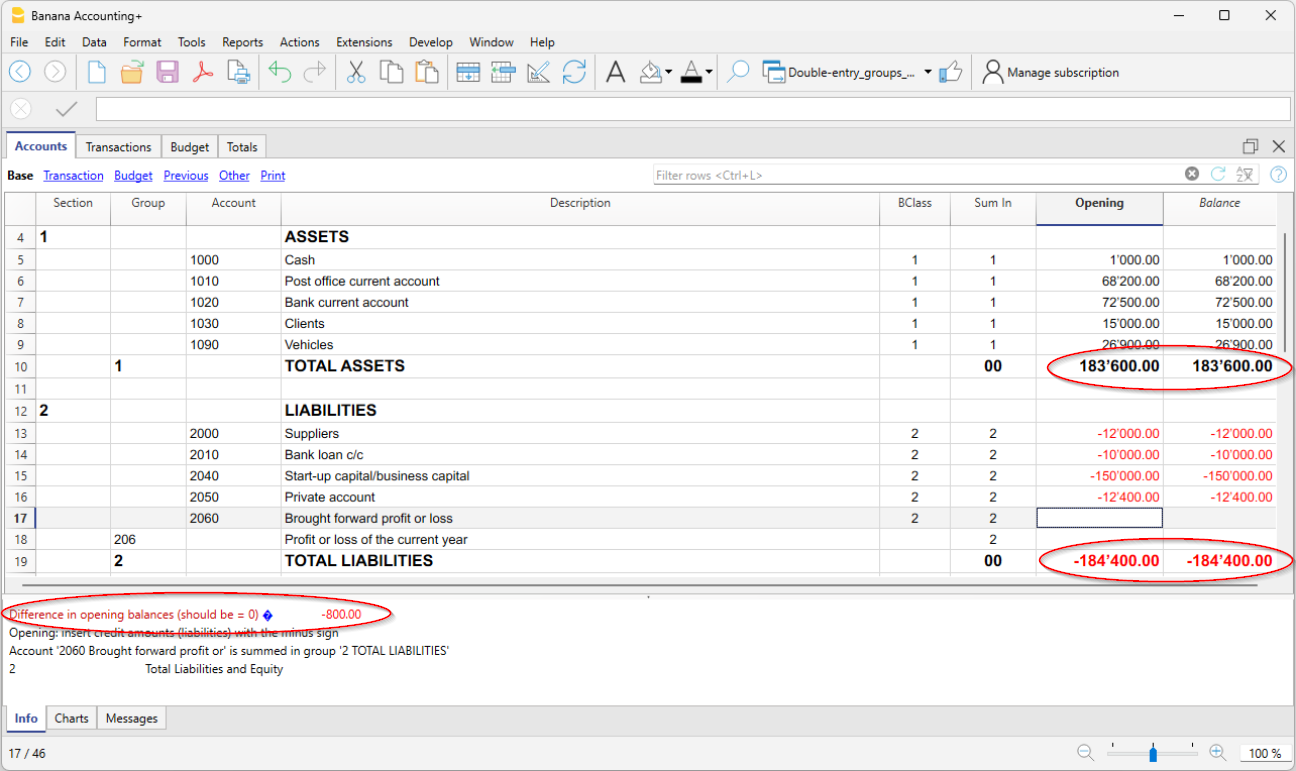
Opening balances of Cost Centers
In the Accounts table, the Opening column can also be used to enter the opening balances of the Cost Centers.
Opening balances for Segments
To enter the opening balances of the segments, opening transactions must be entered instead.
More details are available on the Segments page.
Opening balances for an already started accounting
If you start a new accounting, taking over work already done with other programs, there are two possibilities:
- Start accounting from the beginning of the year, by entering the opening balances for the beginning of the year (Accounts table, Opening column) and the transactions (Transactions table) that have already been previously recorded with other programs (also see Transferring data from other software). Thus you will have all the accounting details in one file.
- Starting from the date when the accounting is resumed:
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
In addition to entering the opening balances of the Assets and Liabilities accounts, it is also necessary to enter those of the Expenses (positive amounts) and Revenues (negative amounts). - The operating result up to that point must be disclosed in the Profit / Loss carried forward account.
If it is a profit, the opening balance must be entered in negative, if it is a loss as a positive. - Check that the sums of the opening balances are zero, so that the program does not signal any differences.
- Enter the new entries in the Transactions table.
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
Opening balances as opening transactions
Opening balances can also be entered as opening transactions in the Transactions table.
For each opening transaction, proceed as follows:
- Indicate the accounting start date as the transaction date.
- In the Doc Type column, enter the code "01".
- Indicate the debit or credit account and the amount.
- The total of the opening debit balances must match those in credit.
Opening balances entered as transactions are used when preparing reports. The opening balance of the transactions is added to the amount entered in the Opening column of the Accounts table.
Balances of the previous year
If you start a new accounting by taking over an existing accounting and you want the previous year's values to appear on the printouts, it is necessary to enter the previous year's balances in the Previous view, Previous Year (Prior) column of the Accounts table:
- Enter the closing balances of the previous year of the Assets accounts.
- Enter the closing balances of the previous year of the Liabilities accounts (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).
- Enter the last year's closing balances of the Expenses.
- Enter the final balances of the previous year of Revenues (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).
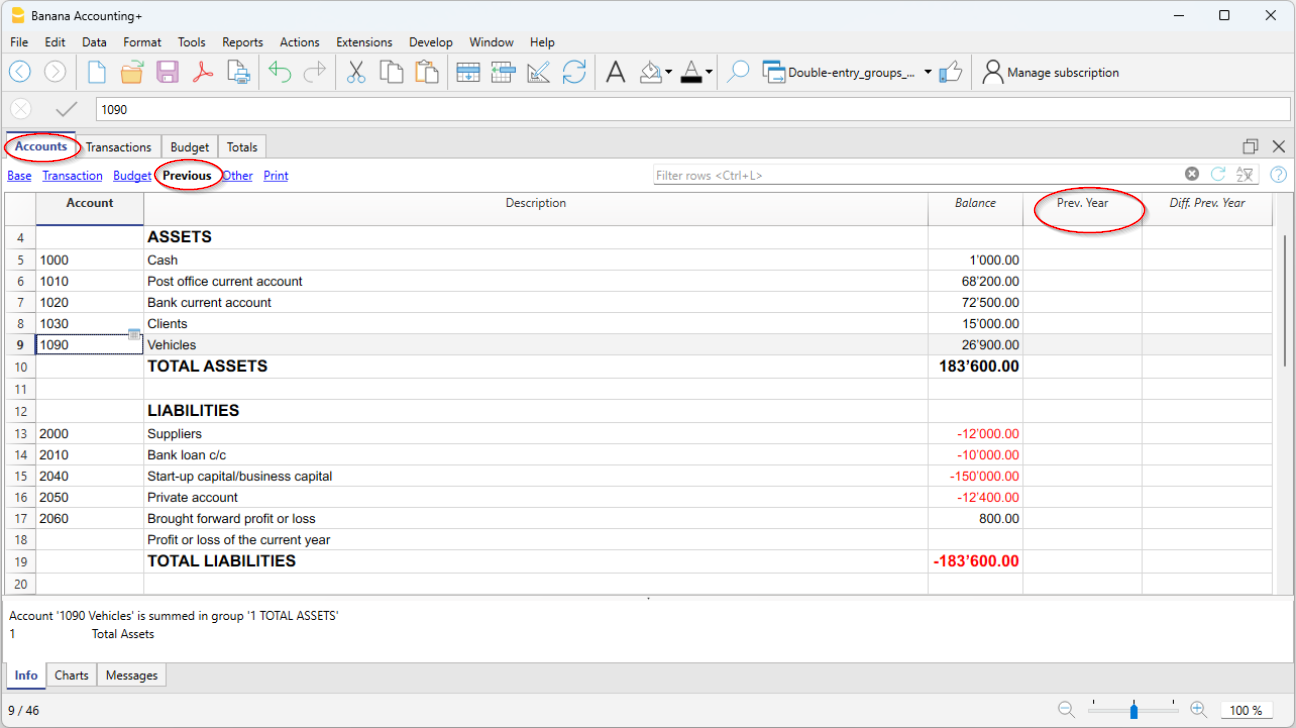
Create new year
When you start the new year, the program automatically carries over the opening balances to the following year.
Consult the Create New Year lesson.
If for some particular need, opening balances need to be changed, these can be modified manually in the Opening column of the Accounts table. After each modification, make sure that there are no accounting differences. Anyway, we recommend carrying over the opening balances with the Create new year command or, if the accounting for the new year has already been created, use the Update opening balances command.
The account card is in automatic and it is not possible to directly enter the opening balance or make changes.
To change an opening balance of an account card, you need to go to the Accounts table, Opening column, whereas to correct movements, you need to change the entry in the Transactions table.
Print opening balances
To print the opening balances:
- To print the contents of the table, use the Print / Preview command, by selecting the rows of the Balance Sheet.
- You can also use the Accounting printouts and set the printout for the Balance Sheet part and the opening column only.
Differences in the opening balances
At the opening of the Accounting year, the amounts of the Total Assets should correspond to the Total Liabilities. Otherwise, the accounting balance will not square and it is necessary to verify the reasons and correct the error, so that there is no Difference in the opening balances message displayed in the information window .
There may be several causes that lead to a difference in the opening balances:
- When using the program for the first time, the liabilities were not entered with a minus sign in front of the amount.
- The result of the previous year was not automatically allocated when creating a new year.
- The balances for expenses and income have been carried over, when creating a new year, whilst they should not have been.
- When opening balances have been entered manually, the previous year's operating result has not been taken into account. In this case the difference corresponds to the carried forward profit or loss.
- When allocating the profit to multiple accounts is performed manually, thousands separators and decimals other than those provided in Banana Accounting were used for the amounts.
The solutions for each single error are explained in the error explanation page, at the https://www.banana.ch/doc/en/contamsg_en_tot_teid11des?portal=banana link.
In the example, the program reports a difference in opening balances of 800.-

After having checked and corrected the opening balances the Total Assets must correspond to the Total Liabilities.
It is also possible to check and square the balances in the Totals Table.
Transactions Table | Double-entry accounting
The Transactions table is the central hub for keeping the accounts, where all the operations with financial and economic impact are entered. The use is similar to Excel. In the Transaction table the movements are always visible and in perfect order and by scrolling them, you instantly have a clear view of all the events.
All the data entered can be modified and corrected, making it easy to have a perfect accounting.
The Transaction Table is also characterized by the Balance Column, which allows identifying any differences between the Debit and Credit columns and especially the row where the difference originated. Additionally, errors and accounting differences are flagged in the information window at the bottom.

Key features:
- Single or compound entries: Single entries record simple transactions with one Debit and one Credit account, while compound entries are entered on multiple lines with different Debit and Credit accounts. The program suggests previously entered text for quick auto-completion.
- Recording Method: Transactions can be recorded using either the accrual or cash method, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
- Management of Repetitive Operations: Stores repetitive operations for quick future recording, reducing data entry time.
- Customizable Columns: Default columns can be made visible at the user's choice, including quantity, price, and other relevant information.
- Automatic Numbering: Automatically assigns document numbers with different numbering simultaneously, maintaining systematic order and facilitating search and archiving.
- Digital Attachments: Links digital justifications such as PDFs or images to files, accessible with a simple click for complete and organized documentation.
- Exception Management: Highlights rows to quickly identify entries to verify or correct, facilitating the review and control process.
- Data Integration: Imports transactions from various digital bank statements and other programs, speeding up entry of records and ensuring data accuracy.
- Cost/Profit Centers and Segmentation: Allows recording operations on cost/profit centers and segments for detailed analysis and better financial management.
- Balance Verification Entries: Before period or year-end closings, quickly identifies and corrects errors between actual balances, ensuring accurate and updated balances.
Fast insertion
The table is similar to Excel, you can scroll up and down and position yourself in any cell.
There are many features that make entering and editing data very fast.
The following operations are possible:
- Cancel and redo.
- Select one or more cells and copy / paste.
- Add, copy, paste and delete lines, individually or in bulk.
- Search and replace texts.
- Sort the rows by date.
- The auto-complete function suggests the values to enter (for example the list of accounts).
- With the F6 key the values of the row are completed, taking over those of the same row.
- The F4 key resumes the values from the previous row.
- The date is completed with the values from the previous row.
- In the Doc column progressive numbers (with different counters) are suggested.
- In the Debit or Credit Account column you can search for the account by typing it's description.
- In the columns of the amounts you can enter formulas, such as "30 + 25" and the program inserts the result.
Further information is available on the pages:
Movements import
By importing transactions from bank, postal or credit card statements, data entry in the Transactions table is speeded up and errors are avoided. Data is recorded exactly as it appears on the bank statement.
- In addition to the account statements, you can also import data from other programs.
- The program automatically completes the missing values.
- Several formats are available for importing.
- You can copy and paste data from other programs.
- Imported data can be completed, modified or deleted.
- Ability to program extensions to import any type of file.
Further information is available on the Import to Accounting page.
Management of multiple information
A lot of information can be indicated for each entry row:
- The value date and that of the document.
- A progressive number of document and protocol, or external reference.
- Any additional information you need by adding columns.
- Link to a digital document file.
- Add and remove links.
- Open the link and view the content.
- VAT management (if the type of accounting with VAT was chosen in the creation of the file):
- By entering the VAT code in the transaction, the program calculates the VAT automatically.
- Break down and post the VAT on the designated account.
- You can define whether the amount is net or gross of VAT.
- You can indicate that it is a reversal by inserting the minus sign "-" before the VAT code.
- You can indicate a VAT percentage that is not recoverable.
- You can encode special cases with additional codes.
- Cost and Profit centres:
- Up to 3 cost and profit centers for each posting line.
- You can post negative by indicating the "-" sign in front of the cost or profit center account.
- Segments:
- For each debit or credit account you can indicate up to 10 segments.
- Supplier management:
- Management both on the basis of competence (setting as ledger) and cash (setting as cost and profit centers).
- Management of due date and payment, to have the report of open and paid invoices.
- Client management:
- Management both on the basis of competence (setting as ledger) and cash (setting as cost and profit centers).
- Management of due date and payment, to have the report of open and collected invoices.
- Invoices to customers:
- Data entry for the creation of invoices.
- Customer account suggestion.
- Quantity and price (make columns visible).
- For billing or cost control.
- Automatic calculation of the amount.
- Item number (if option activated)
- To connect to the items table.
- Automatic calculation of the quantities of products entered and exited.
- Print invoices.
- Indication of further information needed to print the invoice.
Account card
From the Transactions table you can access any account card, just go to the account cell (in the Debit or Credit column) and click on the small icon that appears in the upper right corner of the cell.
When you are in the account card, clicking on the row number of a transaction takes you back to the Transactions table, on the original transaction precisely.
More information on account cards can be found on the Account / Category Card page.
Verify data
Entering values is very secure. Banana Accounting has functions that allow automatic detection and reporting of errors.
- The program verifies that the entered values are correct.
- If there is an imbalance between the Debit and Credit columns, this will be indicated in red in the Info window.
- Transactions you are unsure about can be left pending and completed later.
- For each error message there is a corresponding help page (requires internet connection).
- In the Info window below you have the following information:
- Description, movement and balance of the accounts used.
- Error reports error messages with a link to the help page.
- Reporting of the debit and credit difference.
- By entering the actual bank balances via the #checkbalance function, you can immediately check the correspondence of the balances in the accounting and avoid errors.
- With the Check accounting command, the program rechecks all the data entered and alerts you to oversights and errors.
- You can colour the rows, change fonts and make them bold.
- You can protect the rows.
- Lock transactions with blockchain technology.
Arrangement of columns
To have a more congenial data entry, you can arrange all the columns in your own order.
You can choose to:
- Move the columns to the right or left.
- Display additional columns or hide unnecessary ones.
- Add own columns
- Save the arrangement of the columns (views).
Further information is available on the Columns setup page.
The columns of the Transactions table - Double entry
The Transactions table has a series of columns and views already set.
The columns of the Transactions table
The columns listed hereunder and preceded by an * are usually not visible.
In order to make them visible, use the Columns setup command from the Data menu.
Date
The date the program uses to attribute the transaction to a certain time frame. The date should be within the limits of the accounting period defined in the Basic data of the accounting. In the Options tab, one can indicate whether the transaction date is required, otherwise this value can also be left empty.
If there are locked transactions, the program triggers an error message when a date equal or earlier to the one of the lock is being entered.
*Date Document
The date of the document can be entered, for example the date of issue for an invoice.
*Date Value
The value date of the bank operation can be indicated. This value is being imported from an electronic bank statement.
Document
The number of the voucher that serves as a base for the accounting transaction. When entering transactions, it is advisable to indicate a progressive number on the document, so that the accounting document of the transaction can be easily traced.
The auto-complete feature proposes progressive values as well as transaction codes that have been defined earlier in the Recurring transactions table.
The program proposes the next document number, that can be resumed with the F6 key.
-
In case of a numeric numbering, the program simply increases the highest value found in the Doc column.
- Alphanumeric numbering: the program increases the final numeric part; this is useful when one would like to keep a separate numbering for cash and bank movements:
- If earlier Doc number C-01 has been entered, and one starts to type C, the program proposes C-02.
- If earlier Doc number B104 has been entered, and one starts to type B, the program proposes B-105.
- If earlier Doc number D10-04 has been entered, and one starts to type D, the program proposes D10-05.
In the recurring transactions you can setup transactions groups that can be reloaded with a single code.
In order to add a large number of document numbers, you can also use Excel. You can create the desired quantity of document numbers in Excel and then copy and paste it into Banana, in the column of the Transactions Table.
*Document Protocol
An extra column in case an alternative numbering for the transactions or for the document is required.
The auto-complete feature proposes progressive values that function in the same way as the ones in the Document column. It is used, for example:
- When it is necessary to assign a progressive number to the transactions, different from the document number.
- If the transactions are entered by other people, using another file and then these are imported into the accounting. This way it is possible to use both a progressive numbering referred to the accounting and the original number.
*Document Type
Contains a code that the program uses to identify a type of transaction. If you prefer to use your own codes, it is advisable to add a new column.
- 01 In the reports, this transaction is considered an opening transaction, so it doesn't show in the period but in the opening balances.
- from 10 to 19: codes for customers' invoices
- from 20 to 29: codes for suppliers' invoices
- from 30 to 1000: codes reserved for future purposes.
*Document Invoice
A number of an issued or paid invoice that will be used together with the invoice control feature for Customers and Suppliers
*Document Original
The reference number present on a document, to enter, for example, the number of a credit note.
*DocLink to external file
Serves to enter a link to an external file, usually the accounting voucher.
Clicking on the small icon in the upper part of the cell, the program opens the document. See insert, edit and open links.
- When a link has been inserted in the cell, a small icon appears and clicking on it opens the document, but only if it is an extension considered to be safe.
- The other small icon allows you to insert and edit the link.
*External reference
The reference number that was allocated by a program that has generated this transaction. This value can be used to check whether a given operation is imported twice.
Description
The text of the transaction.
The auto-complete feature proposes the text of an already entered transaction, or of one that has been entered in the preceding year when the appropriate option has been activated. When pressing the F6 key, the program retrieves the data of the preceding row with the same description and completes the columns of the active row.
In case the description begins with #CheckBalance, the transaction is being considered as one that serves to check the balance.
Please consult our page Check accounting for more information on the subject.
*Notes
Useful to add notes to the transaction.
Debit Account
The account that will be charged.
- It is possible to also enter a segment in the Debit account column. These are usually separated by a ":" or a "-" o un "-".
By inserting the segment separator sign, immediately move to the next segment. - If instead the Enter key is being pressed, the input will end and one moves to the next column.
- The auto-complete feature proposes the accounts and segments of the Plan of Accounts.
- Instead of the account, you can enter a search text. The program proposes the list of accounts which contains the text in one of the columns.
*Debit Account Description
The description of the entered account retrieved from the Chart of accounts.
Credit Account
The account that will be credited. We refer to the explanation under Debit account for the rest of the information.
*Credit Account Description
The description of the entered account retrieved from the Chart of accounts.
Amount
The amount that will be entered unto the debit and credit account.
*Balance
The Balance column shows the sum of debit and credit. An amount is therefore only displayed for entries in several accounts. At the end of the entry the balance should be zero. If there is a recurring amount it is because there is an error.
VAT columns
Information on the VAT columns can be found att the VAT columns in the Transactions table page
CC1
The Cost center account preceded by "." to be entered without the ".".
If the initials are preceded by the minus sign "-P1", the amount is recorded in credit.
*CC1 Description
The description of the Cost centre, retrieved from the Chart of accounts.
CC2
The Cost center account preceded by "," to be entered without the ",".
If the acronym is preceded by the minus sign "-P2", the amount is recorded in credit.
*CC2 Description
The description of the Cost centre, retrieved from the Chart of accounts.
CC3
The Cost center account preceded by ";" to be entered without the ";".
If the abbreviation is preceded by the minus sign "-P3", the amount is recorded in credit.
*CC3 Description
The description of the Cost centre, retrieved from the Chart of accounts.
*Expiry date
The date before which the invoice has to be paid. For further information see the Customers and Suppliers pages.
*Payment date
Used in combination with the Show Expiry dates command.
When the invoices customers/suppliers control feature in order to check on the payments is used instead, a transaction has to be entered for an issued invoice and another one for the payment thereof.
*Lock Number, Lock Amount, Lock Progressive, Lock Line
More information at the Lock Transactions page.
Additional columns
From the menu Tools → Add New Features → Add Columns Articles in the Transactions table the following columns are added:
IdItem
The item identifier of the Items table. If you insert an article present in the Items table, the description, unit, unit price, VAT code and account are included.
Quantity
The quantity multiplied by the unit price will produce the total amount (can also be a negative number).
Unit
A description referring to the quantity, for example: mq, ton, pz.
Unit/Price
The unit price multiplied by the quantity, will produce the total amount (can also be a negative number).
If a value is entered in the Quantity or Unit Price columns, the amount is calculated on the basis of the contents in these two columns and converted to a positive value.
Adding new columns
With the Columns setup command, it is possible to display, hide or move the order of columns, add new ones, or indicate that a column should not be included in the printout.
- The added columns in the Transactions table will be added also in the Recurring transactions table, in the Account card and in the VAT report, without being made visible.
In order to display these columns in the other tables, use the Columns setup command. - If a column of the "amount" type is being added, the entered amounts will be added up in the Account card.
Views
When a new accounting is being created, the following views are being automatically created as well:
- Base: the main columns are being displayed
- Cost centres: the CC1, CC2 and CC3 columns are being displayed
- Expiry dates: the columns Expiry date and Payment date are being displayed
- Lock: the columns relative to the Lock function are being displayed.
With the Views setup command, the views can be customized and personal views can be created.
With the Page setup command, you can modify the print mode of the view.
Transaction types
Simple transactions (on one row)
Simple transactions are the ones regarding two accounts (one Debit account and one Credit account) and entered in one single row.
The document number is different for each registration.

Composed transactions (on several rows)
Composed transactions with more than two accounts involved, have to be entered on several rows. The user should enter one account per row. The counterpart account for the entire transaction has to be entered on the first row.
The document number, entered on the different rows, is the same because we are dealing with one and the same transaction.
Note:
In composed transactions, the dates of the transaction rows should be the same, otherwise, when doing calculations by period, there may be differences in the accounting.

Opening transactions
The opening balances are normally indicated in the Accounts table.
Opening transactions are required in special cases such as:
- In multi-currency accounting, when you need to have different opening exchange rates than those indicated in the Exchange rates table, opening exchange rate. See Opening transactions in foreign currency.
- Entering Opening balances for segments.
The opening transactions are created by inserting the transactions with the opening date equal to the accounting start date and the code 01 in the DocType column.
- Opening transactions do not change the opening balance in the Accounts table.
- The opening balance entered with transactions is used in balance sheet printouts, account cards.
- If for the same account there is the opening balance and the recording of the opening balance, the two amounts will be added together.
This way, you can enter opening transactions that correct the opening of an account. - When entering opening balances in the transactions, it is necessary to make sure that the sum of the debit (positive) and credit (negative) are at zero.
For each debit entry there must be a corresponding credit entry.
It may be useful to have an opening account that serves as a counterpart for entering opening amounts.
After all the opening transactions, the balance of this account must obviously have zero balance.
When entering opening balances, only the debit or credit account is generally indicated. However, it is also possible to indicate a counterpart which is generally a specific account for openings.
Verification Balance Transactions (#CheckBalance)
Banana Accounting Plus includes the #CheckBalance function in the Check and recalculate accounting command for verifying and matching account balances.
This check is essential for the accuracy of the accounting. It is recommended to perform the balance verification periodically at the end of each month, in addition to the end of the accounting period, to avoid incorrect balances being carried over from month to month.
To perform this check, follow these steps:
- Record the date to which the balance refers.
- In the Description column, enter #CheckBalance followed by the amount corresponding to the balance to be verified (e.g., the actual cash balance, bank account balance from the bank statement, etc.).
- In the Debit column, indicate the account being checked (bank account, cash, VAT account, or another account to be verified).
- The Amount column must be left empty.
With this command, the program will flag any accounts with mismatched balances in the Messages window if discrepancies are found.
Recording Bank checks
To enter issued bank checks, the user needs to insert an Issued checks account in the Liabilities.

The check is issued at the moment of paying a supplier and later on is being debited from the Bank current account.

The Issued checks account card after the transactions.

Credit card registration with advance payment
Advance payment on Credit cards
Before taking you through the procedure, check that an account for Credit card exists in the liabilities part of the Chart of Accounts. Create it if that is not the case.
The credit card account is added to the group or sub-group of short-term debts, as long as this is pre-requisite of the Chart of Accounts selected. If there are no sub-groups, it must be listed in the liabilities section.
Example:
An amount of CHF 1'000.- is transferred from the bank account to the credit card.
- In Debit the credit card account is recorded
- In Credit the bank account with which the payment is made is recorded.
Register your credit card bill
When the credit card bill arrives, you must record all charges listed on the credit card and reverse the credit from the credit card account.
Example:
The credit card statement shows a total of CHF 749.- (detail: CHF 479.- for computer purchase, CHF 150.- for hotel expenses, CHF 120.- purchase of office supplies) (Doc.10)
Enter on several rows:
- All costs related to the expenses listed on the credit card are recorded as a Debit; you post a cost per line.
- Enter your credit card account as a Credit.

Check the credit card account balance
Each time you pay an advance towards the credit card and once all the costs listed on the credit card have been recorded, you must verify that the credit card balance matches the balance stated on the credit card.
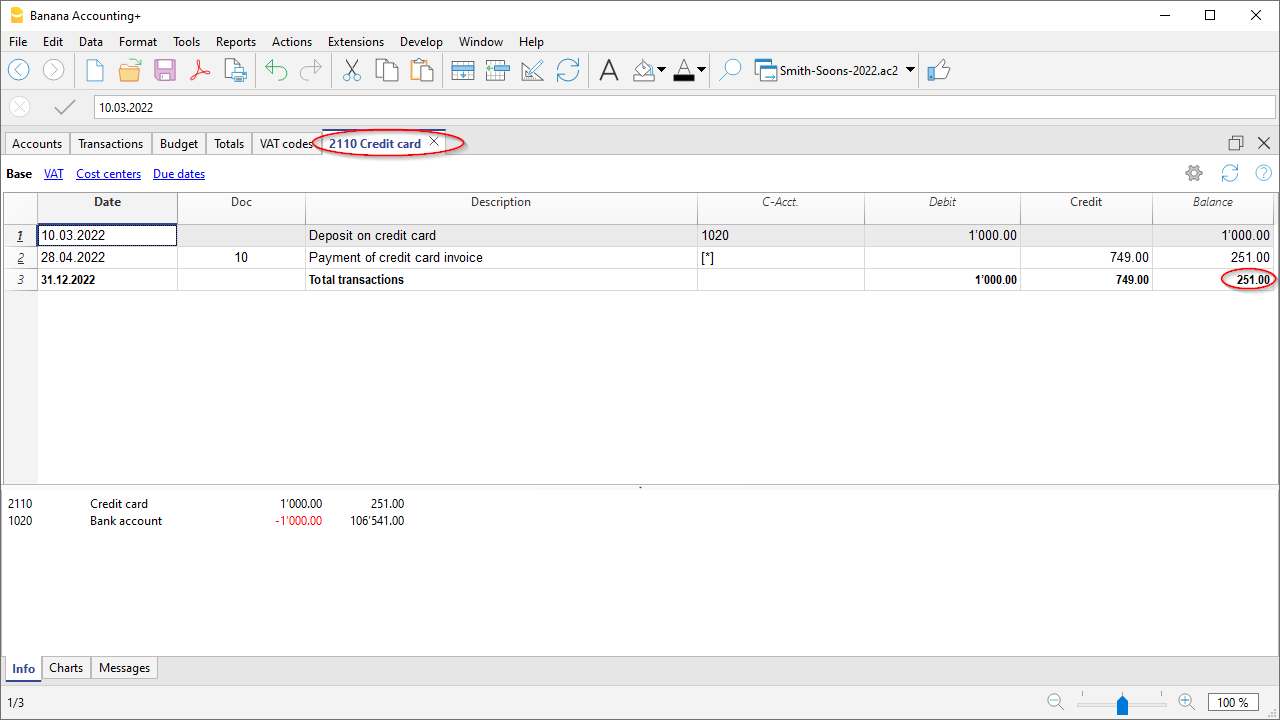
Register your credit card transactions according to the Cash and the Turnover principle
Credit Card with an accounting using the Cash principle
If no down payments are made on the credit card and the invoice is paid in full by the bank, you should record the credit card invoice at the time of payment when the costs should also be recorded.
You need to record on several rows:
- Enter the same date and the same Document No. for each transaction on all the rows that make up for the transaction.
- In the Debit column, enter one account per row, referring to the cost or investment of the credit card transaction.
- Enter the amount of each single transaction recorded in Debit.
- In the Credit column, enter the bank or post office account with which the invoice is paid.
- In the Amount column, enter the total amount paid on the credit card invoice.
- In the case of VAT liability, enter the VAT code for each row in the VAT Code column.

After recording all movements, check your credit card balance by opening the credit card account card.
Credit card and turnover accounting
If the accounting postings are based on turnover, all costs related to credit card purchases are recorded upon receipt of the credit card invoice:
- Enter the same date and the same Document No. for each transaction for all the rows that make up for the transaction.
- All cost accounts are posted as a Debit. Each cost must be recorded on one row.
- In the Amount column, enter the amount of the single transaction recorded in Debit.
- Register your credit card account, as a Credit, as any supplier.
- In the Amount column, enter the total amount to be payed by the credit card.
- In the case of VAT liability, enter the VAT code for each row in the VAT Code column.

When the credit card bill is paid, enter the payment:
- As Debit in credit card account (the debt is extinguished).
- As Credit in the bank or post office account with which the invoice is paid.
- The total amount of the credit card paid is entered as the amount.

Importing transactions from your credit card
Banana Accounting allows the importation of movements from the credit card into the main accounting file.
You must ensure that the chart of accounts includes the credit card account and the transfer account to be used for down payments.
Install the format of your bank
In order to be able to carry out the import it is necessary that the data format, provided by the credit card issuing bank, is compatible with the formats provided by Banana accounting.
To install the extension related to the data format released by the issuing bank, proceed as follows:
- Menu Extensions → Manage Extensions
- Select the issuing bank of the credit card and click on the Install button.
The format will be displayed in the Import into accounting box.
Importing the credit card movements
After having installed the extension for the Banana compatible data format, proceed as follows to import the data:
- Actions Menu → Import into accounting → Transactions:
- Select the format type of the bank that issued the credit card.
- With the Browse button, select the file transmitted by the bank and confirm with OK.
- Enter the period and indicate the credit card account and confirm with OK.
All transactions are imported into the Transactions table. - Enter the counterpart account that refers to the movement for each row.
Import credit card transactions with deposits made
When deposits have been made on the credit card, they are recorded in the accounting system. In this case, after importing the credit card data, there is the problem of the recording of the deposits. In this case a double transaction appears on the credit card account:
- Presence of the credit card account as a counterpart to the bank charges for payments to the credit card.
- Presence of the credit card account in the transactions imported from the credit card.
To avoid this overlap, the transfer account is being used at the time of import.
How to proceed with the import:
- Actions Menu → Import into accounting → Transactions:
- Select the format type of the bank that issued the credit card.
- With the Browse button, select the file transmitted by the bank and confirm with the OK button
- Enter the period and indicate the transfer account. Confirm with the OK button.
All transactions are imported into the Transactions table. - Enter the counterpart account that refers to the movement for each row.
Registrazioni su conto privato
Il conto privato è un conto finanziario, utilizzato nella contabilità per registrare quelle transazioni che non riguardano direttamente l'azienda, ma il patrimonio personale del titolare. Questo conto tiene traccia dei prelievi e degli apporti del titolare a scopi privati; pertanto serve per tenere separate le finanze aziendali da quelle personali, evitando confusione contabile.
Prelievi dall'azienda del privato/socio
I prelievi personali vengono registrati come diminuzione del patrimonio netto. Se il titolare/socio utilizza fondi aziendali per spese personali, l'importo viene addebitato al conto privato.
Esempio di scrittura contabile per un prelievo in contanti:
- Dare: Conto privato (per il prelievo del titolare/socio)
- Avere: Cassa/Banca (per l'importo prelevato).
Apporti nell'azienda dal privato/socio
Gli apporti personali del titolare (es. aumento di capitale o versamenti per coprire spese) vengono registrati come incremento del patrimonio netto.
Esempio di scrittura contabile per un apporto in contanti:
- Dare: Cassa/Banca (per l'importo versato dal titolare/socio)
- Avere: Conto privato (per l'apporto del titolare/socio).
Utili prelevati
Se il titolare/socio preleva utili maturati:
- Dare: Conto utili a nuovo (o Risultato di esercizio)
- Avere: Conto privato
Saldo del Conto Privato/socio
- Saldo positivo: indica che il titolare ha un credito verso l'azienda.
- Saldo negativo: indica che il titolare ha debito verso l'azienda.
Totals Table
The Totals table presents the totals by Group and is used to check the accounting balance.
It is processed automatically by the program and cannot be modified by the user.
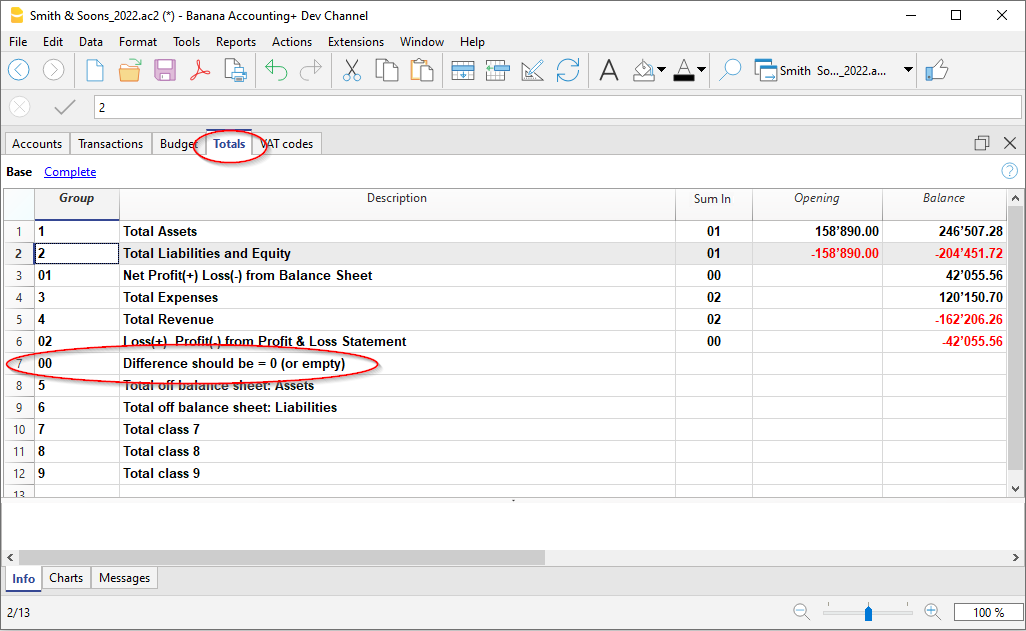
In the Totals table it is possible, to get an idea of the situation of one's own activity at a glance. You see the totals of assets, liabilities, costs and revenues and above all you see if you have a profit or a loss.
The 00 group is very important because it allows you to immediately see if everything is in place or if there are differences in the balances.
Printouts
All the printouts of the Financial Statements, the profit and loss Statement, and the various accounting Reports are available from the Reports menu. Each command has various options for customizing the various printouts.
To print the content of the tables, please refer to the Page setup section (last paragraph).
Enhanced Balance sheet with groups - colored columns
This example has been realized with the following features:
- Enhanced Balance sheet with groups.
- Columns setup to indicate which columns are to be displayed (in the example the columns of the Current and the Previous year are being displayed)
- Style: Lugano (Groups highlighted), Style properties: Groups and totals: Color.

Enhanced Balance sheet with budget
This example has been realized with the following features:
- Enhanced Balance sheet
- Options Include in print : to indicate which columns to display (in the example the Current, Estimate column is displayed).
- Style: Berlin, colored columns.

Enhanced Balance sheet
This example has been realized with the following features:
- Enhanced Balance sheet
- Options Include in print : to indicate which columns to display (in the example the Current, Previous,% Difference columns have been activated).
- Style: Berlin, colored columns.

Subdivision by semester
This example has been realized with the following features:
- Enhanced Balance sheet with groups.
- Columns setup to indicate which columns are to be displayed (Current and Budget).
- Subdivision -> Subdivision by period in order to set up the sub-divsion by period
- Style: Lugano (Groups highlighted), Style properties: Groups and totals: Color.
- Color column properties to color the columns differently.

Subdivision by segment
This example has been realized with the following features:
- Enhanced Balance sheet with groups
- Subdivision -> Subdivision by segment in order to choose the segment level to be displayed.
- Print style:
When printing the segments, it is not possible to set up the colors of the columns.

Pdf dossier with all the accounting data
The file is being created with a summary that provides access to the different printouts in an easy way.
The following data can be saved in Pdf
- Balance sheet and Profit & Loss statement
- Accounts table, Transactions, VAT Codes, Totals
- VAT reports
- Account cards
If you save this file on a non re-writable CD (to keep together with your accounting documents), this will comply with the legal requirements for archiving the accounting data.
This example has been realized with the following features:
File menu, Create Pdf dossier command

Printing an extra column
In order to print an extra column in the Balance sheet, the following features are used:
- Add a new column in the Accounts table, via the Data → Columns setup menu.
- Enhanced Balance sheet with groups
- Columns - advanced, to make the column visible.
Account cards - Ledger
The account card corresponds to the Ledger and allows you to have a comprehensive list of accounting movements concerning the same account, a cost center, segments and groups.
An Account card contains the following information:
- The name of the account represented by the card.
- The date of the financial transaction.
- The type of financial transaction (e.g., sale, purchase, payment, receipt).
- The amount.
- The description (e.g., the name of the supplier or customer, the nature of the goods or services bought or sold).
Banana Accounting automatically records all transactions entered in the Table Transactions table, allocating them to the corresponding specific accounts. Therefore, the ledger cards are updated every time a transaction is recorded in the Transactions table.
Opening the Account card
There are two methods to open an account card:
First method
This method is recommended when you want to display and print all or several account / category cards.
- Select the Reports → Account Cards in the menu

A dialog box will appear, with the following sections:
For detailed information on the sections, click on the corresponding links.
Second method
- Click on the small icon that appears when you select the cell that contains the account, category or group number.
Updating the Account card
The account or category card is temporary and is calculated at the time of the request. If transactions are changed or added in the Transactions table, the account card is not simultaneously updated.
To update the account card, following changes, the Account / category card command must be issued again, or if the account card is still open, click on the symbol shown in the image below.

Deleting or modifying data
In the accountcards or group cards, it's not possible to directly modify or delete data. If changes are required, they must be made in the Transactions table or in the Budget table (if they concern estimate transactions). After recalculating, the changes are automatically applied to the corresponding account card.
If you are in the account card and you notice an error or a modification to be made, you need to:
- Within the account card, position yourself on the row number related to the modification.
- Double-click on the row number, and the program automatically redirects to the Transactions table, right on the row related to the modification.
- Make the modification and recalculate the accounting (press Shift + F9).
The changes are automatically reflected in the corresponding account card.
The Account Selected column
Starting from any Account card, the Account Selected column, can be displayed, via the Data → Columns setup menu, the account on which the transaction took place will be shown.
When you get an account card of one or more accounts, groups and segments, you will see the exact account that has been used.
The contra account in the account cards
In the Account cards, the "Contrp" Account column (C-Acct.) is present, which indicates the account that completes the transaction.

When there are transactions on multiple accounts (transactions on multiple rows) as in the example below, and there is one account entered in debit and several accounts in credit, or the other way round, the software deducts the possible contra account using the following logic:
- In the first transaction row, the 5000 account is considered the common contra account of the transactions that follow.

- On the Account card 5000, the multiple transaction (Gross salaries for the month of December) displays the [*] symbol as the contra account. It is impossible to have the indication of the contra accounts directly in the account card, because the account has several contra accounts (1020, 5700, 5730). For this reason the program indicates the [*] , which signals that we are dealing with a transaction on multiple accounts.

- On the Account cards of the next transaction rows (1020, 5700, 5730), the common contra account is indicated between square brackets [5700], and indicates a deducted contra account.

Cards of groups and classes
In the Account card of a group or a class, all the transactions of the accounts that belong to the selected group or class are being grouped together.
The accounts of the group or the class can be displayed by making the Account Selected column visible.

Budget Account card
If the budget transactions have been entered in the Budget table, it is possible to have the account or group cards of the budget:
- Via the Reports → Account cards → Budget transactions must be activated.

Print the Ledger (all account cards)
To print the Account cards:
- Reports menu→ Account cards command
- Using the Filter, all the account cards that need to be printed entirely or partially (for example, only accounts, cost centers, segments) can be selected automatically.
- In the various sections Period, Options, Customization, activate the desired options (for ex. period, 1 account per page, ...)
- Press OK to confirm, after having selected the desired options.

For the explanations of the different tabs, please visit the next few pages: Accounts/Categories tab, Period and Options.
The program will show the selected account cards.
In order to print, choose the Print command from the File menu.
When you have activated the Budget table in your file, you may choose which transactions you wish to see (actual transactions or budget transactions).
Include a logo in the account cards
From Banana Accounting 9 it is possible to include a logo in the account cards printout as well. After obtaining your account cards details (with the Reports→ Account cards command), use the File -> Print preview command. From the print preview click on the the Setup icon, and in the dialog window that will open, select your logo with the Logo option (instead of the none option).
You can also check the how to setup a logo page.
Save the settings
In case you regularly print the account cards of specific accounts for example, all those that concern the Sales accounts, it is useful to create a specific customization.
- Go to the Customization tab
- Create a new customization, using the New button
- Indicate the name of the customization, for example "Sales accounts", in the Description field.
- Select the accounts that you want to be printed.
- Set the view options for the tab. It is possible to select and change the view, from those available, but not to create a new one. If you change the layout of a column, for example by changing its header, this will be applied to the associated view of all customisations.
Each time you want to print accounts, select the customisation you have created.
Page setup
In Page setup, you can specify the margins & other settings of the page.
Accounts
You can access this windows by choosing the Reports menu > Account cards command (see the Account cards page).

Accounts
The list of all available accounts appears.
Select all
By activating this option, all the accounts that are part of the Chart of accounts are automatically selected.
If you wish to print one or more account cards activate only the desired accounts.
Selecting accounts with the mouse
- Clicking on the account name selects the account, and if a previous selection was made, it is deselected.
- Clicking on the account tick box (within the checkbox) selects/deselects the account and the previous selection remains unchanged.
- To select multiple adjacent accounts at the same time, simply click on the first one, hold down the left mouse button, move the mouse over the list to select the desired accounts, and press the spacebar.
- To select multiple non-adjacent accounts, hold down the Ctrl key (or Cmd on Mac), and use the left mouse button to move over the list, selecting the desired accounts, and then press the spacebar.
Selecting accounts with the keyboard
- You can navigate the account list using the up/down arrow keys, and select/deselect an account by pressing the spacebar.
Search
The option allows the immediate search of one or more accounts. The account number or description of the account is entered in the box; the program filters the accounts using the search values entered.
You can also enter multiple accounts to be displayed simultaneously, or combine accounts and segments (see developer explanations):
- 1000|1001 will display the transactions for account 1000 and 1001.
- 1000:01 will display all transactions of the 1000 account with the 01 segment.
Sort by account number
If this option is activated, the accounts are sorted according to the selection applied in the Filter (at the bottom of the dialog box). If, for example, there are accounts, cost centers or segments with abbreviations, they are listed in alphabetical order.
Filter
This function allows you to filter all account cards or just a selection, specifically:
- Accounts, cost centre and segments - if no selection is made they are filtered by default
- Accounts/categories (existing cost centres and segments are excluded)
- Accounts, Cost centres (only segments are excluded)
- Cost centres (accounts and/or categories and segments are excluded)
- Segments (accounts and/or categories and cost centres are excluded)
- Groups - existing groups will be shown - you need to select the ones to be printed
- Classes - all classes will be shown - you need to select the ones to be printed.
Actual or budget transactions
When you have activated the Budget table in your file, you may select:
- Actual transactions
The entries in the Transaction tab will be processed.

- Budget transactions
The entries in the Budget tab will be processed.
If the Budget table is not present, but amounts have been entered in the Budget column of the Accounts table (Budget View), these amounts are converted into monthly amounts. The division performed by the program is based on the start and end date of the accounting period (if the duration is 1 year, the division will be into 12 monthly installments).

Account card 00 - Differences in accounting transactions
When there are discrepancies in the transactions (see Debit - Credit Difference error page), to identify where the error is located, the account statement for Group 00 is displayed (or the statement for the group in your chart of accounts that includes all accounts from Class 1, 2, 3, and 4).
You will have a list of all transactions with the successive balances, which after each entering should equal zero. The row where the balance is not at zero contains the error.
Viewing the Details of transactions
Using the Group 00 account statement, it is also possible to view the details of the transactions.
Once you have selected the Group 00 account statement, the list of transactions will appear. Select any column, double-click on the column, and a screen will appear to select the visible columns. Select the "TransactionAmount" column. After making this change, the screen opened from the Group 00 account statement will display the "Transaction" column in CHF with detailed specific amounts.
Double-click on a column:
![]()
Select the "MovementAmount" column
Next, a new column "Movement CHF" will be added, which will display the details of the amounts of individual transactions. This modification can be useful, for example, when a transaction includes VAT, and you want to see the details of that transaction while keeping the VAT separate.
Invoice recording with VAT:

Details of the invoice recording with VAT, with Account Card 00 and the "MovementAmount" column activated:

Period Accounting Card
The explanations of the Period tab are the same as those for the Enhanced Balance Sheet with Groups, tab Period.
Options tab
Via the Reports → Account cards → Options menu you can access the various options that can be included or excluded from displaying and printing.

Lines before end of page
This function was created in order to avoid printing an account partially on one page and partially on the following. If the account card to be printed doesn't have at least a number of rows corresponding to the number input in this field, printing the whole card will be moved to the next page.
One account per page
By activating this function, each card will be printed on a separate page (even those with few transactions).
Repeat column's headers
By activating this function, the column headers will be repeated for each account, within the page.
Include accounts with no transactions
By activating this function, cards without transactions will be printed as well.
View
You can select the columns view to be included in the account cards display and printout:
- Base
- VAT
- Cost centers
- Expiration dates
If no criteria are specified the program will keep the order present in the Transactions table.
Sort column
In the account card, transactions can be sorted according to different data criteria:
- Document date
- Value date
- Expiration date
- Payment date
Journal
In Accounting, the "journal" is a book of original entry where all financial transactions of a company are recorded in chronological order. It is a fundamental tool for recording accounting transactions and plays a crucial role in the bookkeeping process.
In Banana Accounting, the Journal is represented by the Transactions table, where transactions are entered in chronological order. From this table, the program provides a detailed and complete record of all financial activities of the company and serves as the basis for preparing other accounting documents such as the general ledger, balance sheet, and income statement.
Each transaction is recorded with detailed annotations, divided into specific columns:
- Date: The date on which the transaction occurred.
- Description: A brief description of the transaction, indicating the nature of the accounting operation.
- Debit Account: The account debited for the amount of the transaction.
- Credit Account: The account credited for the amount of the transaction.
- Amount: The amount of the transaction.
Journal prints can be generated either by selection or by using a command that also allows defining a period.
For further information, please refer to the following pages.
With Banana Accounting the Journal corresponds to the Transactions table. It is possible to print the entire journal or just a part of it, selecting the rows that you wish to print.
There are different methods to print the Journal:
- Position yourself in the Transactions table and click on the Print preview icon; then click on the Print icon
- From the Transactions table and select from the File menu → Print preview → Print icon.
- From the menu Reports menu → Journal by period ...
Period

You can choose whether to print all or a defined period. To print a specific period, enter the start date and the end date.
Sorting

In the Sort column tab it is possible to choose the criteria by which the journal should be sorted and printed.
Customize the printing of the Journal
To customize the printing of the journal, you can change the arrangement and header of the columns. Information can be found on the Columns setup page; while the options to include in the printout are found in the Page Setup lesson.
Enhanced Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet represents all the Assets, Liabilities, Expenses and Income at a specific moment. The difference between Assets and Liabilities determines the equity capital. In Banana Accounting, the embellished Balance Sheet has the following characteristics:
- The grouping of the accounts is done according to the contents of the BClass column.
- The Enhanced Balance Sheet (Reports menu), shown in the preview, can be saved in different formats (PDF, HTML, MS Excel) and can be copied to the clipboard.
- It is possible to calculate, display and print the budget at the end of the year, or for a specific period.
- Transactions without date are considered as opening transactions and will not appear in the printouts of the Profit & Loss Statement.
To calculate, view and print out the Enhanced balance Sheet, click on the menu Report > Enhanced balance Sheet. A window appears with several sections allowing you to set the printing parameters.
See also Printout Examples.

Print pages and Include in printout
In these sections, by activating the different options listed, you can choose the content to be displayed and printed in the Enhanced balance sheet.
The option "Previous year balances" is only available if the field All is selected in the Period section. If a specific period is defined instead, the option is not active. In this case, the Enhanced balance sheet with groups should be used instead.
Page headers
Rows 1 - 4
Rows available to define the heading of the balance sheet.
Logo
It is possible to insert the logo in the header of all pages of the report.
If one or more logos have been added in the menu File > Logo setup, you can select one from the list.
If no logo has been added, the Edit button can be used to add the logo.
Print page number
If this option is activated, the number is printed in footer progression.
Print date
If this option is activated, the date is entered in the footer.
Cover page
Print cover page
Activating the function prints the cover page.
Logo
It is possible to insert the logo in the cover page of the report.
If one or more logos have been added in the menu File > Logo setup, you can select one from the list. If no logo has been added, the Edit button can be used to add the logo.
Column headers
The boxes at the bottom of the enhanced Balance Sheet dialogue box are used to insert the current and previous year headings in the printout.
The first two vertical boxes refer to the dates of the balance sheet, the second to those of the income statement.
At the moment, when opening the dialogue window of the Enhanced Balance Sheet, the boxes for entering the current and previous year are not clearly visible.
To view the boxes mentioned, one must scroll all the way down the vertical scroll bar, located on the right-hand side of the dialogue box.
Current year
Insert the final date of the current accounting.
Previous year
Enter the final date of the previous year's accounting in this field.
When switching to the new year from the menu Actions > Create New Year, the header of the previous year is not adapted automatically, so it must be changed manually. This issue will be resolved in the future.
Dialogue not fully visible
To display the Enhanced Balance dialogue box completely, choose one of two procedures:
- Enlarge the dialogue box.
- Slide the scroll bar, located on the right-hand side of the window, downwards.
Other tabs
The explanations for the other tabs are available at the following pages:
Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups
Banana Accounting automatically calculates, displays, and prints the Balance Sheet and the Profit and Lost account. These are two fundamental financial documents used by businesses to monitor and report their financial and operational activities.
The Balance Sheet and the Profit and Lost account can be customized both based on the period and the columns to be displayed. Balance Sheets can be generated for monthly, quarterly, semi-annual, and annual periods. Additionally, when selecting a period (e.g., semi-annual), the data can be further broken down by periods (month, quarter).
The Balance sheet with groups differs from the Balance sheet for the following characteristics:
- Displays the subgroups in detail.
- Offers the possibility to exclude groups or accounts (for instance, to display only the total of the group and not the accounts of which the total is composed).
- In the Chart of accounts →Sections it is possible to select which accounts to include or leave out from the printouts
- It is possible to sort by a given period (for example in the first semester, you can choose whether to obtain the data by month or by quarter)
- It is possible to have a subdivision by segment.
In order to calculate, display and print the Enhanced Balance sheet by groups, click on Reports → Enhanced balance sheet with groups command from the menu: a window appears, with different sections that allow the user to define the print setup.

Features:
- Reports with actual balance data, or budget data, or both, with indication of variances.
- Free arrangement with groups and subgroups.
- Updated results directly visible in the accounts table.
- Customizable prints:
Watch the video tutorial that shows how to create and print the Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups.- Addition of your own logo.
- Choice of columns to include.
- Choice of sections to include.
- Detailed or grouped printing.
- Prints for a single period.
- Columns with breakdown by period (month, quarter, semester, year).
- Previous year values.
- Comparison with forecast value.
- Columns with breakdown by segment.
- Addition of attached notes.
- Grouping as in the chart of accounts or according to your own scheme.
- Saving customization
- Tabular reports (similar to customizable prints, but with data present in the table).
- Export to PDF for data preservation and export in other formats for data processing.
See also Print Examples.
FAQ
- If I exclude the groups with a zero balance, the title rows that refer to the excluded groups are still being displayed; how can I erase them?
Go to Sections and activate Hide current row on the title rows that you wish to exclude. - I would like to exclude the display of the period in the titles of the printouts ("1st Semester 2013"); how can I do that?
Go to the Headers section and deactivate the Print period option. - On the cover page, when there are long titles, I would like to be able to choose how to subdivide the texts into two rows and wish to apply bold print. Is this possible?
It is not possible to change the fonts on the cover page. - Some amounts are not included in the indicated period. Why?
Transactions without a date are counted as openings and do not appear in the printouts of the Profit & Loss statement. Be sure to enter the date into all the transactions. - The total groups that contain all the accounts of the classes 3 and 4 are being renamed with the text Profit or Loss, depending on the result of the accounting period. How can I change that text?
Go to the Sections and overwrite the original text in the Alternate text zone of the active row. - How can I display the data of the previous year if it is longer than the standard year?
In the "Enhanced Balance Sheet by groups" dialogue box, under the heading "Columns", for the "Income Statement" section, click on the "Advanced" button, in the "Columns" window click on "Add". At this point, activate the "Prior" option in the "Print Columns" window. Then close all windows by pressing the "ok" button. You can customize the header of the columns in the "Columns" window, by clicking on the "properties" button, if necessary.
Headers
In the Page → Headers section are the options for heading the pages and the logo when printing the Financial Statements and Income Statement.

Header 1, Header 2, Header 3, Header 4
Enter as headers the text you wish appearing in the printouts. The headings inserted are shown on the first page (cover page) and on each sheet as main headings.
Logo
It is possible to insert the logo in the header of all pages of the report.
If one or more logos have been added in the menu File→Logo Setup, you can select one from the list.
If no logo has been added, the Edit button can be used to add the logo.
Print period and/or subdivision
This option is active only when a specific period has been defined. When you deactivate this option, the period will not be indicated in the titles of the printouts.
Footer
Print page numbers
By activating this function, page numbers will be printed.
Print date
By activating this function the date will be printed.
Cover page
Print cover page
By activating this function the cover page will be printed.
Logo:
It is possible to insert the logo in the header of all pages of the report.
If one or more logos have been added in the menu File→Logo Setup, you can select one from the list.
If no logo has been added, the Edit button can be used to add the logo.
Layout
In the Page → Layout section you set the font size and the page orientation for printing the Balance Sheet and Income Statement.

Font size
The display of the printout varies according to the entered value.
Page orientation
You can select the page orientation: automatic, landscape and portrait.
Logo
Via the File → Logo setup command it is possible to include a logo and to define its settings (width, height, position). It is also possible to create and save Customizations with different logo settings.
This feature is a simpler alternative to the logo setting with the Documents Table.

To activate the logo option when printing the Financial Statements and Income Statement, it is necessary to select Logo, instead of none.
For the Logo option to be visible, you need to have set up your logo in the File → Logo Setup menu.
Margins
In the Page → Margins section you set the margins for printing the Balance Sheet and Income Statement.

Top, Bottom, Left, Right
It's the distance between the page border and the content.
Header
Is the distance between the page header and the content.
Footer
Is the distance between the page footer and the content.
Increase margins to printable area
If the content exceeds the page margins it will be automatically adjusted to fit the printable area.
Sections
The Section section shows how the chart of accounts is structured and subdivided.
The structure is set up using the Section column in the Chart of accounts.
It allows you to set:
- Items to be printed together.
- Page changes.
- Items to be excluded from the print.
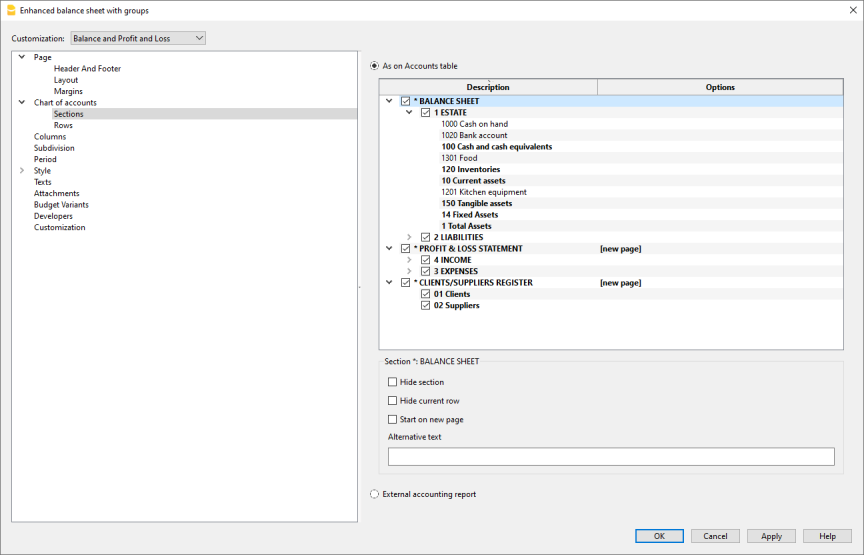
As on Accounts table
The display and the printout settings of the Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups, are the same as in the Accounts table.
By clicking on the arrow on the left you can display the components of the section. Normally only groups with a balance are displayed. To also display the groups with zero balance, go to the Rows section and click on view groups with zero balances.
Depending on the selection, there are different sections with different options:
- Sections 1, 2, 3, 4, 01, 02, 03, 04... refer to the main items of the Balance Sheet
- Account sections refer to the selected account
- Group sections refer to the selected group
Section*
If you select a section with an asterisk, you will have the following options:
Hide section
Click on the section that you wish to hide.
Hide current row
Click on the row that you wish to hide.
Start on new page
Click on the header that you want to have on a new page and activate the option.
Alternative text
Enter an alternative text if you want to have a different one for the selected section or row.
If you select a number or a group section (1, 2, 3, 4.....), there are extra options:

Group for % calculation (%)
Is visible when you select a section (assets, liabilities, costs, income ....).
It is the group that serves as the basis for calculating the percentage of the section accounts and groups.
- Determined by the software.
The group is established by the program. As a rule, it is the last group in the section (total assets, liabilities, costs and income). - Group indicated by the user.
For the income statement, a group must be indicated (for example, total sales).
Hide child rows
If you select a group and you activate this function, child rows of this group won't be printed in the Enhanced Balance Sheet.
Show as account
If you select a group and you activate this function, the group will be displayed as an account in the Balance sheet. 
External accounting report
Print the Enhanced Balance Sheet by groups, based on the structure of the Accounting report file.

Report File
You can select the file of the External Accounting report with the Browse button.
Grouping column
Column in which the accounts refer to the groups defined in the External Accounting report. Available columns: Gr1, Gr2, Gr, BClasse and GrVat.
Signal missing grouping
Checks whether all accounts belong to a group in the External Accounting report.
Rows
In the Chart of Accounts → Rows section you can choose to print the following elements: Accounts, Accounts with zero balance, Accounts with transactions, Groups with zero balance, Empty rows.
Double entry columns setup
The Chart of accounts > Columns section contains the most important options for customizing the columns to be displayed and printed in the Financial Statements and in the Income Statement and Notes.

Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Statement and Notes
If the various options are activated, the following data will be included in the display and printing of the reports:
Account number
In addition to the account description, the account numbers are also included.
Current
The balance or movement in the basic currency, referring to the selected period or to the subdivision of the period.
% of row
Includes the column with the percentage referred to the total (e.g.% total assets).
The total group to base the percentage calculation on can be set in the Sections tab.
The group is set by the program, but especially for the Income Statement, it is not always determined ideally, so it must be set manually.
Foreign currency
This option is only visible in a multi-currency file.
By activating the option in the printout, the balance will also be displayed in foreign currency for the selected period or the subdivision of the period.
Opening
The opening balance for the period.
Budget
The amount of the budget, referring to the selected period or the subdivision of the period:
- If the Budget table has not been set up, the amount in the Budget column of the Chart of accounts is indicated.
The total amount of each account is divided over 12 months. - If the Budget table has been set up, the budget amount of the accounts is calculated based on the transactions entered in the Budget table.
Previous period
The amount for the period prior to the selected period or period split.
Previous year
The amount for the same period of the previous year.
Difference
Is the difference between the amount of the current period and that of the other column (Budget, Previous period, previous year).
% Difference
Is the difference between the amount of the current period and that of the other column (Budget, Previous period, previous year).
Year-to-date
The balance or movement from the beginning of the accounting to the date of the last posting.
Advanced
With the Advanced button you can further customize the arrangement, texts and colors of the columns.
Hide/Show.
You can hide or display a column that is indicated in the list.
Change sequence
Use the Move Up and Move Down buttons or drag the column with the mouse.
Add new column
You can include other columns from the Accounts table or one of the columns calculated by the report in the report.
Remove the column from the list
With the Delete button the column is deleted. You can always add it again:
Special cases
Previous accounting year beyond the current accounting period
If the previous accounting year is longer than the normal duration of the current year (for example, it starts in November or December), the Previous column of the Accounts table is used to correctly display the totals of the income statement of the previous year, as otherwise, Banana accounting calculates the totals of the income statement taking the same duration as the current year and the totals will differ from what is displayed in the financial statements of the previous year.
In this case proceed as follows.
- For the Income statement, deactivate the Previous year and Previous period columns
- Click on Advanced ...
- With the Add ... command, add the Columns table Accounts > Prior column
- With the Properties ... command, enter the text to be displayed as the header for the Prior column
- Row 1 > Text > "2021", "2022", ...
- Confirm and display Enhanced Balance Sheet.
Columns (Advanced)
This dialog allows you to see the list of different columns as they appear in the report and to customize their column display, headers, and column content colors or background colors.
You can change the list of columns with the Add or Remove buttons:
- Accounts table columns
Complete list of columns in the Accounts table - Acounting amounts [A]
List of columns calculated for the current accounting period. (A=Actual) - Budget amounts [B]
List of columns calculated on the basis of data from the Budget table. (B=Budget)

The following options are available:
- Hide/Show columns
With the check you can hide or make a column that is indicated in the list visible. - Change sequence.
Use the Move Up and Move Down buttons or drag the column with the mouse. - Add new column
You can include other columns from the Accounts table or one of the columns calculated by the report in the report. - Remove the column from the list
With the Delete button the column is deleted. You can always add it again. - Change text or background colour.
Columns - add
In the Balance sheet, Profit and Loss Statement and in the Notes, it is possible to add further columns.
Starting from the Reports menu → Enhanced Balance sheet with groups → Columns → Advanced button → Add button.

Available columns list
The dialog lists all the columns that can be included in the report:
- Columns present in the Accounts table.
- Columns with Accounting amounts .
- Columns with Budget amounts.
Activating the column from the list adds it to the report. In the Advanced dialog you can change the sequence and headings.
By removing the check, the column is removed from the report.
Columns present in the Accounts table
You can include any column of the Accounts table, for example:
- Note.
- Aditional description.
- Description in another language.
- Import or other columns added by you.
Accounting amounts
These are the columns with the amounts calculated by the program, the opening balances and the entered transactions, for the indicated period or for the subdivision period
Amount in the Account currency
Only visible for multi-currency files. Account balances in foreign currency are also displayed.
Current
The balances of the current year will be displayed.
Opening
The Opening balances will be displayed.
Previous (period)
The balances of the previous period are being displayed (month, quarter, semester, etc).
Previous Year
The balances of the previous year are being displayed.
YTD (Year To Date)
This column is only available in the Profit & Loss Statement. The balances from the beginning of the year until the last transaction date are being displayed.
Budget amounts
These are the columns with the amounts calculated by the program based on the budget amounts entered in the Accounts Table or in the Budget Table. If you created the Budget table and if some rows have been entered, the program will use the data of this table for its calculation, even if there are values in the Budget column of the Accounts table. Also see informations on Budget.
Budget (Current period)
The amounts related to the foreseen budget of the current period are being displayed.
Budget Previous
The amounts related to the foreseen budget of the previous period are being displayed.
Budget Previous year
The budget amounts are displayed for the same period as the current one, but from the previous year.
Calculation period annotations
The program cannot calculate values for periods that overlap between different accounting years or for years with start and end dates that do not match.
To obtain balances from the previous year that exceed one calendar year, activate the Prior column. This column replaces the "Previous year" column, which only shows the previous year's balances from 01.01.xx to 31.12.xx.
You get to this column from the menu Reports → Enhanced balance sheet by groups → Columns → Advanced button → Add. Clicking on the Account table columns header will display the list of all the columns defined in the Accounts table. Activate the Prior column.
Headers and options (Columns properties)
In this section there are options to change the column headers in reports.

Headers
Row 1/ Row 2 / Row 3
It is possible to change the columns headers by selecting the Text option (from the drop down menu) and by entering the new header. If you select the Column option, the column name of the selected column will be shown.
Options
Visible
If this cell is activated, the column header will be shown.
Display as a total column
If activated, this option only shows the amounts in the Totals column.
Colors (Columns properties)
The dialog box is accessed via the Reports → Enhanced statement by groups → Columns → Advanced button → Properties → Colors menu. There are options to change the colors of the texts and columns.

Change
With this button you can change the text or the background color
Default color
With this button you can restore the default color for the text or the background.
Subdivision
Via the Chart of Accounts section → Subdivision you can access the options to choose the subdivision of the period (year, semester, quarter, month).

None
Only the data for the overall period are present in print.
Subdivision by period
With the breakdown by period, the program creates columns for the indicated periods. For each period you will see the same columns for the overall period.
The function allows you to view the data of the period for:
- day
- month
- bi-monthly
- quarter
- four monthly
- semester
- year
- 5 years
- 10 years.
The selected period appears in the column header.
In order not to have an excessive number of columns in print:
- Limit the number of items you want to print.
- Indicate a shorter period.
- Indicate the maximum number of periods.

Create periods for the entire year
When the accounting period does not coincide with the calendar year, but you want to view all the months anyway, simply activate this function.
Totals column
This function creates a Totals column of the selected periods in the income statement and in the Totals view.
Maximum number of divisions
The maximum number of periods is by default 36. In particular cases, if you want particular statistics that are very detailed and over long periods, you can manually change this value. A very high maximum number of periods can slow down the program.
Subdivision by Segment
The segments allow you to have reports for a certain section of the company. Segments are defined in the Chart of accounts. With the breakdown by period, the program creates columns for the different segments. For each segment you will see the same columns for the overall period.
Each subdivision takes the name of the header given in the Chart of accounts. The split data (based on your selection) is displayed.
The Subdivision by Segment option is active only if segments have been set up in the Accounts table.
You can select:
- All segments - This way, when new segments are added, they will be automatically added to the printout.
- Blank - The amount not assigned to any segment is displayed.
- Choice of segments - Indicate only the segments you want to see in print.

Totals column
When this option is being checked, the totals for the selected segment will be obtained.
Segment header
You can choose the text to be displayed as column header for the segments.
Period
In the Chart of accounts → Period section, you can limit the processing of data, display and print only to an indicated period or, in the case of a budget, it allows you to obtain forecasts over several years.

All
All accounting entries are included.
Period selected
It means the specified period, indicating the start and end date.
In order to get forecasts over several years, it is necessary to enter the end date of the future year of the budget required, in the File Properties, basic data (File menu). Enter the start and end date of the period in the Period section of the Enhanced balance sheet with groups as well.
To have budgets beyond the accounting period, in the Budget table, the movements must have a repetition code.
The forecast will be displayed in the Budget column.
Movements without date
If transactions without dates have been entered in the accounting, they are considered only if All is selected.
If, on the other hand, you enter, for example, from January 1st to December 31st, the transactions without date are not displayed in the report.
Style Tab
This dialog section includes the option to choose the templates and the number format for printing the Balance Sheet and Income Statement. Each template can be customized by changing the style properties and colors. Columns can also be customized in the Columns section.

Use style
There are different models of the Enhanced balance sheet provided. By selecting one, the user can obtain the Enhanced balance sheet of his choice.
Style property
For each style, the color of the fonts and the backgrounds can be defined.
Value / Change... / Default
These functions allow the user to change style or to restore the default style.
Ignore line formatting
If this function is activated, the formatting will not be maintained.
Number formats
In the Style section you can change the number formats and the display type for negative numbers.

Divide by 1'000
If there are big amounts, by activating this option, three zeros will be taken off.
Show cents
By activating this option the cents will be shown.
Show zero amounts
By activating this option it is possible to choose between having the zero amounts shown with the 0,00 number or with the -,- symbol.
Negative numbers
Negative amounts can be shown with a minus sign before the amount, after the amount or the amount can be shown between parenthesis. You can also activate the option to have the negative numbers shown in red.
Texts
Via the Style → Texts section you can change the texts of the fixed headers that the program uses in the printouts.
To change the value, just double click on the Value cell corresponding to the key to be changed and enter the new text.

Attachments
Via the Attachments section you can add texts to be printed together with the report.
- Texts are printed after the Balance sheet and Profit & Loss statement.
- Each document begins on a new page

Documents
All documents listed in the Documents table (Html or text format) are listed here.
- You can change the report sequence, just by dragging the item with your mouse
- All documents with a check mark will be printed.
Edit
A text editor will open allowing you to enter new text or edit the existing one.
Add
Adds a new element without text.
To add plain text or Markdown documents, use the appropriate commands in the Documents table
Remove
This button will remove the selected element and its content. It's the same as removing a row from the Document table.
Add an attachment with Markdown text
- Add a new document with Markdown text as explained on page Markdown Editor
- Check the attachments list for the document with Markdown text.

Notes
- Printing of Markdown text is only available with the Advanced plan subscription.
- This feature is not available in previous versions.
If the file is open with a previous version of the Banana Accounting software, you will get a message that the file is not totally compatible. - If you edit this section and you press OK, in order to undo the operation you need to enter the Undo command more that once.
Customization
Customizations allow you to create and save print settings and recall them later.
See the page relating to Customizations.
End of Year PDF printouts
From the print preview of a document, you can save in PDF format and print.
You can save in a PDF format the following documents:
- Balance sheet and Profit and Loss Statement
- Accounts, Transactions, VAT, Totals tables
- VAT Reports
- Account cards
This PDF file will have an index that allows for easy access for the different printouts.
If you save this file on a non rewritable CD (to be kept along with the accounting documents), you will comply with the requirements for accounting data archiving.
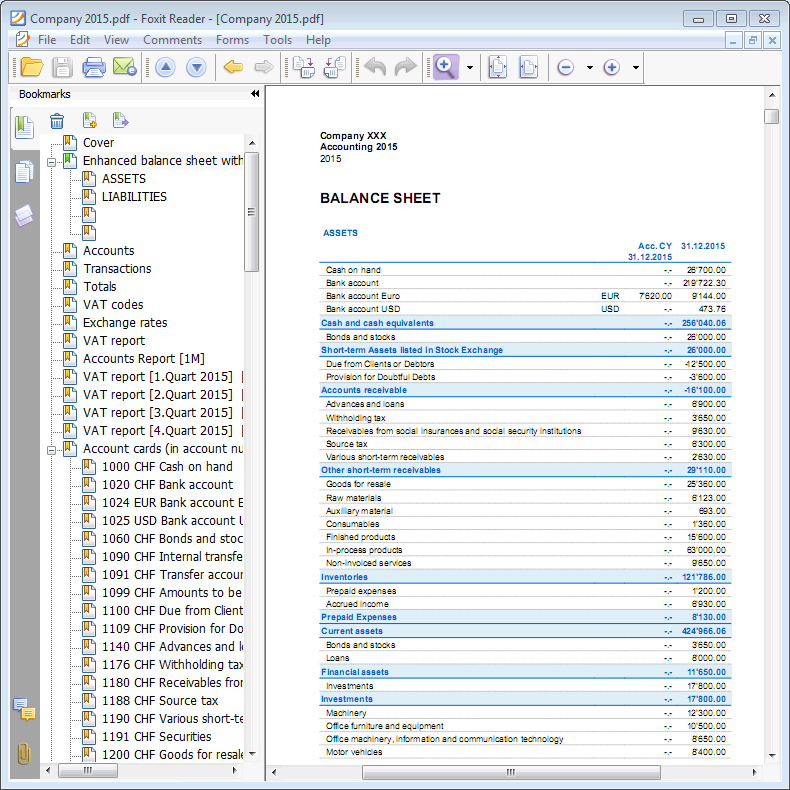
Reports over several years
A statement over several years allows for a simple and immediate comparison of the evolution of your business. Banana Accounting can display balance sheets up to two previous years in the same report, so for example the balances of the years 2022, 2021 and 2020 on a single page.
In order to view the balances over several years it is necessary that the "file previous year" option is indicated correctly in the File and accounting Properties, → Options tab, otherwise Banana Accounting is not able to retrieve the balances of the previous accounting periods, which would therefore remain empty.
In the following example we indicate how to get a report for the years 2022, 2021 and 2020. Here is how to proceed:
- Reports menu → Enhanced balance sheet with groups ...
- Check Current and Previous year in the Columns section.
- Advanced Button (click on the button for both the Balance Sheet and the Profit and Loss Statement).

- From the dialog window that opens, click on the Add button to add a column.

- Scroll down the list until you see -2 Years (we have to go 2 years back, from the current year).

- Confirm with OK to get the report.
Accounting report
- The Accounting Report command from the Reports menu displays and prints the amounts of accounts with a specific grouping, for a specific period or with a specific subdivision.
- Transactions without date are being considered as opening transactions and will not appear in the printouts of the Profit & Loss Statement.
Include a logo in the accounting report printout
To obtain accounting reports with logo, after creating the accounting report, you need to:
- File Menu → Print Preview → select Page Setup
in the dialog box that opens, under Logo, indicate the logo (instead of none).
You can also check the how to setup a logo page.

Base tab
Report
You can select the desired grouping scheme:
- As on Accounts table - the Report will show a list of all accounts just as in the Accounts table with the Opening balance and Balance columns
- Accounts by class - the Report will show the list of the accounts but without subgroups
- External accounting report - the Report will show the data according to a grouping system preset in a separate file (created via File → New → Double-entry accounting → Accounting Report).
Options
You can select the accounts to be included or excluded:
- Show group totals only - only the group totals will be shown
- Include accounts with transactions - only accounts with transactions will be printed
- Include accounts with 0 balance - accounts with zero balance will be printed as well
- Exclude groups without accounts - groups that contain only accounts with zero balance will not be printed.
Other sections
The explanations for the other sections are available at the following pages:
Report result
A new table is created where the results are shown.

VAT summary (only for files with VAT options)
Budget Table
The financial planning entries are entered in the Budget Table. It is similar to the Transactions table, but has some columns specific to help speeding up and make budgeting easier.
You can also modify the data as you require, to own reliable and always perfectly updated budgets.
For more information on the Budget table, see the pages:

Year end closing operations | Double-entry accounting
End of the Year operations include all checking, assessment and time related operation that needs to be at the end of the year before preparing the year's financial statements.
Technical aspects and new year
With Banana Accounting each accounting year has its own separate file; technically there is no concept of accounting closure:
- When a New Year starts a new file is created with the Create New Year command.
- You can keep working on both the New Year's file and the previous year file at the same time. Once the closing operations are complete, you can update the opening balances of the New Year's file.
Fiscal aspects
Before closing the accounting, is is necessary to proceed with a series of operations that have fiscal implications. The inventory account needs to be adapted, transactions for depreciation need to be entered, the transitional income and liabilities, the VAT declaration needs to be completed, establish how and unto which accounts the profit or loss has to be attributed and there are many other operations of verification and checking.
From the program's point of view, there is no difference whether the profit is high or low. There are a lot of implications from a fiscal point of view however. These aspects need to be verified with your own tax advisor or accountant. It can be very useful, especially when you manage an accounting for the first the time and before you proceed with the closing of the books, to consult a specialist in order to understand what is required. Accountants are usually very busy at the beginning of the year and during the period preceding the deadline for the tax declaration. It may therefore prove useful to meet with your accountant or send him the accounting file - a few months before the closing of the books, so that you can inform yourself on how to proceed.
Check accounting command
Banana Accounting allows you to quickly record and also to leave pending operations without interrupting the continuation of the work.
The Actions > Check Accounting command performs a whole series of checks, as if you were re-entering the data from the beginning, and when errors or differences are detected, these are signaled.
It is advisable to use the Check Accounting command with a certain regularity and every time there are differences or error signals, important changes (opening exchange rates, VAT codes) and especially before closing the accounting.
Use the Filter for quick checks and corrections
To quickly perform checks, especially at year-end, we recommend using the Filter function, which allows you to filter all transactions based on a word, a phrase, an account, or a set of elements. The benefit of this function is that you can correct or modify transactions directly on the rows displayed by the filter, without having to scroll through the entire Transactions table to find transactions with the same matches.
For more details, please refer to the page:
- Filter Rows (available only with the Advanced plan).
Checks and Verifications
Before updating the opening balances, to ensure there are no discrepancies between the closing balances and the opening balances for the following year, it is important to complete all checks, verifications, and closing accounting entries. Below is a list of the main steps to follow:
Verification of Opening Balances
- In the Accounts table, in the Opening and Balance columns, the row labeled "Difference must be zero" must not display any amount. If it does, you need to identify and correct the error to ensure the opening balance sheet is balanced.
Note: In the Transactions view, amounts in the Debit and Credit columns are normal and expected. - Ensure that the accrued income and expenses from the previous year are settled.
- Verify that the opening balances match the finalized closing balances from the previous year, which should already have been reviewed and reported to the Tax Office.
- For multi-currency accounting, refer to the dedicated page: Opening Balances in Multi-Currency Accounting.
Verification of accounting balances
The first thing to do is undoubtedly to make sure that the account balances match. The cash account balance must match the actual cash balance. The balance of bank accounts, credit cards, loans, or credit balances must match the balance on the bank statement. The same applies to all other accounts with which you have deferrals, VAT, suppliers, etc.
If there is a difference, you must find out why and correct accordingly either the opening balance or the transactions.
Differences in the Transactions table
In the Transactions table (Info window at the bottom), check that no differences are reported. In addition to the features present in the Check accounting command, in the Transactions table of Banana Accounting Plus there is also the Balance column, which allows you to detect all the rows where differences are created. Just a quick scrolling of the column is enough to immediately identify the accounting differences and correct them, without carrying on the errors in the New Year.
Differences between bank balances of bank statements and accounting balances (CheckBalance feature)
This operation is fundamental for the veracity of the accounting. We advise you to carry on the verification of the balances, #CheckBalance, not only at the end of the accounting period, but periodically at the end of each month, to avoid that any mismatched balances are carried on from month to month.
More information on the verification of balance at the Checkbalance page.
Multi-currency accounting
If you are using multi-currency accounting you must also set up closing exchange rates and record unrealized exchange gains and losses. For this please refer to this page:
Closing accounting transactions
At the end of the year, before moving into the New Year, there are closing accounting operations to be made. These are adjustment entries, value adjustments and adjustments relating to personnel contributions. Here are the main ones:
Import the movements of the cash account in the main accounting file
This operation is only made in case the cash account is kept separately on a separate file from the accounting.
After the import has taken place, verify that the balance of the cash account in the main accounting file corresponds to the balance of the cash file. This verification can also be done with the Check Balance function, described in the previous paragraph.
Import the payroll transactions in the accounting file
This operation is only made if the payroll is managed with a specific accounting software that allows you to import the transactions into the Banana Accounting Plus file.
The import is carried out from the menu Actions > Import into accounting > Import transactions with column header.
Remember to insert the entry of the 13th month of December quota, if this is not created by the payroll software.
Delcredere account adjustment
Companies that record on accrual method, if they foresee potential losses, must settle the Delcredere account.
Depreciation
At 31.12 it is necessary to record the depreciation of movable and immovable assets and to evaluate the possible accelerated depreciation for those assets subject to rapid obsolescence.
You can use our application Fixed Assets Register that automatically creates the depreciation transaction and you can resume them in the accounting file.
Inventory adjustment
Our Inventory application allows you to have accurate counts both by pieces and by value, helping you to determine your inventory settlement faster.
Assess customers and suppliers open invoices at 31.12
To make the process easier, with the feature of open invoices by customer and open invoices by supplier you can quickly detect the values as of 31.12.
Private use
If the company uses a company car, you need to enter the transaction for its private use with the appropriate VAT code.
Closure and VAT declaration
Before submitting the VAT declaration, we recommend the following verification operations:
- Use the Check accounting command. In case of errors and differences, find the messages in the Information window (bottom of the screen), in the Messages section.
- Verify that there are no differences in the Balance column of the Transactions table.
- Check if your bank balances correspond to those shown in the bank statements.
- Verify that, after having reversed the balance in the VAT due account (VAT to be paid to the FTA), the automatic VAT account is zero. The VAT due account must show the amount to be paid or the credit amount to be received.
- Before submitting the last VAT return, take a look at the VAT statements for the previous quarters, to check that the amounts paid to the FTA still match the amounts displayed.
- Use the VAT Report command to view the various reports and create a PDF printout for archiving the data. In the event of tax audits they will be useful.
Settle the account for the "Tax at the source"
After calculating and recording December salaries, proceed to enter the transaction for the "Tax at the source" settlement, based on the statement sent to the "Tax at the source office".
Refunds for upper management
If provided, include the amount allowed by the tax authorities as a lump sum refund in the December salary.
Private account settlement
Verify the balance of the private account. If there is a debit/credit relationship between the business and the owner(s) (or close persons), record the income or expense interests as provided in the loan agreement or according to applicable tax guidelines.
Taxes and fees account settlement
Verify that down payments made during the year relate to the current year. Tax payments that relate to previous years should first be recorded to close the corresponding amounts put aside, and then (if there are any exceeding amounts), they should recorded using the "Direct Taxes" account (assets). If the balance of the provisions is insufficient or excessive, the difference must be recorded as an extraordinary expense/revenue or relating to previous periods.
Recording of AVS/AD/IPG/AD final balances
- During the year, in the AVS contributions account, the down payments made to the Cantonal AVS Compensation Fund (Debit) and the amounts withheld from employees' salaries (Credit) are usually recorded.
- If during the year the family allowances paid to the employees have been recorded in a dedicated account, for example in the "Family allowances contributions" account, in order to reconcile the accounting with the AVS closing statement and to record the relevant settlement, the balance of this account can be transferred to the AVS/AD contributions account.
Recording of Lainf, Lainf complementary, LPP pension final balances
With the recording of the December salaries and the payment of the thirteenth month's salaries, you must print the salary list with the indication of all gross salaries. You must report the total AVS gross amount to the employee's insurance companies, who will determine any adjustments to be paid.
Sending the file to your accountant
If the closures and/or audits are carried out by your fiduciary, just send him/her the accounting file created with Banana Accounting Plus by email or save the data on a USB key.
- If your trustee has Banana Accounting, it is sufficient to send him/her the .ac2 file by email or via USB key. You can also save your file and the digital documents in a shared folder with your trustee on Dropbox. You will no longer have to bring heavy paperwork folders to him/her. Also, the trustee will work faster without having to go through the paper documentation.
- If you your trustee doesn't have Banana Accounting, you can create a PDF file of the accounting data, through the menu File menu > Create PDF dossier and send him/her the file by email. The trustee will indicate to you all the modifications and additions to be recorded in order to correctly close the accounting period.
Alternatively, your trustee can open your accounting file using the Free version of Banana Accounting Plus, by downloading it from our Download page. If your file has over 70 transactions, he/she won't be able to add entries or make modifications, but he/she will still be able to see all the data, get accounts detailed cards just by double-clicking on any account number, etc. and advise you on possible corrections and/or improvements.
Blocking transactions
Once the closing and verification entries have been made, we recommend proceeding locking your accounting transactions.
- Actions menu > Lock transactions command.
The transaction rows will be numbered and have a blockchain code that ensures their security.
Year end printouts
For the accounting year-end printouts you can find the information by clicking on the following links:
- Account cards
- Journal
- Enhanced balance sheet with groups
- Watch the video tutorial that shows how to create and print the Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups.
- Accounting report
- VAT report
- Year-end PDF printouts
PDF Dossier
The Create PDF Dossier command allows you to have all the documents of the entire accounting period (account cards, journal, VAT statements, monthly, quarterly and annual reports...) in a single PDF file.
You can archive the accounting data, saving the accounting file and the PDF printouts. Eventually, make backup copies on an external disk drive.
Documentation for the audit process
On the Preparing the documentation for the Audit page, we have posted a series of notes and suggestions on documentation to send to the auditor. A complete documentation is a good basis for making the auditor's job more efficient and faster.
Profit/Loss allocation
In Banana Accounting Plus, the distribution of the profit or loss takes place automatically at the start of the New Year. For further information consult the page Create New Year.
Changes after closing
Normally, once the closing has been done, there shouldn't be any modifications recorded. However, sometimes there may be a need to adjust the accounting, as in the following cases:
- Unrecorded exchange rate differences at closing
- Unrecorded missing transactions
- Errors in the transactions.
- Make the necessary adjustments in the following year, clearly describing the issue in a document that you will need to attach to the rectification transactions. Of course, depending on the situation, there may be tax consequences, so it is best to seek advice from your accountant.
- In multi-currency accounting, for the issue of unrecorded exchange rate differences, follow the information on the page Differences in the opening balances.
- If the legal framework allows you to make changes to a closed year:
- Proceed with caution, limiting yourself only to truly necessary modifications.
- Double-check the accounting and perform all necessary checks to ensure that the changes do not create problems.
- After the modifications, open the file for the following year and update the initial balances using the Update opening balances command.
Preparing the documentation for Audit
Before preparing documentation to be sent to the auditor, we recommend that you review the information suggested on the Year end closure page. In addition to the information on how to use the program features, there are a number of checks and verifications that should be performed prior to closing.
Firms that are required to be audited must send a number of documents and files to the auditor.
From year to year it is easy to forget what needs to be sent to the auditor. It is therefore advisable to prepare a checklist, which includes all of the documents requested by the auditor in previous years, as well as the closing and adjusting operations to be carried out.
In order to facilitate this task, already during the year, some simple operations can be planned to ease the work for both the person managing the accounting and the one conducting the audit. We recommend the following:
- Create a folder to store scanned documents.
Save ("save as..." command) all scanned documents from the current year's accounting records. - Scan receipts
- Scan all invoices, cash receipts, and OASI statements, social security and insurance contributions.
The digital documents, such as invoices and receipts, can become an integral part of the accounting file. Banana Accounting allows you to insert the scanned document on the row of the contextual record. The auditor, by clicking on the link of the digital document, opens the document and can see its contents without wasting time looking for the information on paper.
PDF printouts to send to the auditor
Below is a reminder of a number of key documents that need to be sent to the auditor:
Declarations for employees
- Declaration of OASI salaries as sent on 31.12 and year-end adjustment
- Declaration for advanced family allowances (already included in the OASI Salary Declaration).
- Employee salary journal
- Employee salary account cards
- Salary certificate
- Non-occupational accident Insurance (NOAI) as sent on 31.12 and year-end adjustment
- Occupational accident insurance (OAI) as sent on 31.12 and year-end adjustment
- Daily allowance insurance declaration (sickness) as sent on 31.12 and year-end adjustments
- Pension fund (OP) extract as on 31.12
- Quarterly IF Swiss Withholding Tax declarations and year-end statement.
Bank/postal account statements
- Final bank and postal account statements as at 31.12
- Bank statements as of 31.12 for possible withholding tax.
- Loan statements as at 31.12
- Investment statements as of 31.12
- Copy of Form 103 sent to the FTA for the payment of withholding tax
VAT/Sales Tax declarations
- VAT/Sales Tax statements of each quarter
- VAT/Sales Tax declarations of each quarter
- Reconciliation of turnover with VAT returns (required at the end of the year)
- Possible VAT/Sales tax difference reporting forms (if differences arise between the booked and reported VAT/Sales Tax during reconciliation)
Accounting closing documents
- List of open customer invoices as of 31.12
- List of open supplier invoices as of 31.12
- Inventory valuation and adjustment as of 31.12
- Details of active and passive accruals
- Details of fixed assets and depreciation (tables, sheets, etc.). Possible accelerated depreciation
- Tax calculation
Official documents
- Minutes of Ordinary Meeting of Assembly previous year
- Extraordinary General Meeting Minutes
- Notification of taxation previous year
- Copy of withholding tax payment order and Form 103 submitted to the FTA for any dividends paid
- Copy of building insurance policy
- Documents in case of patent activation
- Copies of leasing and rental agreements
- Copies of new loan agreements
- Calculation of the expense for other long-term and short-term provisions
- Annual report of the year under review
- Appendix (with explanations) to the balance sheet and income statement
Data export
Accounting regulations require that the accounting data be made available to auditors and inspectors in digital format.
Banana Accounting complies with these regulations because:
- The auditor can use the free plan of Banana Accounting to open the accounting file.
- All accounting data is easily visible in the table.
- The data can be copied and pasted directly into other programs.
- It is possible to export the data in different formats directly from the table.
- The Create pdf file command exports all the accounting data in an ideal format for reading.
Extensions for data presentation and export
There are several extensions for presenting data export in specific formats.
- Audit File Reports create reports that may be useful to the auditor and can be copied and pasted into Excel
- Standard Audit File - for taxation
Data export in XML and other formats according to OECD guidelines and for specific countries. - Search in extensions if there are extensions specific to your country
Other useful information
Below are links where you can find other useful information for optimal accounting and document management:
MWST-Jahresabstimmung
Als Grundregel in Banana Buchhaltung tragen alle Buchungen, die mit einem MWST-Code versehen sind, zur Mehrwertsteuerberechnung und zur Bestimmung der Beträge in den entsprechenden Feldern der MWST-Abrechnung bei. In den Buchungen können verschiedene Ursachen vorliegen, die zu Diskrepanzen bei der Abstimmung des Umsatzes führen:
- Wenn in einer Buchung mit MWST der MWST-Code fehlt, wird der entsprechende MWST-Betrag und der steuerpflichtige Betrag nicht im Faksimile des MWST-Abrechnungsformulars berücksichtigt. In der Buchhaltung hingegen führt eine Verkaufsbuchung auf dem Verkaufskonto dazu, dass der Betrag den Umsatz bestimmt.
- Es wurden Buchungen mit MWST nach der Übermittlung der Mehrwertsteuerdaten an die ESTV hinzugefügt.
- Buchungen mit Mehrwertsteuer wurden, auch versehentlich, nach der Übermittlung der MWST-Daten gelöscht.
- Es wurden Buchungen mit falschem Datum eingegeben und sind in das bereits abgeschlossene Quartal berechnet worden.
- Wenn es Stornierungen gibt und der entsprechende MWST-Code mit einem Minuszeichen nicht verwendet wurde.
- Es wurden MWST-Codes bei Anpassungen und Abschlussbuchungen eingetragen, die normalerweise keinen Mehrwertsteuercode haben sollten.
- Bei Stornierungen von Auslandsverkäufen wurde fälschlicherweise der Code VE-0 eingetragen. In diesem Fall kommt es zu einer Diskrepanz, da bei einer Stornierung der Verkauf als Belastung verbucht wird und somit zu einer Verringerung des Umsatzes führt. Im Gegensatz dazu wird bei Code VE-0 der Betrag des Verkaufs vom Programm als Teil des Umsatzes betrachtet und daher hinzugefügt.
Vorbereitung eines Abstimmungsberichts
- Dokumentieren Sie den Abstimmungsprozess, indem Sie die festgestellten Unterschiede und vorgenommenen Korrekturen vermerken.
- Verfassen Sie einen detaillierten Bericht, der alle Phasen des Abstimmungsprozesses und die erzielten Ergebnisse hervorhebt.
Nützliche Werkzeuge
- Buchhaltungssoftware: Banana Buchhaltung ermöglicht es, auch zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt, Nachbildungen von Mehrwertsteuerformularen, Mehrwertsteuerzusammenfassungen, Jahresabschlussberichte und quartalsweise unterteilte Berichte zu erstellen. Dies erleichtert den Vergleich von Daten über einen längeren Zeitraum hinweg, um Unterschiede oder Fehler bei der Berechnung der Mehrwertsteuer und des Umsatzes zu identifizieren.
- Tabellenkalkulation: Erstellen Sie eine Tabellenkalkulation (z.B. Excel), in die Sie Daten aus Banana kopieren und einfügen können, um Verkaufs-, Einkaufs- und Mehrwertsteuererklärungsdaten zu verfolgen und zu vergleichen.
Empfehlungen
- Regelmässige Überprüfungen: Führen Sie regelmäßige Überprüfungen durch, um Fehler und Diskrepanzen rechtzeitig zu erkennen und zu korrigieren.
- Genauigkeit und Sorgfalt für Details: Seien Sie besonders aufmerksam und sorgfältig bei der Durchführung der Abstimmung, um sicherzustellen, dass alle Daten korrekt sind.
- Unterstützung durch einen Fachmann: Ziehen Sie die Unterstützung eines Steuerberaters oder Fachexperten in Betracht, um sicherzustellen, dass der Abstimmungsprozess richtig durchgeführt wird und mögliche Fehler vermieden werden.
Create New Year | Double-entry accounting
The Actions > Update opening balances command prepares a file for the new year based on the accounting file that is being closed. The command does not modify the current file, so it can be executed without any effect.
Logics of the transition to the New Year
With Banana Accounting you have a separate file for each year. When the new year starts, the operational logic is as follows:
- With the Actions > Create New Year command, the Program creates a new file for the year, using the same chart of accounts, settings and balances of the current year that is about to close.
- Once the new year file is created, save it with a new name.
- The operation of creating the new file can be repeated if you decide not to save the file.
- You can work on both files at the same time:
- In the new one, the transactions of the new year will be entered. It will also be possible to make changes to the chart of accounts, VAT or other, without affecting the previous one.
- In the previous year's file, the operations will continue to be entered in order to complete the year and carry out the typical closing operations, verification of balances, printing of reports etc.
- In the New Year's file, with the command Actions > Update Opening Balances, the changes that were made in the previous year's file are resumed. This operation should be done at the latest when there are no more changes in the previous year.
Once the New Year's file has been created, those who have subscribed to the Professional Plan of Banana Accounting Plus, will see the message Advanced Plan in demonstration mode. This message will appear in the Info window at the bottom of the screen and it will only disappear when reaching 70 transaction rows in the Transactions table.
Checking and closing previous year's accounts
Before updating the opening balances, to ensure there are no discrepancies between the closing balances and the opening balances for the following year, it is important to complete all checks, verifications, and closing accounting transactions.
In Banana Accounting Plus, under the Advanced plan, the Filter function is available. This feature is particularly useful during the closing process to quickly search for rows with the same texts or values based on the key entered for the filter (e.g., word, account, amount, etc.). With this function, it is possible to make corrections directly on the filtered rows, without scrolling through the entire Transactions table—especially at year-end, when the number of transactions is high.
For more details, please refer to the following pages:
- Filter (Filter rows paragraph)
- Checking and closing of a Double-entry accounting
- Closing and exchange rates for the Multi-currency accounting
Specific information for setting up closing exchange rates and recording unrealized exchange profits and losses.
Operations performed by the Create new year command
The Create new year command performs automatically the following operations, taking into account the parameters set by the user:
- Creates a new file (with no name) with the chart of accounts and all the settings identical to your current file, but without transactions.
- Copies the data from the Balance column of your current file to the Opening column of the new file (only for the selected classes)
- Adds the profit or loss of the previous year to the opening balance of the indicated Balance Sheet account or accounts for the breakdown (usually the Profit / Loss carried forward account is indicated).
- Copies the data for all the Balance Sheet accounts from the Balance column of your current file to the Previous Year column of the new file.
- Updates the File and accounting Properties:
- Sets the start and end dates, adding 1 year to the existing ones.
- In the Options section, sets the previous year's file name and enables the option to use the previous year's transactions for autocompletion.
- In Multi-currency accounting, enters the closing exchange rates of the previous year as opening exchange rates.
- If there are data in the Budget table, it carries over the operation rows in the new year taking into account the settings.
- If the Segments option is activated, it creates opening transactions for the segments.
Create New Year dialog
The Create New Year dialog allows you to specify the parameters for creating the new year file:

Carry forward account opening balances
The opening balances of the selected options are carried forward:
Balance Sheet
Carries forward the balances of active, passive and equity accounts. This option should generally be activated.
Profit and Loss statement (not recommended)
The balances of the expense and income accounts must NOT be carried forward to the new year.
This option is only used in special situations. Activate this option only if you are sure of what you are doing.
Off balance sheet
Reports accounts with BClass (5 and 6)
Cost centers
They must be activated if the cost centers are used to manage positions that must be continuous over time, such as customers, suppliers and partners.
Cost center CC1
Those starting with a dot ".".
Cost center CC2
Those starting with a comma ",".
Cost center CC3
Those starting with a semicolon ";".
For further information see the Cost / Profit Centers page.
Segments
The opening balances of the Segments are created with opening transactions in the Transactions table.
- For further information see the Segments page.
- The program creates a transaction for each account and segment matching, exactly resuming the final situation of the previous year.
- It is recommended not to enter opening balances of the segments using the Opening column. If this was done in the previous year, the program will report the balance again in the New Year's Opening column.
Note: settlement operations such as the recognition and closure of transitional accounts, these must be entered manually.
Allocation profit/loss
When the opening balances are carried over into the new year, the profit carryover accounts are added to the figures shown.
Total to allocate
The program will automatically indicate the profit/loss amount that needs to be allocated.
Accounts
Select the account or accounts (up to three) into which the operating result is to be divided. If there are several accounts for the allocation of the financial year result, the amount must be entered manually in the appropriate boxes.
If only one account is indicated, the amount will be automatically entered into the account selected from the list. The program automatically updates the opening balances. The total assets corresponds exactly to the total liabilities.
Allocation of the result of the accounting period on more than three accounts.
In this case, allocate the result of the accounting period automatically on the Profit or loss brought forward account as usual, and continue to proceed with the creation of the new year.
In the Transactions table of the new year (new file), perform a multiple posting to attribute the operating result from the Profit and loss account carried forward to the desired accounts.
Postponing the allocation of the profit or loss for the year
If you do not want to allocate the year's profit or loss yet, you can proceed to the creation of the new year anyway, by clicking on the OK button. Afterwards you can proceed to allocate the operating result from the menu Actions > Update opening balances. The program displays the same window that appears with the Create New Year command.
Save the new file
The program creates a new accounting file for the new year:
- Confirm the File and accounting properties for the new year. The program resumes the headings of the previous year and automatically enters the start and end date of the new year.
- Via the File > Save as.. command, indicate the folder where the new accounting file needs to be saved.
We recommend that you enter the company name and year as the name.
See also Organise accounting files locally.
If there are differences or other error messages, you may also not save the created file and repeat the new year file creation operation later.
Message: Plan Professional with Advanced functions up to 70 rows
The message that appears in the Professional Plan in use, Active Plan: Professional Plan. Advanced Plan functions are available up to 70 rows, only confirms that the Advanced Plan functions are also active and you can benefit from them free of charge, up to 70 lines of transactions, without interfering in any way with the use of the Professional Plan, where you can continue recording without any limit. This message disappears automatically when you exceed 70 lines.
Update Opening Balances
After having entered the last modifications in the previous year, use the Actions > Update Opening balances command, to retrieve the opening balances and attribute the profit of the last year anew.
This operation can be repeated several times and can be carried out safely, as the integrity of the data during the changeover is guaranteed and there is no loss of information.
If you wish to switch to another type of accounting for the new year (with multi-currency or with VAT) proceed with the creation of the new file and then use the command Tools > Convert to new file.
If you want to create a copy of the file, without reporting the balances, use the command Tools > Create file copy
Modifying balances carried forward
Once the balances have been carried over into the new year (new file), if there is a need to change the opening balances, they can be changed manually by changing the amounts in the following columns:
- Opening column of the Accounts table.
- Previous column, for balances relating to the previous year.
- In the Transactions table for the Segments.
If you have made changes in the previous year's file, click on the menu Actions > Update Opening balances, to resume and update the opening balances again.
Update opening balances
The Update Opening Balances (Actions menu) command takes data from the previous year's file and updates the opening balances for the current year.
When do you need to use the Update Opening balances command?
The Update Opening Balances command is required in the following cases:
- You have created the New Year with the Create New Year command, but you still made changes to the previous year's file (additional transactions, new accounts, ..).
- You decided to change the allocation of the the profit or loss for the year.
Check the previous year accounting
In order to avoid differences between the previous year closing balances and the New Year and opening balances, it is important, before using the Update opening balance command, to make sure that you have carried out all the checks, verification operation and all the closing accounting entries as indicated in the Year end closure page.
The Update Opening balances dialog window
In order to access this dialog, use the Actions menu → Update opening balances command.
You need to enter the path to where the previous year's file is located:
- The program will suggest the name of the saved file
- If the file's name or the location path is changed you the Browse button

Operations carried forward by this command
The command resumes the data from the previous year, without changing its contents. This command can therefore be repeated without any impact on the previous year's file.
The command performs the same operations as in Create New Year , except those referring to the creation of the file.
If the opening balances of the Profit and Loss Account accounts were reported in error, follow the information on the Difference in opening balances page (item 5 Solutions) to correct this.
Change of the Chart of Accounts of the previous year
If after creating the New Year you add accounts to the previous year and carry over the balances, the program may indicate an error.
- Update the Chart of Accounts for the current year.
- Repeat the Update Opening balances operation
You can import changes with the Import Accounts command.
Edit current year chart of accounts
If, after creating the new year, you change the numbering of the accounts, when you issue the command Update opening balances, the programme will indicate that it cannot find the accounts.
In this case, you must update the account balances manually:
- Opening column ( Accounts table > Base view)
- Previous column ( Accounts table > Previous view)
How to reclassify the balance sheet and income statement
In Banana Accounting Plus, the reclassification of the balance sheet and income statement is done through the External Accounting Report, a file separate from the accounting, designed to set up a customized presentation of the data. This allows accounts to be grouped differently from the standard chart of accounts structure.
The grouping scheme defined in the External Accounting Report is linked to the accounting file to extract, total, and present the accounts according to the new desired classification. This feature is available exclusively with the Advanced plan of Banana Accounting Plus.
Create an Accounting Report File
To create an Accounting Report file:
- Menu File > New > Accounting Report
- You can choose from an existing template or start from a new one
- Once created, save the file with a name.
Below is an example of a predefined Accounting Report used to create a reclassification of the Balance Sheet according to Art. 959 of the Swiss Code of Obligations.
Everyone can choose to have their own, starting from an empty file.
- When creating your own Accounting Report, groups and totals can be freely defined.
- It is also possible to customize the Accounting Report used in this example by downloading it from our program, as indicated in the previous sections, and customize the accounts or groups for your own reclassification.

The Columns of the Accounting Report
The Accounting Report table includes the same columns found in the Accounts table, where the Accounts or Groups for Totals are set up based on a custom scheme.
In the example, groups and totals were created for the reclassification of the Balance Sheet according to Art. 959 of the Swiss Code of Obligations.

Section
This column is used to indicate the value to be used in the presentation.
For the different options, see the Documentation on sections.
Group
Indicates the group in which to totalize the accounts retrieved from the accounting and the total group.
Account (visible only in the Complete view)
The account from the accounting file to be included in the accounting report.
- If accounts are entered, only those specified accounts will be included when the Report is executed.
- If no accounts are entered, the accounts from the accounting will be included, linked via the group.
Description
Description of the grouping or account.
Sum In
In the Sum In column, the Group (total row) in which the row should be totalized is indicated.
Tot
If set to "Yes", only the total row is displayed, not the individual account rows that make it up.
See Show only group totals in the Accounting Report.
Keep
Normally, the report includes total rows that contain accounts with balances.
If set to Yes, this column ensures the row is always shown. It can be applied to both groups (totals) and accounts.
With Mov.
Applies to groups with a zero balance.
The row is displayed if there have been movements during the period.
**Traduzione blocco 3** ```html
Methods for Reclassifying the Balance Sheet and Income Statement
To reclassify the balance sheet and income statement, you must first prepare the Accounting Report file.
There are two methods to set up the Accounting Report file for the reclassification of the balance sheet and income statement:
1. Reclassify Based on the Group Column
This method allows the reclassification of the balance sheet and income statement using the Group column of the Accounting Report file.
In the Accounting Report, you create your own system of groups and subgroups
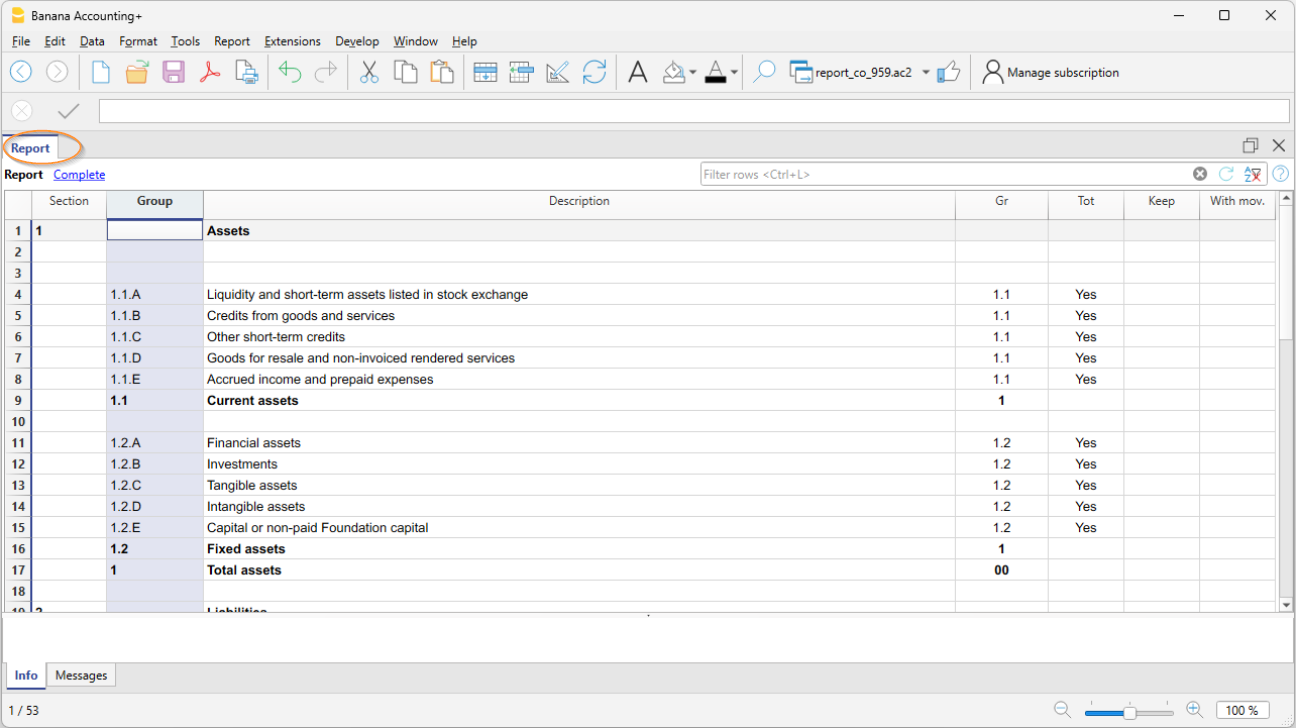
In the Section column, a number is inserted to define the title of the various sections in the printout.
- In the Group column, enter the groups that will total a series of accounts from the accounting file.
In the example, Group 101A of the accounting report totals the liquidity accounts (cash, bank, post, etc.). - In the Gr column, insert the group that will totalize the individual groups listed in the previous rows.
In the example, in the Gr column, 1.1, which corresponds to Group 1.1, will totalize the Current Assets.
In the accounting file, to link with the Accounting Report, you must set the GR1 column

- In the Accounts table, column Gr1 or Gr2, insert the group set in the Accounting Report, in which the account should be totalized.
In the example, in the GR1 column all liquidity accounts have the group 1.1.A, which in the accounting report totalizes the Liquidity accounts.
If the Gr1 column is not visible, use the command Data > Columns setup. - Accounts without any linkage will not be included in the Report.
2. Reclassify Based on Accounts
This method is useful when you want to include only certain accounts from the accounting in the Accounting Report file
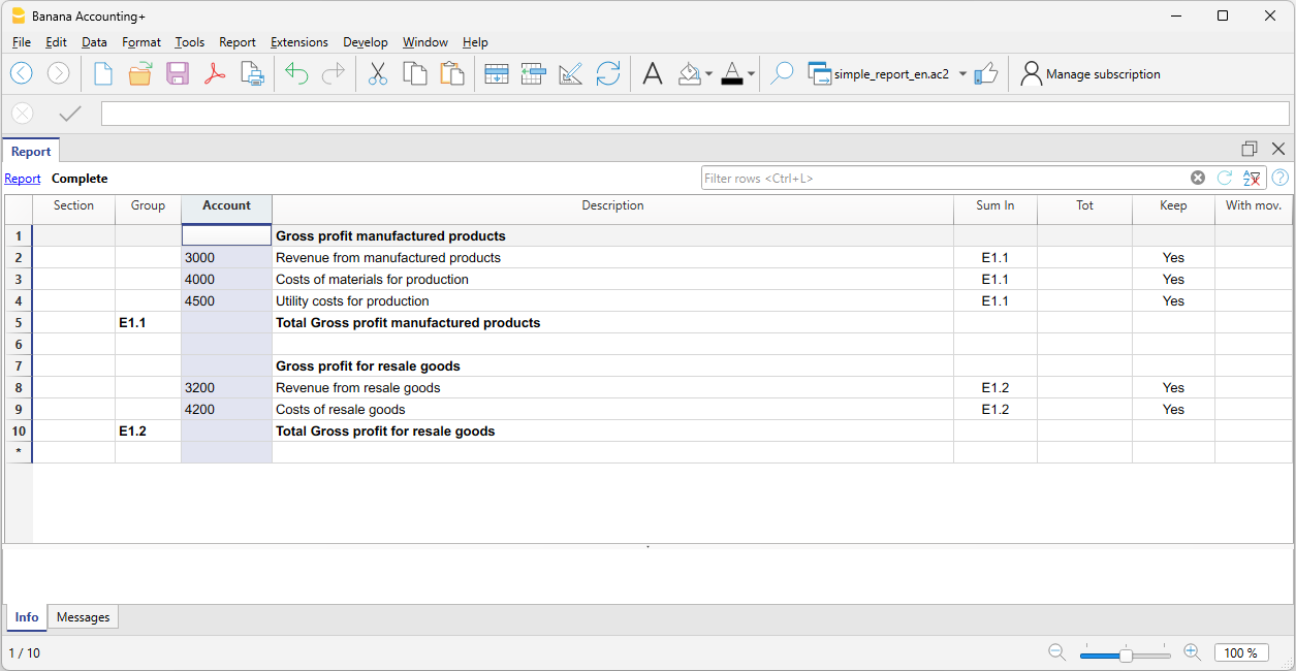
- In the Section column, a number is inserted to define the title of the various sections in the printout
- In the Group column, the groups that total each account imported from the accounting are defined
In the example, Group E1.1 of the accounting report totals accounts 3000, 4000, 4500 from the Accounting Report - In the Account column, enter the same account numbers from the accounting that you want to include in the Accounting Report
Only the specified accounts will be included in the report. - In the Description column, enter the description of the accounts
In the Sum In column, enter the totalization group (e.g. E.1, E1.2...).
Print the Accounting Report
The Accounting Report that reclassifies the balance sheet and income statement is displayed and printed from the accounting file :
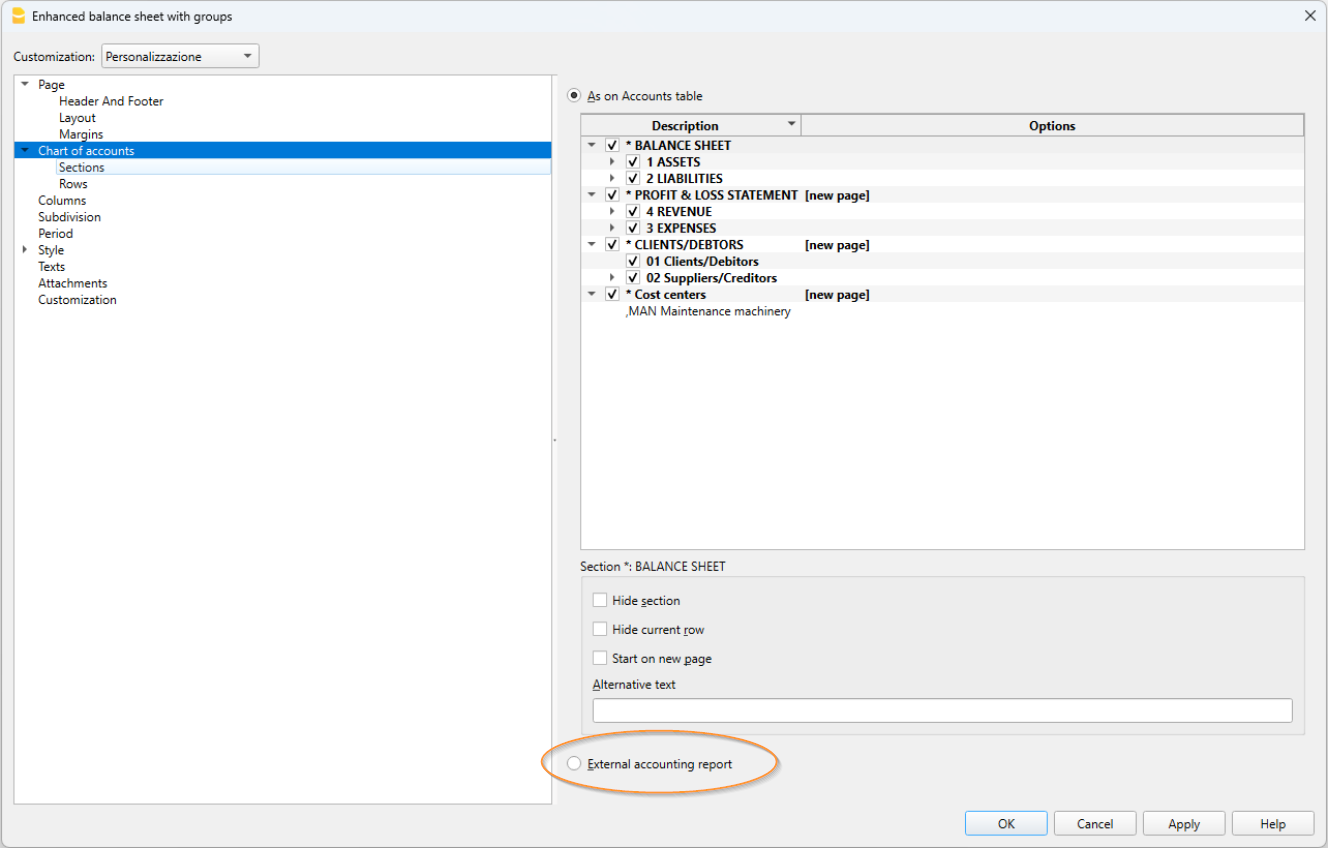
- Menu Reports > Enhanced balance sheet with groups
- Section Chart of Accounts > External Accounting Report
- In the dialog window, in the grouping column, select the column through which you want to apply the grouping (GR1, BClasse, VAT, etc...).
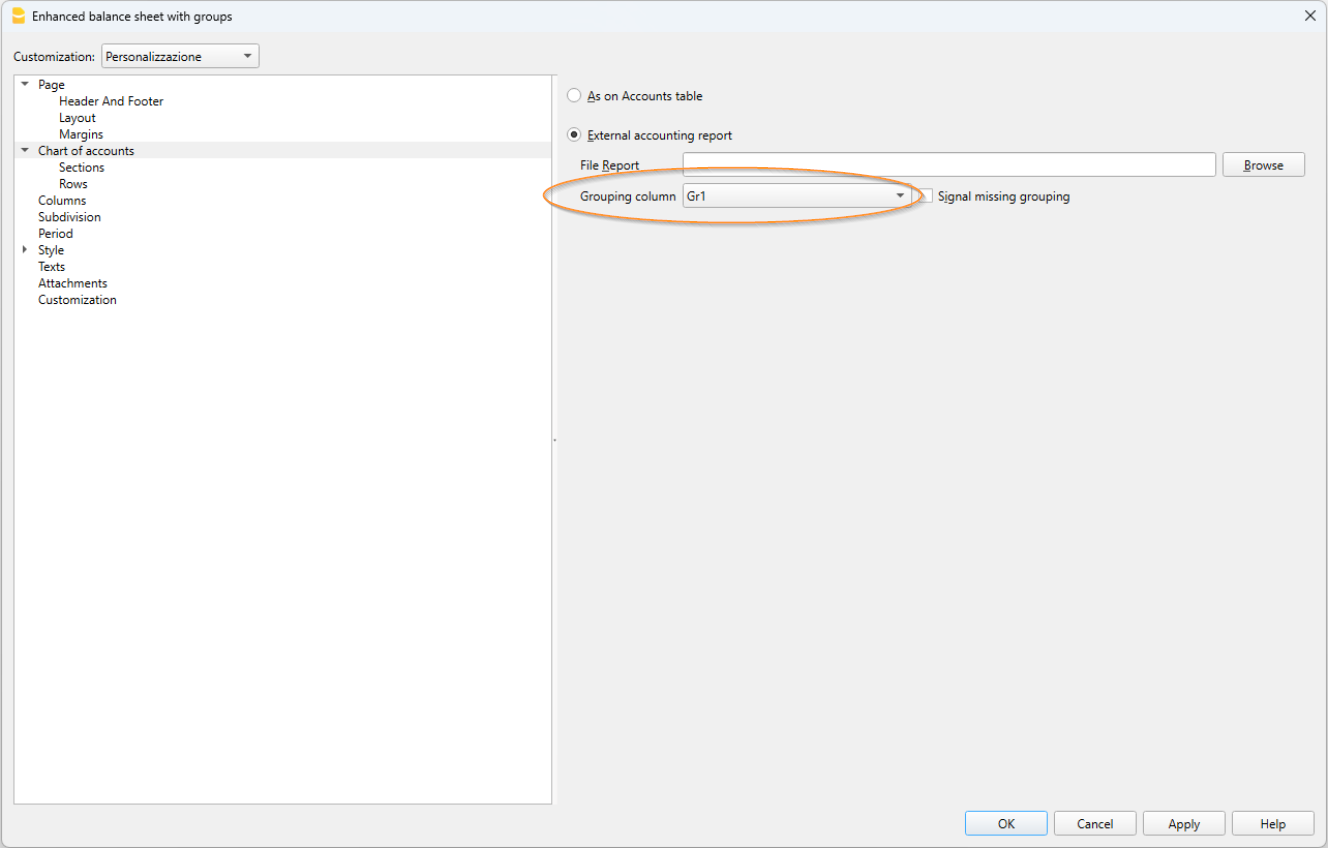
You obtain a printout like the Enhanced Balance Sheet with Groups, but with your own reclassification.
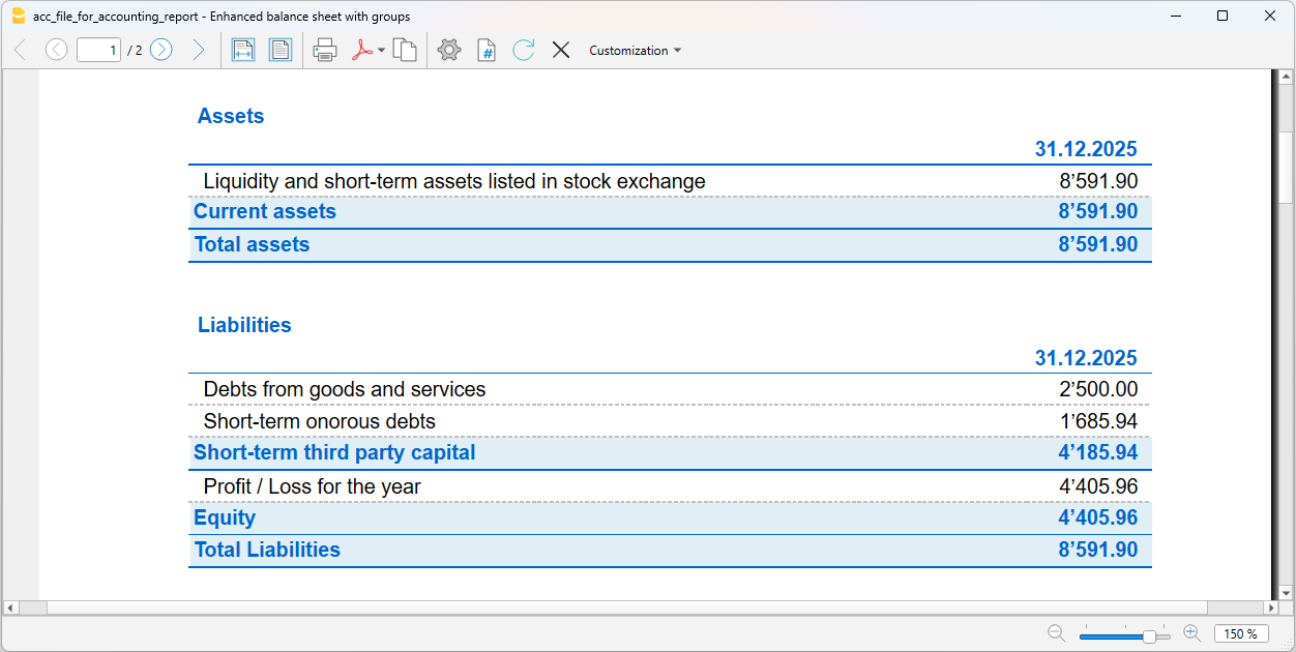
You obtain a printout like the Enhanced Balance Sheet with Groups, but with your own reclassification.
Or:
- Menu Report > Accounting Report
- In the Basic section, select the External Accounting Report option.
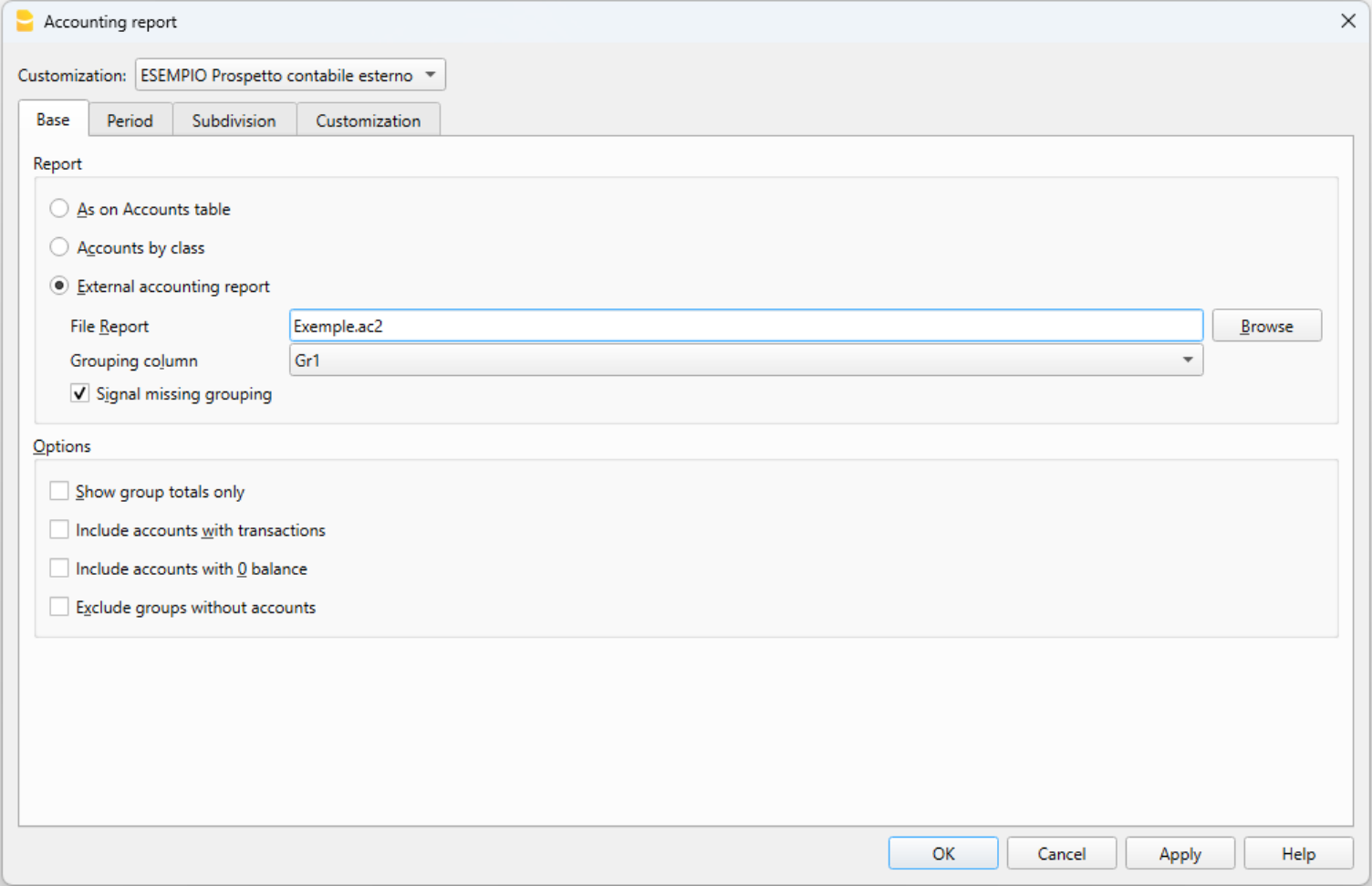
A table view is displayed, similar to the Accounts table, but with your own reclassification
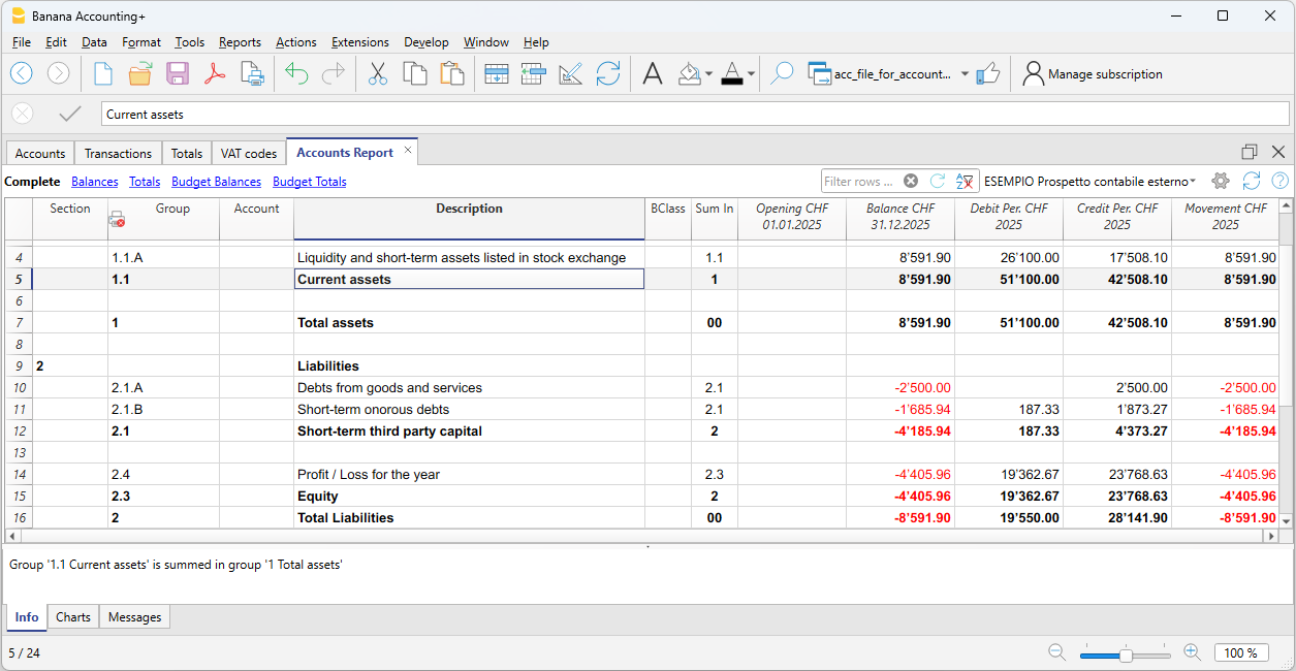
Multi-currency accounting
Multi-currency double-entry accounting is an application of Banana Accounting Plus, to manage accounts in any foreign currency. It is free up to 70 transactions in the Free plan of Banana Accounting Plus. In the Professional and Advanced plans it is instead unlimited.
Ideal for those who work abroad or with foreign countries and want to professionally manage accounts in different currencies.
- ▶ Video: How to start a Multi-currency accounting
- Discover all the Multi-currency accounting characteristics

Powerful and immediate calculations
- Based on double-entry accounting
- Management of accounts in any foreign currency
- Automated calculations and exchange rate differences
- Account statements with values in base and foreign currencies, Journal, Report
- Balance sheets also in a second currency
- Multi-currency financial forecasts
Multi-currency accounting documentation
Multi-currency accounting is a double-entry bookkeeping with the addition of multi-currency management, with many topics common to double-entry bookkeeping. For topics that are missing in the multi-currency documentation or for more in-depth information, please consult the Double-entry accounting pages.
Basics of multi-currency accounting
Chart of accounts, file properties and exchange rates table
We recommend to select one of the already configured examples and to personalize it according to your requirements. Please note that the Chart of Accounts must include accounts in foreign currencies as well as an account for profit and loss from foreign exchange.
- Setup the chart of accounts
- Groups and subgroups
- File properties - foreign currencies tab
- Setup the Exchange rate table
Transactions
Accounting transactions must be entered in the same way as the double-entry accounting transactions
Printouts
Convert double-entry accounting into multi-currency accounting
If, during the year, you need to convert your double-entry accounting file into a multi-currency accounting you can do that easily. In order to add multi-currency features to a double-entry accounting file, please visit the Convert to new file page.
Insights
- Organising Accounting receipts
- How to start a multi-currency accounting
- Accounting with multiple languages
- VAT management.
How to start a multi-currency accounting
▶ Video: How to start a Multi-currency accounting file. Learn how to set up a professional Multi-currency Accounting. Quickly get detailed cash, balance sheet and profit and loss forecasts for the days, months and years to come.
Creating an accounting file, starting from a template
Banana Accounting Plus includes templates for all legal forms, divided by country and by category. They can be opened directly in the program, from the File menu, New... command, or they can be downloaded from our Templates page.
Here is how to start choosing a template directly from the program:
- File menu → New command
- Select the Region, the category and the accounting type (with or without VAT).
- From the list of the templates that appears, select the template that is closest to your own needs.
- Click on the Create button.
You can search for a template by entering a keyword in the Search box; the program displays the templates containing the keyword entered.
It is equally possible to start from a blank file, by activating the Create blank file option. In any case, in order to facilitate the start and avoid grouping errors, we recommend that you always start from an existing template.
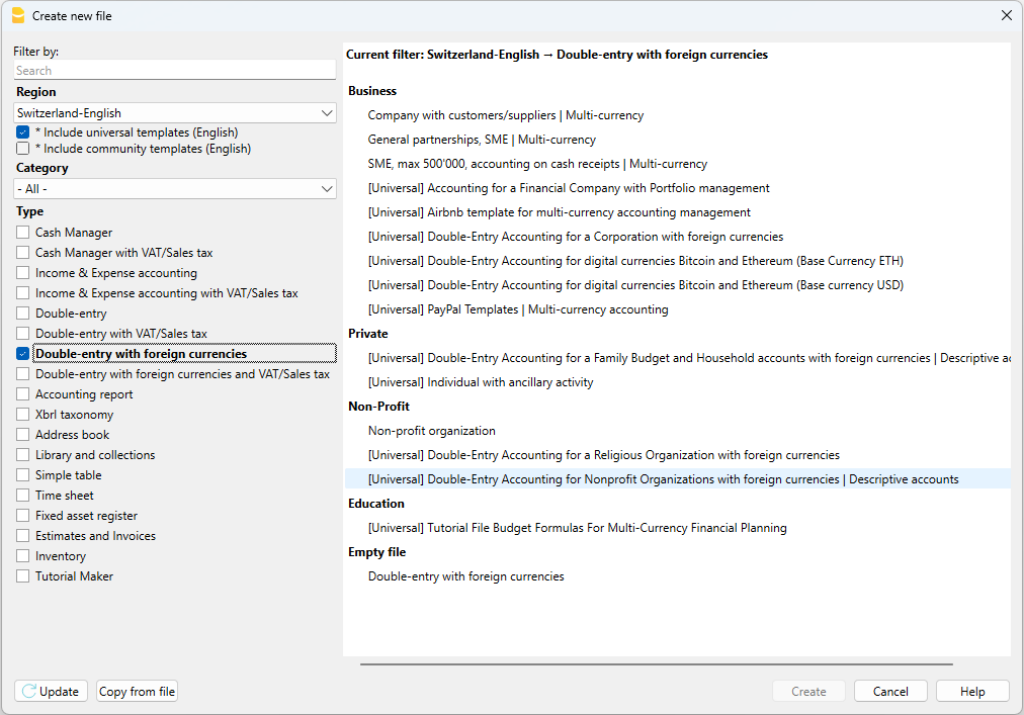
More information on how to create a new file is available on the Create New File page.
Setting up the file properties (basic data)
- Set up the various data sections required via the File → File properties command.
Accounting tab
- Indicate the company name that will appear in the headers of the printouts and on the other data.
- Select the basic currency, with which the accounting will be kept. You can enter it manually or choose it from the list.
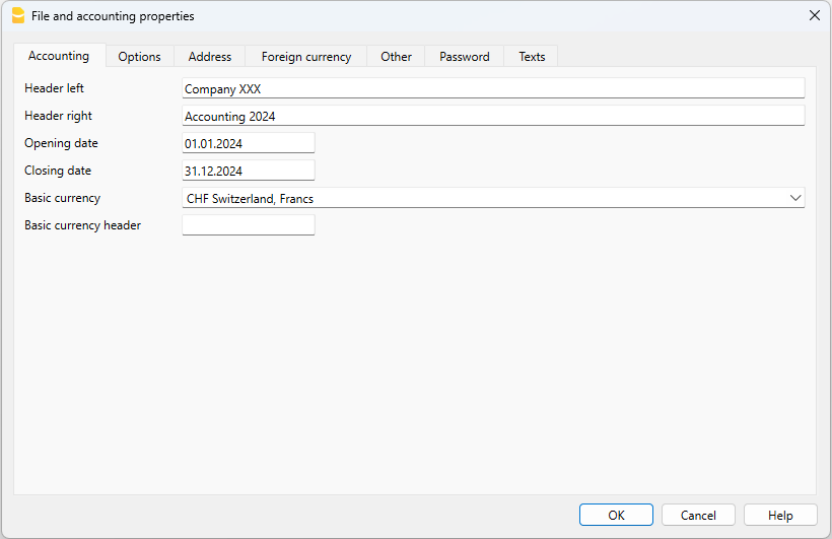
Save to disk
Via the File→ Save As command, save the data and also assign a name to the file. The typical save dialog of your operating system is displayed.
- It is advisable to use the name of the company followed by the year "Company-20xx.ac2" to distinguish it from other accounting files.
- You can keep as many accounting files as you need and each one will have its own name.
- You can choose the path or support you want (save on drive, USB or cloud).
If you also expect to have documents linked to the current year's accounts, it is suggested that you create a separate directory for each accounting year where all the files are to be grouped. Please also visit the Organizing your files page.
General use of the program
Banana Accounting Plus is Excel-inspired. User commands are kept as similar as possible to the ones of Microsoft Office.
For more information on the general use of the program, please visit our Program interface page.
Exchange rates table
In the Exchange rates table, you set the currency codes and the exchange rates that will be used in the Account and Transactions tables.
Customising the Chart of accounts
In the Accounts table, customise the Chart of accounts and adapt it to your own requirements:
- Add accounts and /or delete existing accounts (see Adding new rows)
- Modify the account numbers, the descriptions (for example, enter the name of your own Bank account), enter other groups, etc.
- To create subgroups, please consult our Groups page.
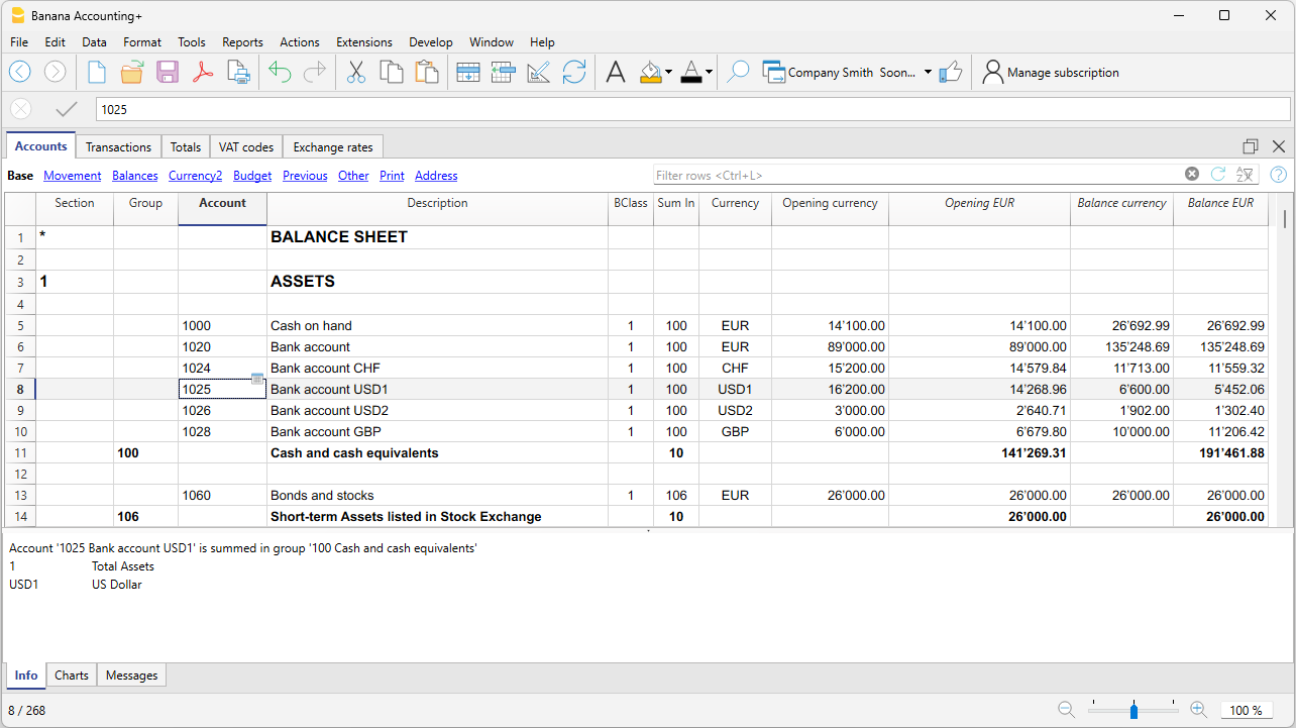
The Transactions table
Multi-currency transactions need to be entered into the Transactions table; together they make up the Journal.
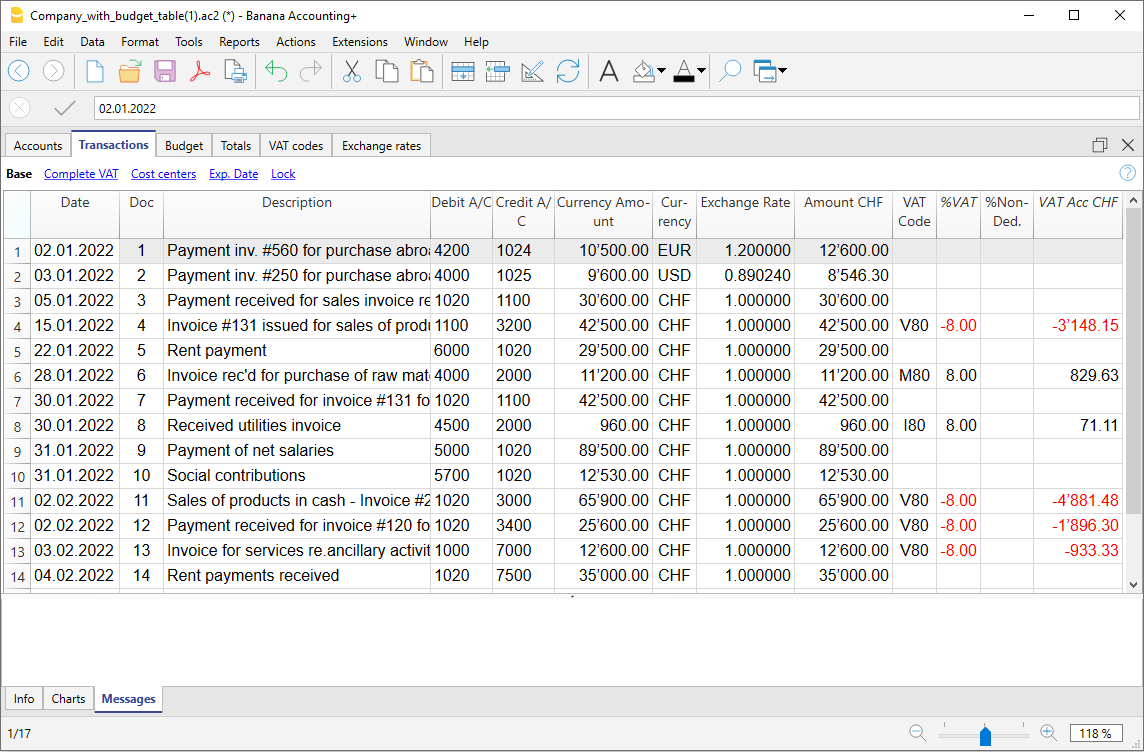
Speeding up the recording of the Transactions
In order to accelerate the recording of the transactions, you can use the following functions:
- Text auto-completion - allows the automatic auto-complete of data that have already been entered at an earlier date
- Recurring transactions - used to memorize recurring transactions into a separate table
- Import Transactions from your bank statement - for automatic import of your bank, post account or credit card statement.
Make visible the Balance column in the Transactions table
The new Balance column is a very useful feature: it allows you to immediately spot possible differences.
The Balance column is not visible by default: you can make it visible via the Data → Columns setup menu.
- Watch the Video: Using the Balance column to spot differences
- More information on the Balance column
Checking customer and supplier invoices
Banana allows you to keep an eye on the invoices to be paid and the receivable, issued invoices. Please refer to:
The Account cards
The Account card automatically displays all the transactions that have been recorded on the same account (for example, cash, bank, clients, etc).

To display an account card, just position yourself with the mouse on the account number and click on the small blue icon that appears.
Account cards by period
To display the account card with the balances referring to a specific period, click on:
- Reports menu → Account card → Period section → Selected
- Enter the Start and the End date of the period.
For further details, consult the page Period.
Printing the Account cards
In order to print one account card, just display the card from the Accounts or the Transactions table and launch the print from on the File menu.
To print several or all account cards, click on the Reports menu → Account card command and select the account cards to be printed. By using the Filter in the window, you can automatically select all accounts, cost centers, segments, groups, etc.
For further details, consult the page Account Card.
The Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Statement
The Balance sheet shows the balances of all the Balance sheet accounts, Assets and Liabilities. The difference between the Assets and the Liabilities determines the Share capital.
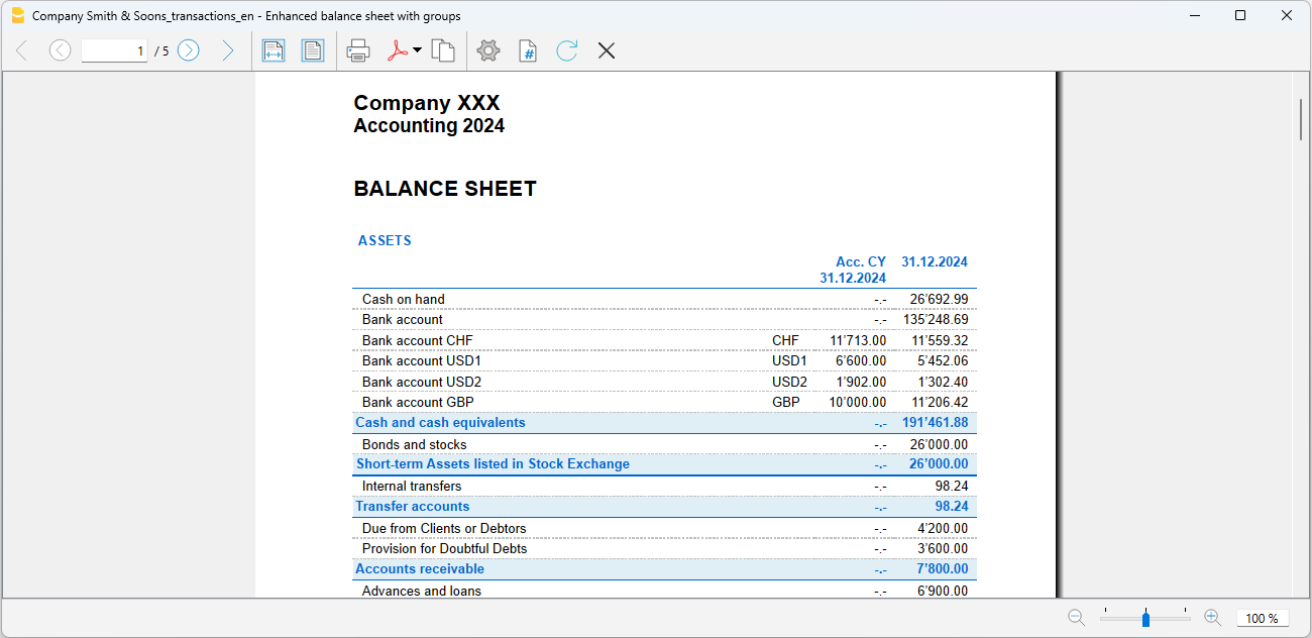
- The Enhanced statement command simply lists all the accounts without distinguishing Groups and Subgroups
- The Enhanced statement with groups command lists all the accounts whilst subdividing groups and subgroups; besides, it presents numerous features to customize the presentation, functions that are not provided in the Enhanced statement.
Data archiving in PDF format
At the end of the year, when the entire accounting has been completed, corrected and audited, all the accounting data can be archived via the Create PDF dossier command.
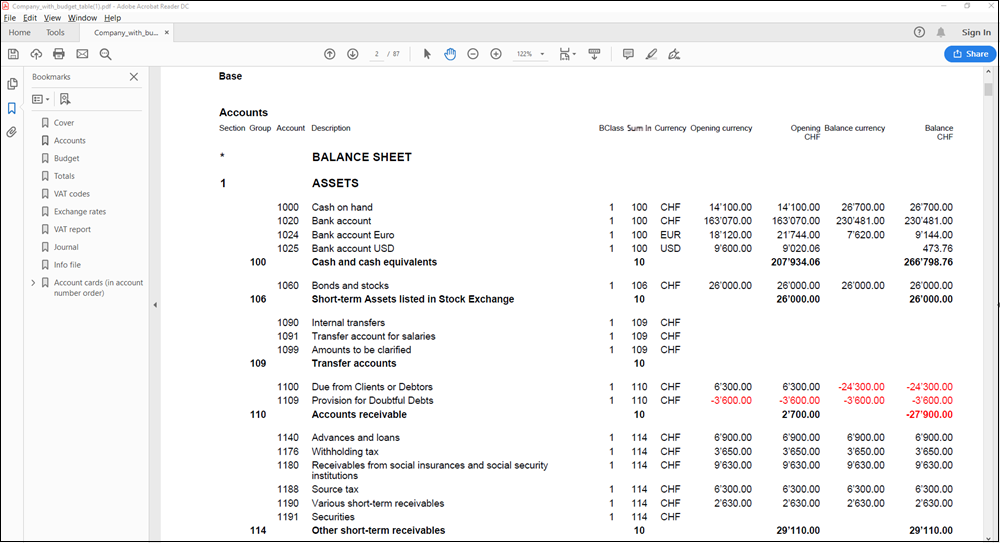
The Budget
- Accounts table, Budget column. For each account, the annual budget amount is being indicated.
In this case, when you set up the Budget from the Reports → Enhanced statement with groups command, the Budget column displays the amounts that refer to the entire year. - In the Budget table, that can be activated via the Tools → Add new functionalities command.
In this table, you can enter all the budgeted costs and revenue by means of entering transactions. If you activate this table, the Budget column of the Accounts table will be automatically deactivated.In this case you can set up a detailed budget, taking into account the possible variations over the year and in different periods of the year.
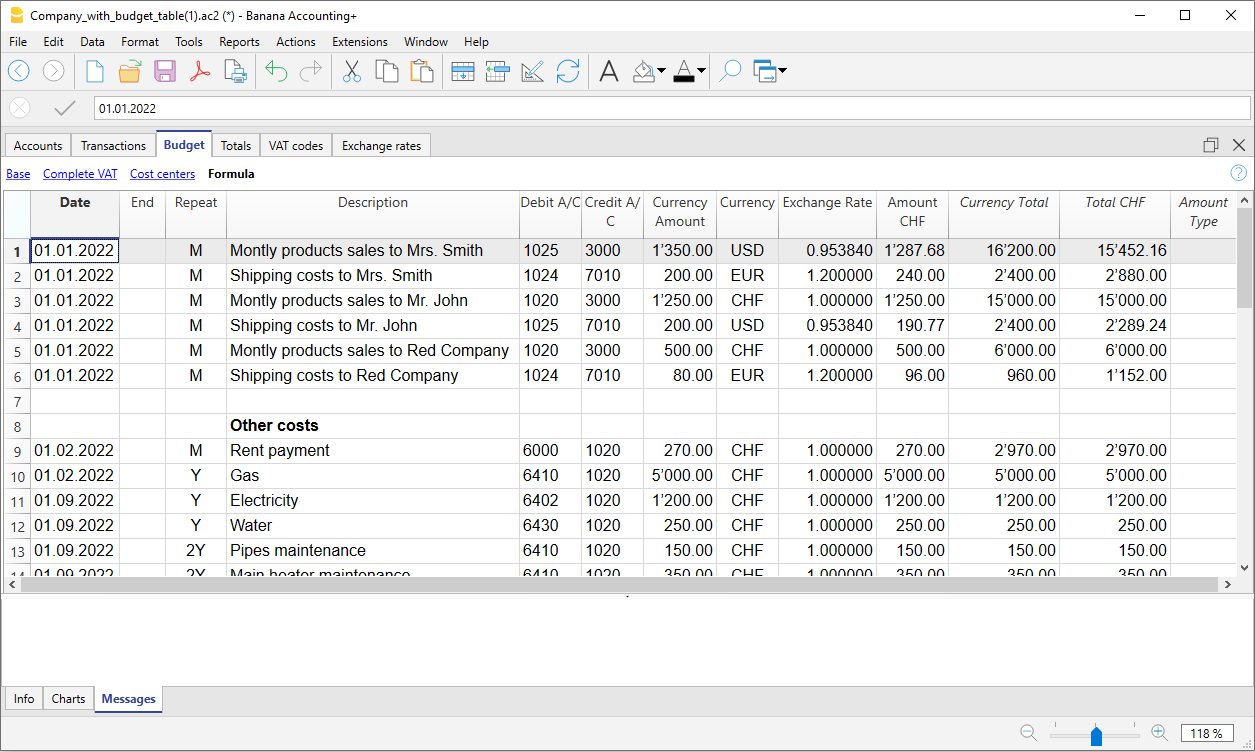
For more details, consult the Budget page.
Characteristics of the Multi-currency accounting
Thanks to Banana Multi-currency accounting, you can easily work on an international level, in the language you want and with the foreign currency accounts you need. Again, the structure is that of spreadsheets, similar to Excel and with all the resources of the other Banana applications. The functions are based on the Double-entry accounting methodology. Should you need to manage VAT you can activate the VAT features at any time.
It will prove particularly interesting for those who have foreign operations, for associations that generally operate all over the world or run projects and simply for those who require accounts in foreign currency in their bookkeeping.
The multiple functions of Multi-currency
- Manage as many accounts as you wish in foreign currency
You don't need to have separate managements to handle accounts in other currencies. In the same Chart of Accounts used for your accounting, enter the accounts in foreign currency, set the exchange rates in the exchange rate table for exchange differences and you are ready to transact. - You can set any currency, standard or freely defined curdrency codes (to use any digital currency).
- Decimals for currencies can be set from 0 to 28. Generally 2 decimals are used, but the accounting can be set to use 0 decimals, or 3 decimals (Tunisia) or more if it is used for crypto currencies. 9 decimal (Bitcoin) or 18 (Ethereum)
- Same methodology as double-entry accounting
You will work with the same double-entry accounting method, therefore register the debit and credit and you will have all the reports and details of a professional accounting. - Automatic exchange rate calculation
The moment you create a foreign currency account, you will not need to calculate the equivalent in foreign currency manually, the program automatically calculates the exchange rate. You can enter the exchange rate either by updating the exchange rate in the Exchange rate table or directly in the Transactions table in the Exchange rate column. - Transactions in different currencies
You are able to enter all necessary cases of transactions in foreign currency, including transfers and those that do not include the basic currency. This allows for complex operations to be carried out in your accounting. - Complete reports with balance sheet, income statement
Accounts of both the balances in foreign currency and of the equivalent value in the basic currency (national currency) will be displayed in the Balance Sheet and Income Statement.
If you have foreign business relationships and you need to present the Balance Sheet and Income statement in a second currency, this is possible without creating separate reports in Excel, just go to the Accounts table, select the Currency2 tab and you will have the display of all the accounts in the second currency and as well as in the basic currency.- Watch the video tutorial that shows how to create and print the Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups.
- Account cards with amounts in foreign currency and basic currency
The account cards can be viewed with the columns of the amounts in basic and foreign currency. This allows you to evaluate the balances in both currencies. - Free exchange rates in the Exchange table
You can set the exchange rates for various needs: variable exchange rates, fixed exchange rates, different exchange rates for the same currency, for example to manage investments and without affecting accounts with the same currency. - Automatic exchange rate differences
When you need to calculate the exchange rate differences, just update the exchange rate in the Exchange rate table and use the relative command; the differences will be entered in the Transactions table automatically. - Budgets are also possible with the Multi-currency
In the Multi-currency accounting file you can also budget the liquidity of the accounts in a foreign currency, as well as all the budgets related to the Balance Sheet and Income aspects. You can print Budgets and forecast reports, or combine them, with the columns of the Budget, Balance Sheet and relative variations. - Automatic check for unrecorded exchange differences
When using the Check Accounting command, you will no longer have unrecorded exchange differences, because if they exist, they will be reported. This function is particularly important to avoid having exchange rate differences in the opening balances when you create the new year. - Financial statements, economic accounts and reports, also in a second currency.
Multi-currency accounting, based on the double entry has many other characteristics identical to the double-entry accounting, which you can refer to on the following page:
Theory of multi-currency accounting
In this section, the basic theoretical notions about currency exchange are being explained.
Exchange rates and accounting issues
Every nation has its own currency and to obtain another currency it is necessary to buy it using the appropriate exchange rate. The price of a currency, as compared to another one is called the exchange rate. To exchange money means to convert the amounts of one currency into another. The exchange (exchange rate) varies constantly and indicates the rate of conversion.
For example, on January 1st
- 1 Euro (EUR) was equal to 1,22637 US Dollar (USD)
- 1 US Dollar was equal to 0,81529 Euro
- 1 EUR was equal to 1,08222 Swiss Franc (CHF)
- 1 EUR was equal to 126,52 Japanese Yen (JPY)
Basic Currency
Amounts referring to different currencies cannot be totaled directly. It is necessary to have a basic currency to refer to and to be used for the totals.
The central point of accounting is that the totals of the “Debit” balances must correspond to the totals of the “Credit” balances. To verify that the accounting is balanced, there must be a single currency with which to do the totals.
If there are different currencies, the basic currency must be indicated before anything else. Once the basic currency has been selected and some transactions have been executed, the basic currency can no longer be altered. To change the basic currency, the accounting must be closed and another one created with a different basic currency.
The basic currency is also used to establish the Balance Sheet and to calculate the profit or loss of the period.
Each amount has its equivalent in basic currency
To be able to add the totals and verify that the operations balance, it is necessary to have the equivalent in basic currency for every transaction. This way you can check that the total of the Debit entries is the same as the total of the Credit ones.
If the basic currency is EUR and there are transactions in USD, there needs to be an exchange value in Euros for every transaction in US Dollars. All the EUR amounts will be totaled to verify the accounting balances.
Account currency
Each account has its own currency symbol which indicates in which currency the account will be managed.
You must therefore indicate what the currency of the account will be. Each account will then have its own balance expressed in its own currency.
Only transactions in that currency will be permitted on this account. If the account is in EUR, then there can only be EUR entries on this account; if the account is in USD, then there can only be entries in USD currency on this account.
When you have to manage entries in YEN, then you have to have an account whose symbol is the YEN.
Account Balance in basic currency
For each account, alongside the balance in the account’s own currency, the balance in basic currency will also be kept, in order to calculate the balance sheet in basic currency.
The account card for the USD bank account has to correspond exactly to the bank statement as far as the USD amounts are concerned.
The value in basic currency will always be specified for each accounting entry. If the account is in USD, in the entries there will also be its value in EUR, beyond the amounts in USD. The EUR balance will be determined by the sum of all the entries expressed in EUR. The actual balance in basic currency will depend on the exchange rate factors used to calculate the exchange value of each single entry to EUR.
If on a given day you take the actual balance in USD and convert it to EUR at the prevailing daily exchange rate, you will get an exchange value that differs from the balance of the account in basic currency. This difference is due to the fact that the exchange rate used for entries on a daily basis is different from the actual daily exchange rate.
Thus there is a difference between the actual value at the daily exchange rate and the accounting balance in basic currency. This accounting difference is called the exchange rate difference.
The difference between the balance in basic currency and the calculated value has to be registered, when the accounting is closed, as an exchange rate profit or loss.
Balances in another currency (currency2)
All the accounting reports will be calculated in basic currency. If you take the basic currency values and change them into another currency, you will get the balance in another currency. The program has a Currency2 column where all the values are automatically entered and presented in the currency specified as Currency2. The logic for the conversion of the amounts is the following:
- If Currency2 is the same as the account or operation currency, then the original value will be used.
- If the account is in USD and Currency2 is USD, the USD amount will be used.
- In all other cases the basic currency amount will be used and changed into Currency2.
- The daily exchange rate is used. Even for past entries, the exchange value in Currency2 will be expressed on the basis of the most recent exchange rate, and not on the historical one used on the day of the entry.
You need to pay attention to the fact that a balance converted to another currency will show small differences in the totals. Often the converted value of a total is not equal to the sum of split exchange values, as can be seen from the following example:
|
Basic currency EUR |
Currency 2 USD |
|
|
Cash |
1.08 |
1.42 |
|
Bank |
1.08 |
1.42 |
|
Total Assets |
2.16 |
2.84 |
|
Personal capital |
2.16 |
2.85 |
|
Total Liabilities |
2.16 |
2.85 |
In the basic currency, total assets are equal to total liabilities. It is permitted to present a Balance Sheet that contains differences only if they are understandable and if it is indicated that they were due to calculations from another currency.
Accounts table, Currency 2 view

Converting currencies
Open a multi-currency model of Banana Accounting Plus
Learn more about the multi-currency feature of Banana Accounting Plus
Below, we explain the theory of how exchange rates work.
Variability of exchange rates
The purchase/sale of currencies occurs in a free market. The price (exchange rate) is based on the law of supply and demand. The differences in the exchange value can be more or less important according to the fluctuations of the exchange rate.
The exchange rates in the following examples, are not the actual daily ones, but are fictitious to explain the problematic.
| Date | Exchange rate EUR/USD | Equivalent in EUR of USD 1000.00 | Equivalent value difference compared to 01-01 |
| 01-01 | 1.32030 | 1'320.03 | |
| 31-03 | 1.33350 | 1'333.50 | 13.47 |
| 30-06 | 1.34750 | 1'347.50 | 27.47 |
| 30-09 | 1.42720 | 1'427.20 | 107.17 |
The exchange rate
The exchange rate refers to the basic currency. There are always two different exchange values between two currencies, according to the currency that is used as the basic currency.
For the USD and Euro currency, there are therefore two different exchange rates:
- If the basic currency of the exchange is EUR then the exchange rate is 1.32030
1 Euro (EUR) corresponds to 1.32030 US Dollars (USD) - If the basic currency of the exchange is USD then the exchange rate is 0.75800
1 US Dollar corresponds to 0.75800 Euros
In the current document, the Euro will be regularly used as the basic currency, to which other currencies will be compared.
Inverse exchange rate
Having the exchange of EUR/USD at 1.32030, it is possible to find the exchange rate of USD/EUR by dividing 1 by the exchange rate.
| Exchange rate | Inverse exchange rate 1/exchange rate | Inverse exchange rate rounded to 6 digits |
| EUR/USD 1.32030 | 0.75800 | 0.758000 |
The exchange values calculated with an inverse exchange can turn out to be different from the original one due to rounding.
| Exchange rate | Inverse exchange rate | Exchange value 10000 x original exchange rate | Exchange value 10000 x inverse exchange rate | Difference |
| EUR/USD 1.32030 | 0.75800 | 13'203.00 | 13'192.61 | 10.39 |
Don't use inverse exchanges rates in order to avoid differences.
For the transition to the Euro, for example, the use of inverse exchange rates was prohibited.
Multiplier
There are currencies that have very large exchange rate values.
Always on January 1st
- 1 US Dollar = 670,800 Turkish Lira
- 1 Turkish Lira (TRL) = 0.00000149 US Dollar (USD)
Instead of using that many zeros, it can be said that
- 1000 Turkish Lira (TRL) = 0.00149 US Dollar (USD)
In this case, the multiplier is 1000 instead of 1.
Preciseness
As a rule, an exchange rate is specified with a preciseness of at least 6 figures after the decimal.
There are, however, cases where it is necessary be more precise.
- 1 Turkish Lira (TRL) = 0.00000149 US Dollar (USD)
When the preciseness is changed and the exchange is rounded in a different way, the amounts also change. The preciseness with which the exchange is specified is very important.
Minimum denomination
Especially for paper money, minimum denominations are used. As a rule the lowest denomination for Swiss francs is five centimes (0.05). When an exchange occurs, for example EUR/CHF:
1 EUR = 1.60970 CHF
| EUR | Exchange rate | Actual exchange value in CHF | Rounded to lowest CHF denomination | Difference | Effective exchange rate |
| 10.00 | 1.60970 | 16.09 | 16.10 | 0.01 | 1.61 |
Calculation of exchange rates and values
When the Euro is the basic currency
The exchange factor for EUR/USD is 1.32030
1 Euro (EUR) is equal to 1.32030 US Dollars (USD).
Calculation of the exchange value:
Multiply the basic currency amount by the exchange factor:
EUR 100 x 1.32030 = USD 132.03
Calculate the basic currency amount:
Divide the destination currency by the exchange rate:
USD 132.03 / 1.32030 = EUR 100
Calculate the exchange factor:
Divide the basic currency amount by the destination currency amount:
Exchange rates for purchases and sales
Banks carry out the purchase and sale of currencies and include a transaction margin. They apply different exchange rates depending on whether a determined currency is being bought or sold.
Sale: the bank receives domestic money and provides (sells) foreign money.
Purchase: the bank receives (purchases) foreign money and provides domestic money.
Currency exchange and banknotes exchange (premium)
Currency exchange: exchange for scriptural transactions (from one account to the other).
Banknote exchange: exchange for banknotes.
Premium: commission for converting a scriptural amount to cash.
To exchange currency, the banks maintain a lesser margin (the difference between purchase/sale) compared to exchanging banknotes. When a scriptural value is to be transformed (credit on the account) into cash currency, the bank applies a commission, called a premium.
Differences when changing back to basic currency
When an amount is exchanged into another currency, it is expected that the reverse exchange will result as identical to the original amount .
| Basic amount | Exchange rate | Exchange value | Return |
| 100.00 | 1.32030 | 132.03 | 100.00 |
However, you do not always come up with the same amount when converting currency back. Because of rounding errors, there may be cases where the same return value cannot be obtained.
| Basic amount EUR | Exchange rate | Exchange value in USD | Return in EUR | Difference in EUR |
| 328.67 | 1.32030 | 433.94 | 328.66 | |
| 328.68 | 1.32030 | 433.95 | 328.67 | 0.01 |
| 328.69 | 1.32030 | 433.96 | 328.68 | 0.01 |
Differences of totals through splitting
The total exchange value of the components of an amount does not always result in the same exchange value as the overall amount.
In this example, the amount of 2.16 EUR produces an exchange value in USD of 2.85. By splitting the amount and adding the two exchange values, 2.84 will result.
| Amount in EUR | Exchange rate | Exchange value in USD |
| 2.16 | 1.32030 | 2.85
|
| 1.08 | 1.32030 | 1.42 |
| 1.08 | 1.32030 | 1.42 |
| Total 2.16 | 2.84 | |
| Difference | 0.01 |
These mathematic differences cannot be eliminated if they are not recorded properly.
Revaluations and exchange rate differences
Exchange rates vary all the time and therefore the exchange value to basic currency also varies. Between one period and another, there will inevitably be exchange rate differences.
Exchange rate differences are not accounting errors but simple adjustments of the values made necessary in order to keep the accounting figures in line with fluctuations.
As you open the accounting, the figures in the balance column are equal to those present in the opening column. When there are entries, these will update the figures in the balance column.
The calculated balance column contains the exchange value of the basic currency for the account balance, at the daily exchange rate (of the exchange rate table). The difference between the balance in basic currency and the calculated balance is the exchange rate difference.
|
|
Currency at opening |
Exchange value at opening in EUR |
Basic currency balance in EUR |
Calculate balance at 30.03.200xx in EUR |
Exchange rate difference |
||
|
Exchange rate |
|
|
1.32030 |
1.32030 |
1.30150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Cash |
EUR |
93.80 |
93.80 |
93.80 |
93.80 |
|
|
|
Bank |
USD |
100.00 |
75.74 |
75.74 |
76.83 |
1.09 |
|
|
Real estate |
EUR |
1'000.00 |
1'000.00 |
1'000.00 |
1'000.00 |
|
|
|
Total Assets |
|
|
1'169.54 |
1'169.54 |
1'170.63 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loan |
USD |
-500.00 |
-378.70 |
-378.70 |
-384.17 |
-5.47 |
|
|
Personal capital |
EUR |
-790.84 |
790.84 |
-790.84 |
-790.84 |
|
|
|
Total Liabilities |
|
|
-1'169.54 |
-1'169.54 |
-1'175.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss |
|
|
|
|
-4.38 |
|
|
On March 30th the EUR/USD exchange rate is different from the one at the beginning of the year. In the above example, there were no accounting entries during the three-month period. The situation, from an accounting point of view, has not changed since the beginning of the year. Despite this the total of the updated balance, using the rate at the end of March, is different when compared to the beginning of the year. The credit bank balance and the loan in USD have a different value in EUR. There are therefore consequences for the accounting even though there have been no entries.
In the above example, you will notice that the Euro is now worth less against the dollar compared to the beginning of the year. The dollar is therefore worth more against the Euro.
The exchange value of the balance on the account in USD is greater than it was at the beginning of the year. You have a greater value of the asset and therefore a profit on the exchange rate.
On the liability side there is a USD 500.00 loan. Now the exchange value in EUR is greater compared to the value input at the beginning of the year. The value of the loan has increased and brings about a loss due to the exchange rate difference.
In the following example we shall use the hypothesis that there has been the opposite development. We imagine that the Euro has increased in value and is therefore worth more against the USD. The exchange value in EUR of an amount in dollars is less than the one at the beginning of the year.
|
|
|
Currency at opening |
Exchange value at opening EUR
|
Calculate balance at 30.03.20XX Eur (Hypothetical) |
Exchange rate difference |
|
Exchange rate |
|
|
1.32030 |
1.36150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash |
EUR |
93.80 |
93.80 |
93.80 |
|
|
Bank |
USD |
100.00 |
75.74 |
73.44 |
-2.30 |
|
Real estate |
EUR |
1'000.00 |
1'000.00 |
1'000.00 |
|
|
Total Assets |
|
|
1’169.54 |
1'167.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loan |
USD |
-500.00 |
-378.70 |
-367.24 |
11.46 |
|
Personal capital |
EUR |
-790.84 |
-790.84 |
-790.84 |
|
|
Total Liabilities |
|
|
-1’169.54 |
-1'158.08 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Profit |
|
|
|
9.16 |
9.16 |
As a consequence of an increase in the Euro/dollar exchange rate, you have a USD bank deposit with an exchange value in EUR which is less than at the beginning of the year. The total worth has diminished and there is therefore a loss.
The USD loan has a lower exchange value in EUR. A lesser liability is an advantage for the company and there is thus an exchange rate profit.
Exchange rate profit
You have an exchange rate profit when:
- The exchange value of your assets increases (increase of the investments)
- The exchange value of the liabilities decreases (decrease of the loans).
Exchange rate losses
You have an exchange rate loss when:
- The exchange value of your assets decreases (decrease of the investments)
- The exchange value of the liabilities increases (increase of the loans).
Accounting features for exchange rate differences
Exchange rates can evolve in different ways. Often they rise, only to fall again. The principle rule for accounting is that the figures provided on the Balance Sheet must be true ones. When you present your Balance Sheet, the exchange values of foreign currency accounts must be made at the exchange rate on the day of presentation.
The exchange rate difference is calculated as if you had to definitively convert the amount to basic currency. In reality there is no definitive conversion so you are only dealing with a correction to the accounting.
Closing exchange rate
At the end of each year it is necessary to prepare the complete Balance Sheet. The exchange rates thus have to be updated with the closing exchange rates. It is also necessary to enter the exchange rate differences once and for all; if these are not entered, then there will be differences in the opening balances.
Entering exchange rate differences
|
|
|
Currency balance |
Account balance EUR |
Calculate balance at 30.03.xx EUR (hypothetical) |
Exchange rate difference |
|
Exchange |
|
|
1.32030 |
1.36150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank |
USD |
100.00 |
75.74 |
73.44 |
-2.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exchange rate difference |
EUR |
|
-2.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank |
USD |
100.00 |
73.44 |
73.44 |
0.00 |
As can be seen from the above example, the bank balance is USD 100.00. For the accounting it has been valued at 75.74 EUR. Today’s actual value, though, is only EUR 73.44. There is a difference of EUR 2.30 EUR in basic currency. The entry must therefore decrease the EUR amount. You proceed with a transaction that debits the bank account and credits the exchange rate loss account by EUR 2.30.
As you can see, the actual bank account balance of USD 100.00 has not been altered. The entry only alters the basic currency balance.
When entering the exchange rate difference, you need to ascertain that the exchange value in basic currency corresponds to the actual exchange value, calculated at either the daily exchange rate or the closing one.
The figures in the account currency must not be altered. You must therefore proceed to make an entry that only alters the basic currency balance on the specific account.
You will have the exchange rate profit or loss account on the contra account.
Transactions at purchase exchange rates
Transactions valued at the purchase exchange rate
When the positions, valued with exchange rates at the time of purchase (historical) are increased or decreased, you will have to calculate the exchange rate of the exchange rate table, taking into account the development of the amounts of increase.
|
|
USD amount |
Exchange |
EUR exchange value |
Total USD |
Total EUR |
Historical Exchange |
|
Acquisition of shares |
100'000.00 |
0.9416 |
106'202.00 |
100'000.00 |
106'202.00 |
0.9416 |
|
Increase of shares |
50'000.00 |
0.8792 |
56'870.00 |
150'000.00 |
163'072.00 |
0.919839 |
Investments and special exchange rates
Investments valued at the exchange rate of the time purchase
Certain investments (shares, real estate abroad) are valued using the exchange rate of the time of purchase (historical exchange) and not the current one. The exchange rate profit and loss is not accounted for until it is actually realized. You must therefore make certain these accounts do not get valued using the current exchange rate.
In order to input a fixed historical exchange rate, you need to create an additional currency on the Accounts table (e.g. USD1) with a fixed exchange rate.
It is essential that in the Fixed column of the Exchange table, when viewed in Complete, for each currency with a fixed exchange rate, Yes must be inserted; otherwise, the currency and its related account are still revalued.
This currency will then only be used for this specific account ( ex: USD1) with a fixed rate.
If you have to make a transfer from the USD account to the USD1 account, you proceed exactly as if you were working with two different currencies. For this reason you will have to use a two-row entry.
Opening with special exchange rates
By inputting the opening balances in the Opening column, foreign currency amounts will be converted to basic currency at the opening exchange rate.
If this system does not prove flexible enough (i.e. you need various special rates or there are rounding differences) the opening can be done manually by making normal entries, indicating the amounts and the exchange rates you want for each account. In this case, the "Opening” column of the Accounts table will be left blank.
File properties multi-currency accounting
See also the File Properties (Basic Data) page for information about the other sections of the dialog.

Account for exchange rate profit
From the accounts list, select the account for the exchange rate profit present in the Chart of Accounts.
You can only choose from class 3 and 4 accounts that are in basic currency.
In the Accounts table, it is also possible to specify the exchange rate difference account for each individual account.
Account for exchange rate loss
From the accounts list, select the one for the exchange rate loss present in the Chart of Accounts.
Currency2
It is possible to select a second currency in order to view the balances in a currency different from the basic one.
It is possible to add new currencies that might be missing from the list, proceeding as follows:
- in the Exchange rates table enter a new row; in the Ref.Currency column enter the basic currency for your accounting file, in the Currency column enter your desired currency
- From the File menu > File and accounting properties command, in the Currency tab, the added currency will also be visible and it can be chosen as Currency2.
Decimal points Currency2
This is the number of decimal points to be used when rounding the amounts in currency2.
Conversion of amounts into Currency 2
Currency 2 is displayed in the Currency2 view of the Accounts table and used when you wish to have an estimate of all account balances, including those in base currency, in the foreign currency, defined as currency 2.
It serves for information purposes only, to know the values of the balance sheet and profit and loss account in a currency other than the base currency at a given time. The conversion is based on the exchange rate set in the exchange rate table, Exchange rate column. If the exchange rate in currency 2 is changed in the exchange rate table, the amounts in currency 2 will be recalculated.
The conversion may lead to differences between balances in currency and those in currency 2. More information can be found on the Exchange Rates page.
The conversion of the amounts into Currency 2 takes into account the currency of the account, with the following logic:
- If currency 2 is equal to the account currency, the amount in the account currency is used.
- Otherwise, if currency 2 is equal to the basic currency, the basic currency amount is used.
- Otherwise (if the amount is in any other currency) the amount in basic currency is converted into Currency 2 at the current exchange rate set in the Exchange rates table, therefore historical exchange rates are not used for the conversion.
Exchange rates table
In the Exchange Rates table, the basic currency (accounting currency) and foreign currencies with all their related parameters are entered.
Before setting up the Exchange Rates table, it is necessary to set up in the Accounts table, foreign currency accounts with their respective codes; you also need to define the basic currency in the File menu > File and accounting properties.

Exchange rates with and without date
There are two types of exchange rates:
- Exchange rates without date
For each currency used there must be an exchange rate line without date.
The exchange rate rows without a date are used as reference rates to convert foreign currencies into the basic currency according to the current exchange rate. They are used:- When there is no historical exchange rate (exchange rates with dates).
- At year end, to define official closing rates and calculate exchange rate differences (end of the accounting period).
During the closing process, it is mandatory to use exchange rate rows without a date in order to calculate exchange rate differences.
- Current exchange rate and closing exchange rate
- It is the exchange rate entered in the Exchange rate column; it is the current exchange rate or the closing exchange rate.
- This exchange rate is automatically used in the transactions, when there is no historical exchange (exchange rows with date).
If you modify the exchange rate in the Exchange rates table, the exchange rates and amounts previously used in the journal rows are not changed. - It is used for the calculation of the balance column calculated in the accounts table and for the conversion to Currency 2.
- Every time transactions in foreign currency are recorded, the resulting exchange rate differences are displayed in the Calculated Balance column of the Accounts table (Balances view). These differences are the foundation for calculating exchange rate differences and for the conversion into Currency 2.
- Closing exchange rate
- It is used as an exchange rate for exchange rate differences postings.
- It becomes the opening exchange rate when creating a new year.
- Opening exchange rate
It's the exchange rate entered in the Rate Opening column and it is used in the following cases:- When first creating a multi-currency file in Banana Accounting Plus
- When creating the new fiscal year, the opening exchange rate is automatically taken from the previous year's closing rate (in the Exchange Rate column).
The opening exchange rate is automatically used in the Accounts table to convert the opening amounts in foreign currency into the opening amounts in the basic currency of your accounting file.
If you need to edit the opening exchange rate, you must use the Recalculate accounting command.
- Current exchange rate and closing exchange rate
- Exchange rates with date (historical exchange rates)
When dates are entered in the Exchange Rates table, and foreign currency transactions are recorded in the Transactions table based on a date specified in the Exchange Rates table, the program selects the exchange rate with the date equal to or closest to but not exceeding the date of the transaction entry.
The program uses the historical exchange rate in these cases:- When entering transactions at a specific date and in the Exchange rates table there is an historical exchange rate.
- When creating exchange rate differences and specifying to use historical exchange rate.
In exchange rates with a date (historical exchange rates), no opening exchange rate should be indicated (Opening Rate column).
Columns of the Exchange rates table
All the columns available for the Exchange rates table are visible in the Complete view.
Date
Rows without a date are used as reference exchange rates by the program. Rows with a date are used as historical exchange rates.
Ref. Currency
It is the starting currency (basic currency) for the exchange (EUR in the example).
Currency
This is the destination currency (foreign currency). It's value is converted into the Reference currency.
Text
A text to indicate the foreign currency description
Fixed
True or false. If there is a fixed exchange rate, enter Yes in this column. In this case, for the foreign currency with a fixed exchange rate, the same rate is used consistently until it is modified. Typically, a fixed exchange rate is applied when there are accounts whose value should not undergo continuous fluctuations, such as real estate investments.
Mult. (Multiplier)
The multiplier is usually 1, 100 or 1000 and is used to obtain the effective exchange rate. The multiplier is used for currencies which have a very low unit value in order to avoid having to insert exchange rates with many zeros. In our templates, the negative multiplication (-1) is used in the Multiplier column of the Exchange rates table.
In this case:
- In the Ref. (Reference) Currency column, the base currency of the accounting system is entered
- In the Currency column, the foreign currency is entered.
When in the Ref. Currency and Currency columns the abbreviations of the currencies are reversed, the Multiplier 1 (positive exchange rate) must be entered in the column.
If transactions have already been made with the same currency, do not change the multiplier, otherwise the programme will report errors in the entries due to incorrect exchange rates.
Exchange rate
It is the current or closing exchange rate of the currency against the reference currency.
This is also used to calculate exchange rate differences. Before calculating exchange rate differences, it is necessary to update the rate in this column according to the official closing rate.
The exchange rate and the multiplier are being applied according to the following formulas
- With multiplier > 0
Currency amount = Ref. currency amount* (exchange rate / |mult.|)
- With multiplier < 0
Ref. currency amount = Currency amount * (exchange rate / |mult.|)
Opening Exchange rate
This is the exchange rate at the moment the accounting is opened. To be indicated only on a row without date.
- It is used to convert the opening amount of the foreign currencies into the opening amount of the accounting’s basic currency.
- Should be corresponding to the closing exchange rate of the preceding year.
When transitioning to the new fiscal year, the opening exchange rate is automatically updated based on the closing exchange rate from the previous year entered in the Exchange Rate column (Exchange rates table).
If the closing exchange rates are not equal to the opening exchange rates, the Assets and Liabilities might result into different totals; see Differences in the Opening Balances. - The opening exchange rate should never be changed in the course of the year, otherwise exchange rate differences are being created in the total of the opening balances.
- The opening exchange rate should not have a date.
Minimum
The minimum exchange rate accepted. If an inferior exchange rate is used for the transactions, there will be a warning.
Maximum
This column shows the maximum exchange rate accepted. If a superior exchange rate is used for the transactions, there will be a warning.
Decimal Points
The number of decimal points to be used when rounding the amounts of the foreign currency.
Modifications in the Exchange rate table
The current exchange rates for foreign currencies can be modified in the Exchange rates table, specifically in the Exchange rate column for rows without a date. In this scenario, when a transaction with an account in a foreign currency is entered in the Transactions table, the program automatically uses the exchange rate set in the Exchange rates table. If a change is made to an exchange rate in the Exchange rates table, there are no repercussions on previously entered transactions; the new exchange rate is applied to future transactions.
It is also possible to manually modify the exchange rate directly in the Transactions table by entering the desired rate in the Exchange rate column. This modification does not affect the exchange rate present in the Exchange rates table.
- Modification of the Opening exchange rate
If the opening exchange rate is modified, the next time you recalculate the accounting, the balances in basic currency of the accounts will be recalculated with the new exchange rate. Therefore, if you have opening balances, pay attention when modifying the Opening exchange rates.
If you modify the opening exchange rates and there are opening balances, it is important to recalculate the accounting. - Modification of the multiplier
- When changing the multiplier of a currency already used in the Transactions table, the program will report a warning as soon as the accounting is being recalculated. The transaction amount and the correct amount in the basic currency will have to be reentered.
- When the accounting is being recalculated, the opening balances in basic currency will be recalculated as a result.
Direct exchange rates
Direct exchange rates are those where the basic currency and the foreign currency are indicated on the same row.
In the example below, the direct exchange rate is EUR → USD.

Indirect exchange rates
Indirect exchange rates are those where a direct exchange between two currencies is not being indicated (not recommended).
The exchange rate is deducted by the program based on other combinations of entered exchange rates

Historical exchange rates
As explained above, if an exchange has a date, the program considers it to be a historical exchange rate.
In the cases indicated here, the program chooses the exchange rate with a date equal to or less than the date of the transaction row.
- When entering transactions, if there is a historical exchange rate, it is proposed and used as the default exchange rate.
- When the exchange rate differences transactions are created and the option to use the historical exchange rate is activated.
- In rows with a date, the opening exchange is not used.

If you import several historical exchange rates at the end of your accounting period, that is, when you have already entered accounting transactions, simply manually delete the transactions exchange rates (Exchange rate column, Transactions table) to make sure that the program uses the imported exchange rates instead of those entered in the transactions.
Monthly average exchange rate
When entering a monthly average exchange rate, this must be inserted manually in the Exchange rate table, in a row without date. In the Transactions table, for foreign currency accounts, the average exchange rate will always be included until it is updated again in the Exchange rate table.
For the monthly average exchange rate, we recommend consulting the page of the exchange rates proposed by the Swiss Confederation, available in Italian, French or German.
Incompatible exchange rates from previous versions
When the basic currency is entered as the reference currency, the exchange rates with a multiplier greater than 1 can present calculation differences between Banana Plus and the previous versions. In these rare cases, while opening an accounting file of a previous version, a warning message appears and the file is being opened as "read only".
- Open the file in Banana Plus and confirm the warning message;
- Recheck the accounting (Shift + F9);
- The warning messages "Transaction multiplier is not the same as the one in the Exchange rate table" can be ignored;
- Verify whether the balances and the result of the accounting period present differences compared to those displayed in earlier versions. If there are no differences, just save the accounting under a new name; otherwise, it is necessary to proceed as follows:
- In the Exchange rate table, correct the exchange rate by multiplying it with the value of the multiplier and define the multiplier as 1 for the exchange rates with a multiplier greater than 1. For example, if we have a multiplier of 100 and an exchange rate of 0.9944608, correct the exchange rate to 99.44608 and the multiplier to 1.
- Recheck the accounting (Shift + F9).
- The warning messages "Transaction multiplier is not the same as the one in the Exchange rate table" can be ignored, or it is possible to delete them by clicking, in the corresponding transaction row, on the amount in basic currency and by pressing the F6 key
- Verify whether the balances and the result of the accounting period correspond with the ones indicated in earlier versions
- Save the file under a new name
- At this time, you can define the exchange rates and the multiplier in the preferred format, reverse or direct, with or without multiplier, verifying the balances and the result of the accounting period after each modification.
Chart of accounts | multi-currency accounting
In contrast to Double-entry bookkeeping, Multi-currency Accounting has the Exchange rate table and columns for calculating foreign currency amounts and balances.
Grouping of the Accounts table
For the Accounts and Groups grouping system, please refer to the Grouping System page.
Setting the basic currency
The base currency is set from the menu File > Accounting properties
Account Currency
Each account has a currency abbreviation, which may be that of the base currency or a foreign currency abbreviation, indicated in the exchange rate table.
Assets and liabilities accounts can be set up in different foreign currencies in addition to the base currency (in the example EUR).
- Foreign Currency Accounts
Accounts in foreign currencies are set up in the Accounts table. In the Currency column , for each foreign currency account the currency code must be entered.
In the Exchange rate table, for each foreign currency, the abbreviations of the foreign currencies, set in the Accounts table, and the opening exchange rate must be entered.
In the example below, the base currency is EUR. The abbreviation of the base currency EUR appears in the column headings with the amounts in base currency.
- Accounts in base currency (accounting currency)
Accounts in base currency are set up in the Accounts table. In the Currency column, the abbreviation of the base currency must be entered.

Income and Expense accounts, other than in basic currency (EUR in the example), can also be set in different currencies.

Explanation of multi-currency accounting columns
Currency
Enter the symbol of the account currency. For foreign currency accounts, the symbol must also be present in the exchange rate table.
Opening currency
The initial balance is entered for each account, whether it is a basic or foreign currency account
Opening balance (basic currency)
- A protected column calculated by the program.
- The initial balance in basic currency is calculated by the program.
- For basic currency accounts, the opening balance in the Opening currency column is reported.
- For foreign currency accounts, the balance is converted according to the exchange rate in the exchange rate table.
Balance currency
- Protected column used by the program.
- The balance is calculated by the programme and corresponds to the sum of the opening balance (for accounts in foreign currency, this is the balance converted into the base currency) and the amounts of the transactions in base currency and in foreign currency (amounts converted according to an exchange rate, which can be found in the exchange rate table).
Balance
- Protected column used by the program.
- The balance is calculated by the program and corresponds to the sum of the opening balance (for accounts in foreign currency it is the balance converted into basic currency) and the amounts of the transactions in basic currency and in foreign currency (amounts converted according to an exchange rate present in the exchange rate table).
Calculated balance
- Protected column used by the program.
- This is the currency balance of the account converted at the current exchange rate (exchange rate from the exchange table of the undated row).
- In this column, the currency account balances converted to basic currency may differ from those in the Balance column, as exchange rate differences are present.
Exchange rate difference account
- Visible in the Other view.
- In this column, you can enter an exchange rate profit or loss account for a given account.
The account you enter will be used by the Create Exchange Rate Difference procedure instead of the exchange rate profit and loss accounts defined in the multi-currency file properties. - In the Exchange Rate Difference Account column you can specify:
- "0;0" This means that no exchange rate difference is to be calculated for this account.
It is used for historical exchange rates, which must not change. - Two accounts separated by semicolons, "Currency Exchange loss account; Currency Exchange rate profit", e.g. "6949;6999".
If there is a loss the first account will be used, if there is a profit the second. - "One account only" for example "6949".
This account will always be used whether there is an exchange rate profit or loss.
- "0;0" This means that no exchange rate difference is to be calculated for this account.
Opening balances
Information on how to enter opening balances in multi-currency accounting is available on the Opening balances page in multi-currency accounting.
Exchange Profit and Loss Accounts
In the chart of accounts, it is necessary to insert the predefined accounts for the exchange gain and loss to be reported in the File menu File properties → Foreign currency.
Accounts for exchange rate differences must have BClass 3 (Costs - Exchange Loss) or 4 (Revenue - Exchange Profit).

Revaluation accounts and historical exchange rates
Exchange rates are fluctuating. The actual value of the balance in the account currency varies therefore depending on the foreign exchange fluctuation.
The basic currency amount of an account is being calculated using the opening exchange rate and the exchange rates that are indicated in the transactions. Because this value corresponds to equivalent of today's exchange rate, it is necessary to revaluate the account.
The revaluation takes place by calculating the exchange rate differences. With the automatic calculation of exchange differences, the software enters an amount in basic currency (exchange difference) so that the balance in basic currency is equal to the counter value (calculated balance column).
There are accounts (related to investments, for example) for which a so-called historic exchange rate is being used. By an historical exchange rate, we mean an exchange rate that doesn't vary over time.
There are two ways to have currencies that do not vary:
- Create an additional currency code in the exchange rate table (e.g. USD2) to which the same exchange rate will always be attributed.
- In the currency description, indicate that this is a historical exchange rate.
- This currency must then be used for the account with the historical exchange rate and of course also in the entries for the account.
- For each new account with a different historical exchange rate, create a new currency symbol.
You can create as many currency symbols as you need for different accounts with historical exchange rates. - Change the exchange rate of the historical account if there are additional purchases or sales that require an adjustment of the value, while creating a transaction for the exchange rate profit or loss.
- Entering opening balances as Opening transactions.
- Instead of using the opening balances column, the opening balances are entered as transactions. You can assign the opening exchange rate you want.
- In the Account exchange difference column enter the value "0;0" indicating that the account should not be revalued.
Group totals in foreign currency
Normally, the columns with amounts in foreign currency don't have totals, as it makes little sense to calculate totals for values in a different currency.
If you have a group that includes only accounts in a specific currency, the currency symbol can be indicated at a group level and, in the Accounts table, the program totals these amounts. If there were to be accounts with various currency symbols, there would be no amount indicated (the program would not report an error either).
Transactions multi-currency accounting
Explanations of the columns
In the Transactions Table of the multi-currency accounting, other than the columns of the double-entry accounting, there are the following extra columns:
- Currency amount
This is the amount of the currency specified in the column with the currency symbol.
This amount is used by the program to update the balance of the related account in currency. - Currency
This is the currency symbol of the currency to which the amount refers.
The currency symbol has to be the one of the basic currency, specified in the File and accounting properties (File menu), or the currency symbol of an amount indicated in the Debit A/C or Credit A/C columns.You can also use a different currency as long as the indicated Debit A/C and the Credit A/C are basic currency accounts.In this case the amount in currency is used as a reference, but will not be used for accounting purposes - Exchange rate
Used to convert the foreign currency amount in its basic currency equivalent. - Amount in Basic currency
The transaction amount, expressed in basic currency.
This amount is used by the program to update the balance of the related account in basic currency. - Exchange rate multiplier
Normally not visible in the view, this value is multiplied by the exchange rate.
Useful advice
- While being positioned on the Currency Amount column and pressing the F6 key, the program rewrites all values with the earlier explained logic, as if there were no values present. This feature is useful when the Debit A/C or the Credit A/C is modified.
- If there is a registration with a single account in basis currency (in 'Multiple transactions' - see Transaction types) and its value of the Currency column has been changed manually in a currency symbol of a foreign currency, it is necessary to be positioned on the cell of the Currency column and press the F6 key in order to update the exchange rate and calculate the amount in basic currency.
- Smart fill for the Exchange rate column
The program suggests several exchange rates, picking them up from the Exchange rates table or from exchange rates previously used in the transactions.
Types of transactions in multi-currency accounting
All amounts, whether in basic currency or foreign currency must always be entered in the Currency Amount column.
As regards the exchange rates, multiplier and historical exchange rates, please refer to the Exchange rates table page.
Attention: in the transaction examples, the basic currency is the Euro.
For each transaction, there are two accounts (debit account and credit account). In the program, only one foreign currency per transaction row can be used. So there can be the following direct combinations:
- Entries between two accounts in basic currency with the amount in basic currency (in the image, transactions n.1 in the Doc column). The account currency is the basic currency.
- Entries between two accounts in basic currency with the amount in foreign currency (Doc 2)
The indicated accounts are in basic currency, but the currency symbol and the amount in currency, indicated in the transaction row, are not in basic currency, but in a different currency.To insert the different currency, the user has to manually change the currency symbol.This is being used when one goes abroad and money is being exchanged in order to pay in local currency. In this case we do not have a specific account.For the calculation of the balance (both accounts being in basic currency) only the amount of basic currency column is being used. - Entries between an account in foreign currency and one in basic currency (Doc 3)
The currency needs to be the one of the account in foreign currency.
For the calculation of the balance of the account in foreign currency, the program uses the amount in foreign currency and for the balance in basic currency, the program uses the amount in basic currency. - Entries between two accounts with the same foreign currency (Doc 4)
The currency needs to be the same as the account currency of both accounts (USD1 and USD2). In order to update the exchange rate and calculate the amount in basic currency, it is necessary to be positioned on the cell of the Currency column and press the F6 key. - Entries with two accounts in different foreign currencies (Doc 5)
For example, the bank makes an exchange operation between two foreign currencies:
In this case, the transaction needs to be recorded on two rows.
The amount in basic currency needs to be the same. It is useful to use an amount close to the current exchange rate to avoid excessive exchange rate differences.
In order for the amounts in basic currency to be equal, the amount in basic currency needs to be indicated manually, and the program will calculate the exchange rate. - Exchange rate differences (Doc 6)
The goal of this transaction is to realign the balance of the basic currency account with the equivalent of the Foreign currency account at today's exchange rate.
On the Foreign currency account, only the amount in basic currency related to the exchange rate differences is being recorded.
They are automatically generated with the Create transaction for exchange rate variation command.- For the exchange rate profits, the program automatically indicates the account to be revaluated in debit and the exchange rate profit account in credit. The exchange rate profit account is indicated in the File and Accounting properties (Basic Data), or in the specified account -> Exchange rate differences account column of the Other view (intended for one or several specific accounts).
- For the exchange rate losses, the program automatically indicates the account to be revaluated in credit and the exchange rate loss account in debit. The exchange rate loss account is indicated in the File and Accounting properties (Basic Data), or in the specified account -> Exchange rate differences account column of the Other view (intended for one or several specific accounts).
- The Currency amount is being left empty
- The Currency symbol is the basic currency
- In the Basic currency amount column, the amount of the revaluation of the account (profit or loss) is being indicated.
Establishing the exchange rate
The accountant is the one who decides which exchange rate to use for each single operation. Generally, the following rules are being applied:
- For normal operations, the exchange rate of the day is being used
- For buying or selling currency, the values indicated by a money exchange office or a bank are being used.
First the amount in foreign currency is being indicated in the program and then the amount in basic currency. The program calculates the exchange rate. The exchange rate indicated by the bank can be slightly different, because banks specify exchange rates with few figures after the decimal point and often round the amounts. - When several operations with the same exchange rate are being recorded, it is useful to update the exchange rate in the Exchange rates table, so that the program can automatically apply it.
- For operations from abroad that are subject to VAT, the national authority might impose a standard exchange rate. In this case, that exchange rate should be inserted in the Exchange rate column of the transaction
- To purchase real estate or equity investments, an historical exchange rate is being used. In that case, a currency symbol needs to be created in the Exchange rates table (for example USD1) with an historical exchange rate, that is not being subject to the fluctuations of the exchange rate.
One can create as many currency symbols as desired for all historical exchange rates.
Transactions with VAT
The VAT account and the account from which the VAT is being deducted have to be in basic currency. It is impossible to use a VAT code to deduct the VAT from a foreign currency account. In order to record operations with VAT that have accounts in foreign currency as their counterpart, two transaction rows have to be used:
- First, the amount of the purchase is being recorded on an Internal transfers account in basic currency and the related VAT code is being applied. The amount in basic currency has to be calculated using an exchange rate in accordance with the requirements of the Tax administration.
- In a second row, the balance of the Internal transfers account is being put to zero; as its counterpart, the account in foreign currency should be entered.
The amount used for this transaction, both in basic currency and in foreign currency, has to be excluding VAT. Obviously, the exchange rate that has to be used is the same one as the one being used in the preceding transaction.
In the example, the basic currency is the EUR. We are dealing with a national purchase, but paid from a foreign currency account (USD).

VAT and foreign currency transactions
In transactions with foreign currency accounts, it is possible to record VAT with a gross amount (Amount type 0, with VAT).
If you enter net values (Amount type 1, without VAT), the program indicates an error, because the calculation of the gross value would in many cases be incorrect due to the rounding up of VAT and of the exchange rate.
In these cases it is advisable to enter the gross value. See also the Explanations of the error.
Automatism while entering multi-currency transactions
When a new transaction is being entered, the data in the above mentioned columns have to be completed.
When some values of the transaction row are modified, the program completes the transaction with the predefined values. If these values do not satisfy the user's requirements, these have to be modified in the transaction row.
The modification of the values in the Exchange rates table have no effect on already entered transaction rows. Thus, when the exchange rate in the Exchange rates table is modified, this has no influence whatsoever on already inserted transactions.
- When the amount in currency is entered and there is either a Debit A/C or a Credit A/C, and no other values are entered, the program operates as follows:
- the currency symbol is retrieved from the account in use, giving priority to the account that is not in basic currency;
- the exchange rate, defined in the Exchange rates table, is applied with the following logic:
- the historical exchange rate is applied, with a date earlier or equal to the transaction date
- tf there is no historical exchange rate to be found, the exchange rate from the row without date is applied.
- the multiplier, defined in the Exchange rates table, is applied or the number 1 if it is the basic currency;
- the amount in basic currency is calculated.
- When the amount in currency is modified (and there are already other values present), the program operates as follows:
- the amount in basic currency is calculated with the existing exchange rate
- If the currency symbol is modified the program operates as follows:
- the exchange rate with the multiplier is applied and the amount in basic currency is calculated (like above)
- If the exchange rate is modified the program operates as follows:
- the amount in basic currency is calculated using the entered exchange rate
- When the amount in basic currency is modified the program operates as follows:
- the exchange rate is recalculated.
Info window
In the info window, the program indicates:
- Differences, if any, between the Debit and Credit total movements in basic currency
- Explanation on the different uses of the F6 key
For the accounts related to the transaction row on which one is positioned, the program always indicates in the Info windows:
- the account number
- the account description
- the transaction's amount in basic currency
- the current account balance in basic currency
- the account currency symbol
- the transaction's amount in the account currency (if different from the basic currency)
- the current account balance in currency (if different from the basic currency)
Transactions for opening balances
For multi-currency accounting, when entering the opening balances in the Accounts table, the program converts the amounts into basic currency, using the opening exchange rate defined in the Exchange rates table, Opening exchange rate column.
To use historical exchange rates as opening balances, you can create another currency symbol or create transactions in the Transactions table with the opening balances. This way you can use different exchange rates for different accounts.
- Enter a single transaction for each account with an opening balance (Assets and Liabilities), indicating the initial accounting date and the Debit or Credit account.
- In the DocType column enter the "01" value to indicate that it is an opening value.
- In the Banana Accounting reports or printouts this amount will be shown as opening balance.
- However the transaction doesn't update the Opening balance column in the Accounts table
When using opening transactions, please consider that:
- In order to avoid the revaluation of the accounts with the current exchange rate, in the Accounts table, enter the "0;0" value in Exchange rate difference account column
- The software allows you to add both some opening balances in the Accounts table and some opening transactions in the Transactions table (Assets and Liabilities).
In both cases the amounts are considered in the calculations and, if it is the same account, they are added together.
We do not recommend using the two methods simultaneously to avoid hard-to-find errors and differences. - Opening transactions must be entered manually.
Any debit and credit differences are shown as a transaction difference.
Data transfer from earlier versions
In version 4 or earlier, the absence of a currency symbol in the Transactions table was being interpreted as a transaction in basic currency.
In version 7 and in version 8, each transaction needs to have its own currency symbol. Therefore, when you update from version 4 to version 7 or 8, in the accounting file, the transactions without a currency symbol need to be completed. To do this, a new Currency column must be added to the Transactions table by executing the Columns setup command from the Data menu.
Registrazioni contabilità multimoneta
Tipi di registrazione multi-moneta
Con l' applicativo di contabilità multimoneta è possibile registrare anche i movimenti con conti in moneta estera. Nella tabella Registrazioni si inseriscono, oltre ai movimenti in valuta base, anche quelli in valuta estera: si indicano tutti gli elementi della registrazione, l'importo e il conto in moneta estera, il cambio che si applica alla registrazione, mentre l'importo in moneta base viene dato in automatico per conversione in base al cambio inserito.
Tutti gli importi, sia in moneta base che in moneta estera devono essere inseriti sempre nella colonna Imp. Moneta.
Per quanto attiene ai cambi, moltiplicatore e cambi storici, si rimanda alla pagina Tabella cambi.

Attenzione: negli esempi di registrazione, la moneta base è Euro.
Per ogni registrazione ci sono due conti (conto dare e conto avere). Il programma permette di avere per ogni riga di registrazione una sola moneta estera. Ci possono quindi essere queste combinazioni dirette:
- Registrazione fra due conti in moneta base con importo in moneta base (nell'immagine la registrazione n.1 nella colonna Doc 1)
La moneta del conto dare e avere è quella di base. - Registrazione fra due conti in moneta base con importo in moneta estera (Doc 2)
I conti indicati in dare e avere sono in moneta base, ma la sigla moneta (colonna moneta) e l'importo moneta indicati nella riga di registrazione non sono in moneta base, ma in una moneta estera.
Per inserire la moneta estera si deve cambiare manualmente la sigla moneta base proposta in automatico.
Si usa quando si va all'estero e si cambia del denaro per pagare nella valuta locale. In questo caso nella contabilità non abbiamo un conto specifico.
Per il calcolo del saldo (essendo tutte e due in moneta base) è usato solo l'importo della colonna moneta base. - Registrazione fra un conto in moneta estera e uno in moneta base (Doc 3)
La moneta deve essere quella del conto in moneta estera.
Per il calcolo del saldo del conto in moneta estera, il programma usa l'importo in moneta estera e per il saldo in moneta base è usato l'importo in moneta base. - Registrazione fra due conti con la stessa moneta estera (Doc 4)
La moneta deve essere uguale a quella dei conti usati (USD1 e USD2). Per aggiornare il cambio occorre posizionarsi sulla cella Moneta e premere F6. - Registrazione con due conti che hanno la moneta estera diversa (Doc 5)
Per esempio la banca fa un'operazione di cambio fra due monete estere.
In questo caso è necessario registrare su due righe (con la stessa data).
L'importo in moneta base deve essere necessariamente uguale. È utile usare un cambio vicino alla realtà per evitare eccessive differenze di cambio.
Perché gli importi in moneta base, nelle due righe siano uguali, bisogna indicare manualmente l'importo in moneta base e lasciare che sia il programma a calcolare il cambio. - Registrazioni differenze di cambio (Doc 6)
Lo scopo di questa registrazione è quello di riallineare il saldo del conto in moneta base al controvalore del conto in moneta estera al cambio odierno.
Si registra sul conto in moneta solo l'importo in moneta base relativo alla differenza di cambio.
Sono generate in automatico con il comando Calcola differenze di cambio.- Per gli utili di cambio, il programma inserisce in automatico il conto da rivalutare in dare e il conto utili di cambio in avere, presente nelle Proprietà file, dati base, oppure nel conto indicato nella colonna Differenze di cambio della vista Varia (Tabella Conti) - previsto per uno o più conti specifici.
- Per le perdite, il programma inserisce in automatico il conto da rivalutare in avere e il conto perdite di cambio in dare, presente nelle Proprietà file, dati base (menu File), oppure nel conto indicato nella colonna Differenze di cambio della vista Varia (previsto per uno o più conti specifici).
- L'importo in moneta è lasciato vuoto
- La sigla moneta è la moneta base
- Nella colonna importo in moneta base si indica l'importo della rivalutazione del conto (utile o perdita)
Stabilire il cambio
È il contabile che decide il cambio da utilizzare per ogni singola operazione. Di regola valgono le seguenti regole:
- Per le operazioni normali si usa il cambio del giorno.
- Per le operazioni di compravendita di moneta si usano i valori indicati dall'ufficio cambio o dalla banca.
Nel programma si inserisce prima l'importo in moneta e poi l'importo in moneta base ed è il programma che calcola il cambio. Il cambio indicato dalla banca potrebbe essere leggermente diverso perché le banche indicano un cambio arrotondato a pochi decimali. - Se si fanno diverse operazioni sempre al medesimo cambio è utile aggiornare il cambio nella tabella Cambi, in modo che il programma lo possa riprendere in automatico.
- Per operazioni estere soggette all'IVA è possibile che l'autorità nazionale prescriva un cambio standard. Nel caso, inserire questo cambio nella colonna Cambio della registrazione.
- Per l'acquisto di immobili o partecipazioni si usa il cambio storico. In questo caso è necessario creare nella tabella Cambi una sigla moneta (p.es. USD2) con il cambio storico, che non subirà le fluttuazioni di cambio.
Si possono creare delle sigle moneta per tutti i cambi storici che si desiderano.
Registrazioni con IVA
In una contabilità multimoneta con IVA, per registrare correttamente senza segnalazioni di errori, è fondamentale che Il conto IVA e il conto dal quale viene scorporata l'IVA siano in moneta base. Non è possibile applicare un codice IVA su un conto in moneta estera.
Per registrare operazioni con IVA che hanno come contropartita dei conti in moneta estera si devono usare due righe di registrazione:
- Prima si registra l'importo dell'acquisto su un conto d'appoggio in moneta base e si applica il relativo codice IVA.
L'importo in moneta base deve essere calcolato usando il cambio conformemente alle prescrizioni dell'amministrazione delle contribuzioni. - In una seconda riga si azzera il conto d'appoggio e come contropartita si mette il conto in moneta estera.
L'importo usato per questa registrazione, sia in moneta base che in moneta estera, dovrà essere quello al netto dell'IVA.
Ovviamente si dovrà usare il medesimo cambio della registrazione precedente.
Nell'esempio, la moneta base è EUR. Si ipotizza un acquisto nazionale, ma con il pagamento da un conto in moneta estera (USD).

Registrazioni con IVA e moneta estera
Nelle registrazioni con conti in moneta estera, è possibile registrare l'IVA con importo al lordo (Tipo importo 0, IVA inclusa).
Se si inseriscono dei valori al netto (Tipo importo 1, IVA esclusa) il programma segnala un errore in quanto il calcolo del valore al lordo, risulterebbe in molti casi non corretto per via dell'arrotondamento dell'IVA e del cambio.
In questi casi si consiglia di inserire il valore al lordo. Vedi anche Spiegazioni in merito all'errore.
Automatismi durante l'inserimento delle registrazioni multi-moneta
Quando si inserisce una nuova registrazione si devono completare i dati nelle colonne citate in precedenza.
Se si modificano certi valori della riga di registrazione, il programma completa la registrazione con i valori predefiniti. Se questi valori non soddisfano le proprie esigenze, questi devono essere modificati nella riga di registrazione.
La modifica dei valori della tabella Cambi non ha alcuna ripercusione sulle righe di registrazione già inserite. Quindi se si modifica il cambio nella tabella Cambi, questo non avrà alcuna influenza sulle registrazioni già inserite.
- Quando si inserisce l'importo in moneta e c'é almeno il CtDare o il CtAvere e non ci sono altri valori, il programma opera come segue:
- la sigla moneta viene ripresa dal conto utilizzato, dando priorità al conto non in moneta base;
- viene ripreso il cambio definito nella tabella Cambi con la seguente logica:
- viene ripreso il cambio storico con la data minore o uguale a quella della data della registrazione
- se non viene trovato un cambio storico, viene ripreso il cambio della riga cambi senza data
- Viene ripreso il moltiplicatore definito nella tabella Cambi o 1 se è si tratta della moneta base.
- Viene calcolato l'importo in moneta base.
- Quando si modifica l'importo in moneta (e ci sono già gli altri valori) il programma opera come segue:
- viene calcolato l'importo in moneta base con il cambio esistente
- Se si modifica la sigla moneta il programma opera some segue:
- viene ripreso il cambio con il moltiplicatore e calcolato l'importo in moneta base (come sopra).
- Se si modifica il cambio il programma opera come segue:
- viene calcolato l'importo in moneta base usando il cambio immesso.
- Se si modifica l'importo in moneta base il programma opera come segue:
- viene ricalcolato il cambio.
Finestra Info
Nella finestra info il programma indica:
- Eventuali differenze fra totale movimenti dare e totale movimenti avere in moneta base.
- Indicazioni circa l'uso del tasto F6.
Per i conti relativi alla riga di registrazione su cui ci si trova, il programma indica sempre nella finestra Info:
- numero di conto
- descrizione del conto
- importo della registrazione in moneta base
- saldo attuale del conto in moneta base
- sigla della moneta del conto
- importo della registrazione in moneta del conto (se non in moneta base)
- saldo attuale del conto in moneta (se non in moneta base)
Registrazioni per saldi d'apertura
Per la contabilità multi-moneta, quando si inseriscono i saldi d'apertura nella tabella Conti, il programma converte l'importo in moneta base, usando il cambio di apertura definito nella tabella Cambi, colonna Cambio d'apertura.
Per usare dei cambi storici nei saldi d'apertura, si può creare un'altra sigla moneta oppure creare delle registrazioni nella tabella Registrazioni con i saldi d'apertura. In questo modo si possono usare dei cambi diversi per i conti.
- Inserire una registrazione per ogni conto con saldo di apertura (Attivi e Passivi), indicando la data d'inizio della contabilità e il conto in dare o in avere.
- Nella colonna DocTipo inserire il valore "01" per indicare che è un valore di apertura.
- Nei calcoli e stampe di Banana Contabilità, questo importo sarà inserito come saldo di apertura.
- La registrazione non aggiorna però la colonna saldo di apertura nella tabella Conti.
Da considerare se si usano registrazioni di apertura:
- Per evitare la rivalutazione dei conti al cambio attuale, nella tabella Conti, per il conto che non deve essere rivalutato, inserire "0;0" nella colonna Conti differenza di cambio.
- Il programma permette di inserire i saldi di apertura sia nella tabella Conti sia delle registrazioni di apertura (Attivi e Passivi) nella tabella Registrazioni.
In entrambi i casi gli importi sono considerati nei calcoli e se si tratta del medesimo conto vengono sommati.
Si sconsiglia di usare i due metodi contemporaneamente per evitare errori e differenze difficili da trovare. - Le registrazioni di apertura devono essere inserite manualmente.
Eventuali differenze dare e avere, sono indicate come differenza nelle registrazioni.
Consigli utili
- Premendo il tasto F6 mentre ci si trova sulla colonna Importo in moneta, il programma riscrive tutti i valori con la logica spiegata prima, come se non esistesse alcun valore. Questa funzione è utile se si cambia il CtDare o il CtAvere.
- Nel caso in cui esista una registrazione con un singolo conto in moneta base (nelle registrazioni composte) e nella colonna Moneta la sigla sia stata cambiata in moneta estera, per aggiornare il cambio occorre posizionarsi sulla cella Moneta e premere F6.
- Smart fill per la colonna Cambi
Il programma propone diversi cambi, riprendendoli dalla tabella Cambi o dai cambi utilizzati in precedenza nelle registrazioni.
Ripresa dati da versioni precedenti
Nella versione 4 o precedenti, l'assenza di una sigla moneta nella tabella Registrazioni veniva interpretata come divisa Base.
Nella versione 7, ogni registrazione deve avere la propria sigla moneta, pertanto, quando si passa dalla versione 4 alla versione 7, nel file occorre completare le registrazioni dove manca la sigla moneta. Per questo, è necessario aggiungere una nuova colonna Moneta alla tabella Registrazioni, eseguendo il comando Disponi colonne dal menu Dati.
Exchange rate differences
Create transactions for exchange rate differences
For theoretical aspects please visit the Revaluations and exchange rate differences page.
- The exchange differences transactions are adjustment transactions that balance out the foreign currency account balance with the basic currency calculated balance. In essence, it is a matter of re-adjusting the values in the basic currency, taking into account exchange rate loss or gain, due to the fluctuations of the exchange rates.
- If these exchange rate differences are not recorded, there may be differences in the opening balances of the following year.
- The exchange rate differences can be calculated at the end of the closing year or during the accounting period (for example at the end of a quarter). In this case the historical changes can be useful, as they allow you to have different exchange rates at specific dates.
- The program calculates the exchange rate difference based on the balances at the specified date. It is therefore possible to calculate the exchange rate difference at a specific date, even if you have entered transactions after that date.
- For further explanations, see also the Exchange rate differences not booked page
- Exchange rate differences are not calculated on the accounts belonging to the profit and loss account. Exchange rate profit/losses, which are generated by exchange rate differences, are financial and non-operating items and are therefore not included in the determination of operating income or the profit and loss account.
The Calculate exchange rate differences dialog
The Create transaction for exchange rate variation... command, from the Actions menu, calculates the revaluations for the foreign currencies accounts.

Date of the transactions for the exchange rate differences
The program is able to calculate the exchange rate difference on a date even if there are postings beyond the date.
- Enter the date for your exchange rate differences transactions.
- The program will suggest the final date of the current month, related to the last entered transaction.
- If there are transactions for exchange rate differences with the same date, the program asks whether they should be replaced. The program considers the transactions for the exchange rates differences as existing if they have the same date, doc, description, accounts and currency and when there is no amount in the account currency.
Document number
Enter the document number your exchange rate differences transactions should have.
Use historical exchange rates (exchange rate rows with date)
- Use when option is not activated
- If in your Exchange rate table there are no historical exchange rates (exchange rates with a date) this option is not activated.
- The program will use the exchange rate in your Exchange rate table of the rows without date
- if you are using historical exchange rates for the year closure, be careful that the exchange rate used should be the same as the current one.
- Use when option is activated
- The program will indicate the date of the exchange rate, found in the Exchange rates table, that will be used to calculate the exchange rate difference.
This is going to be the exchange rate with a date equal or prior to the indicated date. - When calculating exchange rate differences at year end we suggest this option not to be activated
- When booking exchange rate difference transactions at year end, the historical exchange rate must be the same as the current exchange rate, otherwise you get an error message saying that the exchange rate differences have not been calculated (even though they have been).
- The program will indicate the date of the exchange rate, found in the Exchange rates table, that will be used to calculate the exchange rate difference.
Values used to create the transactions
For more information, we refer to our page Multi-currency transactions.
Amount of the transaction
- Transactions for exchange rate differences are being created only for the accounts in foreign currency which, at the specified date, have a different balance in basic currency compared to the calculated one.
- For the amount in basic currency, the difference between the account balance in basic currency and the account balance in foreign currency converted in basic currency is being used.
Account balance
For the calculation of the exchange rate differences, the balances in the account currency and in basic currency are being used, at the specified date.
Exchange rate profit and exchange rate loss accounts
As exchange rate profit and loss accounts are being used, in order of priority:
- The indicated accounts entered in the specific column of the chart of accounts.
- The exchange rate profit & loss accounts indicated in the File and Accounting properties.
Position of inserted rows
When using the command, while in the Transactions table, the rows are being inserted at the position of the cursor.
Otherwise, they will be inserted at the end or at the previous position in case they are replacing existing transactions.
Before using the command
- In the File and Accounting properties of the File menu, Foreign Currency section, make sure that the Exchange rate profit and loss accounts are being indicated. It is equally possible to indicate the same account for both the exchange rate profits or losses.
- Make sure that the accounts in foreign currency are being updated and that the balances in foreign currency of these accounts (for example bank accounts) correspond to the balance indicated by the bank.
- Update the current exchange rates of the Exchange rate table.
You should indicate the closing exchange rates or those of a period's end in the rows without a date, in the Exchange Rate column (do not modify the opening exchange rate in the Rate Opening column). In order to calculate the Exchange rate differences, the program uses the exchange rates of the rows without a date. If these last ones are absent, the program produces an error message.

Opening exchange rates for the New Year
To make the Opening balances of the New Year in Basic currency correspond exactly with the closing balances of the preceding year, the Opening Exchange rates of the New Year, indicated in the Exchange Rate table, have to be the same as those being used for the closing of the accounting, so:
- The closing exchange rates have to be indicated in the Exchange rate column of the rows without a date;
- The opening exchange rates have to be indicated in the Rate Opening columns of the rows without a date.
The procedure of creating a new year or of the updating of the opening balances, copies the closing balances (Exchange rate column, rows without date) of the previous year into the opening exchange rates (Exchange rate table, Rate Opening column, rows without date) of the new year's file.
Exchange rate differences with cost centers
The Create transaction for exchange rate variation... command does not include any exchange rate differences present in cost centers in currencies other than the accounting currency. These differences must be recorded manually at the end of the year. The transaction should present only the accounting currency amount; indicate this amount first, then the cost center involved and the cost center currency. When the currency is entered, the amount in the currency of the accounting will be deleted and must be re-entered.
Budget
In the Budget Table the financial planning is entered. The entry of the transactions is identical to that of the Transactions table.
Depending on the type of accounting there can be different columns for the Budget.
There are also columns for entering Quantities and Prices and calculation formulas.
For more information about the Budget, see the Budget Table page.
Change the basic currency in the multi-currency accounting
In multi-currency accounting all amounts are shown both in the account currency and in the basic currency. If you change the basic currency all exchange rates and amounts in basic currency must be re-entered manually.
It is recommended to change the base currency at the beginning of the year, when there are no operations yet. Anyway, you can still do it during the year, for example, if you want to change the basic currency of an existing accounting file (for example if your accounting file is in EUR and you want it in USD), proceed as follows:
- Save the file under a different name
- In the File properties
- Indicate the new basic currency
- Delete the reference to the previous year file ('Options' section)
- In the Exchange rates table enter the exchange rates referred to the basic currency:
- If there are many transactions to be converted, you can enter median exchange rates for each month in the exchange rate table, indicating the beginning of the month's date).The program will use the historic exchange rate in the transactions.
- In the Chart of accounts:
- Replace the old currency with the new one
You can use the Find and Replace function - If there are opening balances, you need to re-enter them in the new currency
- Also, the Previous year balance, budget and other columns must be converted
- Replace the old currency with the new one
- In the Transactions table:
If there are transactions, you need to correct them row by row:- For those transactions that are already in the correct currency, with the F6 key the program recalculates the amount in the new basic currency.
- For other transactions you need to enter the right amount in the basic currency and then press F6.
- In the Budget table:
Proceed just as in the Transactions table - Use the Check accounting command of the Actions menu, fix possible errors, and keep using the Check accounting command until there are no more error messages.
Opening Balances in Multi-Currency Accounting
Opening balances when starting with Banana Accounting
When using Banana Accounting for the first time, the opening balances must be entered manually to generate the Balance Sheet.
Before proceeding to enter the opening balances, it is important to make some fundamental settings:
Exchange rates table
- In the Exchange rates table, set the foreign currencies and the corresponding opening exchange rate, referred to the basic currency.
The opening exchange rate is only inserted if Banana Accounting is used for the first time, and is automatically updated in the subsequent years, when creating the new year via the Actions → Create new year menu, based on the final exchange rate of the the previous year's file. - The opening exchange rate must always be indicated in an undated row and must never be modified, except for errors or in case of special situations.
- The opening exchange rates must be identical to those of the previous year. See Differences in opening balances.
Accounts table
- Make sure that there is an account to record the exchange differences in the Chart of Accounts (Income Statement) and that this has been indicated in the File → File Properties (Basic Data) → Foreign currency menu.
- The opening balances must be entered in the Base view of the Accounts table, Opening currency column, for both the basic currency and the foreign currency.
- The Opening column (basic currency) is protected. The program automatically calculates the exchange value for the basic currency according to the opening rate indicated in the exchange rate table.
- Liabilities balances must be entered with a minus sign in front of the amount.
- After entering the opening balances of the financial statements, check that the total Assets are equal to the Liabilities, so that the accounting is balanced. If there are any differences in the opening balances, they must be checked and corrected.
- Go to the Accounts table, Base view, Opening column.
- Manually report the opening balances of the Assets and Liabilities accounts. Liabilities balances must be entered with a minus sign in front of the amount.
- Check that the total Assets is equal to the total Liabilities to have a balanced accounting. If there are any differences in the opening balances, they need to be checked and corrected.

Opening balances of Cost Centers and Segments
In the Accounts table, the Opening column can also be used to enter the opening balances of the Cost Centers.
To enter the opening balances of the segments, opening transactions must instead be made. More details are available on the Segments page.
Start with Banana Accounting during the year
If you start a new accounting, taking over work already done with other programs, there are two possibilities:
- Start accounting from the beginning of the year, by entering the opening balances at the beginning of the year (Accounts table, Opening column) and the transactions (Transactions table) that have already been previously recorded with other programs (also see Transferring data from other software). Thus you will have all the accounting details in one file.
- Starting from the date when the accounting is taken over:
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
In addition to entering the opening balances of the Assets and Liabilities accounts, it is also necessary to enter those of the Expenses (positive amounts) and Revenues (negative amounts). - The operating result up to that point must be disclosed in the Profit / Loss carried forward account.
If it is a profit, the opening balance must be entered in negative, if it is a loss, in positive . - Check that the sums of the opening balances are zero, so that the program does not signal any differences.
- Enter the new entries in the Transactions table.
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
Opening balances as opening transactions
Opening balances can also be entered as opening transactions in the Transactions table, both for all balance sheet accounts and for some categories of accounts, such as those of the segments, which must be manually posted in the Transactions table.
For each opening transaction, proceed as follows:
- Indicate the accounting start date as the transaction date.
- In the Doc Type column, enter the code "01".
- Indicate the debit or credit account and the amount.
- The total of the opening debit balances must match those in credit.
Opening balances entered as transactions are used when preparing reports. When there are opening balances in the Opening column of the Accounts table and the opening balances of some accounts are also manually entered in the Transactions table (e.g. opening segments balances), these are automatically added to those present in the Opening column of the Accounts table.
Entry via transactions can be useful if different opening rates than those of the exchange rate table are required. If you use this procedure, you need to be clear about the accounting and legal implications.
Balances of the previous year
If you start a new accounting by taking over an existing accounting and you want the previous year's values to appear on the printouts, it is necessary to enter the previous year's balances in the Previous view, Previous Year column of the Accounts table:
The previous amounts are displayed in the printouts of the Enhanced balance sheet in the Previous Year column.
- Enter the closing balances of the previous year of the Assets accounts.
- Enter the closing balances of the previous year of the Liabilities accounts (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).
- Enter the last year's closing balances of the Expenses.
- Enter the final balances of the previous year of Revenues (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).

Create new year
When you start the new year, the program automatically carries over the opening balances to the following year.
Consult the Create New Year lesson.
Print opening balances
To print the opening balances:
- To print the contents of the table, use the Print / Preview command, by selecting the rows of the Balance Sheet.
- You can also use the Accounting printouts and set the printout only for the Balance Sheet part and the opening column.
Year end closing operations | Multi-currency accounting
At the end of the accounting year, before moving into the New Year, in addition to checking for errors and differences in the accounts, it is necessary to perform a series of closing operations. These are very important because they give a correct and complete overview of your business, and they also have fiscal implications.
Technical aspects and new year
With Banana Accounting each accounting year has its own separate file; technically there is no concept of accounting closure:
- When a New Year starts a new file is created with the Create New Year command.
- You can keep working on both the New Year's file and the previous year file at the same time. Once the closing operations are complete, you can update the opening balances of the New Year's file.
Tax matters
Before closing the accounting, a series of operations with tax implications must be carried out. This includes balancing the inventory account, recording depreciations, accruals (both active and passive), filing VAT declarations, determining how and on which accounts profit should be allocated, and performing various other verification and control operations.
From a program perspective, the amount of profit at the end of the year may be irrelevant, but it significantly changes from a tax standpoint. These aspects need to be reviewed with your tax advisor and accountant. If you're managing accounting for the first time, it can be helpful to consult an expert before proceeding with closures to understand the requirements. Accountants are usually very busy towards the end of the year and in the months leading up to the tax filing deadline; therefore, it may be useful to meet with your accountant or send them the accounting records a few months before closing to determine the appropriate course of action.
The Check Accounting command
Banana Accounting allows you to quickly record transactions and even leave some operations pending without interrupting the workflow
The Actions > Check Accounting command performs a series of checks, as if entering the data again from the beginning, and whenever errors or discrepancies are detected, they are reported.
It is recommended to use the Check Accounting command regularly and every time there are differences or error reports, significant changes (initial changes, VAT codes), and especially before closing the accounts.
Control and verification operations
Before printing the final financial statements it is important to proceed with the verification operations:
Checking the opening balances
- Differences in opening balances
Current year opening balances must correspond to previous year's final balances, and there must be a balance between the Assets and Liabilities payable, otherwise the accounting is not correct. - In the Accounts table, in the Opening and Balance columns, the row 'Difference must be zero' should not have any amount. Otherwise, it is necessary to find the error and correct it to have the opening balance squared. Note: In the Movement view, in the Debit and Credit columns, it is normal to have amounts
- Differences in opening exchange rates
As a rule, opening exchange rates are set at the beginning of the year. It may happen however that some verification procedures have been left pending; therefore before closing the accounting it is important to make sure that:- The exchange rates at the beginning of the year are the same as the final ones on 31.12 of the previous year,
- The exchange rates used are the ones provided by the Federal Administration, as indicated below.
- Differences between bank balances on bank statements and account balances (CheckBalance function)
It is important to check the correspondence of bank, postal, credit card, and other account balances that have to be included in your tax returns. - Differences in the Transactions table
In the Information window at the bottom of the screen, no difference must be shown. Banana Accounting Plus, in the Transactions table, also offers the possibility to view the Balance column, which allows you to detect all the rows where differences are created. - Ensure that the active and passive carryovers from the previous year are closed.
- Verify that the opening balances match the final balances of the previous year, already audited and declared to the Tax Office.
- For multi-currency accounting, refer to the specific page Opening balances for multi-currency accounting
- Detailed explanations can be found on the Double-entry accounting closing operatitions page.
- The Actions > Check Accounting command performs a series of checks and reports any differences and errors.
Closing accounting transactions
In a multi-currency accounting, as in double-entry accounting, before moving on to the New Year, some closing accounting operations are necessary. These are adjustment transactions, value adjustments, and adjustments related to personnel contributions. Here are the main ones:
Import payroll transactions into the accounting file
This operation is only applicable if the payroll is managed using specific software that allows for the import of transactions into the Banana Accounting Plus file.
The import is performed from the Actions menu > Import into accounting > Import transactions with column headers.
Remember to include the recording of the December thirteenth salary installment if it is not generated by the payroll software.
Adjustment of the Delcredere account
Companies that include potential losses in their turnover must adjust the Delcredere account.
Detecting open invoices from customers and suppliers as of December 31st.
To streamline the process, you can quickly identify the values as of December 31st using the function for open invoices by customer and open invoices by supplier.
Closures and VAT declaration
Before submitting the VAT declaration, we recommend the following checks:
- Use the Check Accounting command. In case of errors and discrepancies, you will find messages in the information window at the bottom, in the Messages section.
- Verify that there are no differences in the Balance column of the Transactions table.
- Check bank balances to ensure they match those sent by the bank.
- Verify that the automatic VAT account after reversing the balance in the due VAT account (VAT to be paid to the tax authority) is zero. The due VAT account should show the amount to be paid or the credit amount to be received.
- Before submitting the final VAT declaration, review the VAT statements from previous quarters again to ensure that the amounts paid to the tax authority are still consistent with those displayed.
- Use the VAT Summary command to view various reports and create a PDF printout for data archiving. These will be useful in case of tax audits.
Adjust the Source tax account
After calculating and recording the December salaries, based on the calculation sent to the Source Tax Office, register the adjustment.
Reimbursements for upper-level employees
If applicable, include in the December salary the amount specified by the tax authorities as a flat-rate reimbursement.
Adjustment of Private Account
Verify the balance of the private account. In the case of debit/credit relationships between the company and the owner(s) or related individuals, record active or passive interests according to the terms of the loan agreement or prevailing tax regulations.
Adjustment of the Taxes and Duties Account
Verify that the installments paid during the year correspond to the current year. Payments of taxes related to previous years should be recorded when closing the related provisions that appear in the "Direct Taxes" account (balance sheet). If the balance of the provisions is not sufficient or is excessive, the difference should be recorded as extraordinary expense/income or related to previous periods.
Registration of AVS/AD/IPG/AD Adjustments
- Throughout the year, in the AVS contributions account, advances paid to the AVS Compensation Fund (credited) and contributions withheld from employees' salaries (debited) are usually recorded.
- If family allowances paid to employees during the year have been recorded in a dedicated account, for example, in the "Family Allowance Contributions" account, to reconcile the accounts with the AVS closing balance and record the corresponding adjustment, the balance of this account can be transferred to the AVS/AD Contributions account.
Registering Lainf, Complementary Lainf, and LPP Pension Adjustments
When recording the last salaries of December and the payment of the thirteenth salaries, it's necessary to print the list of salaries showing all gross salaries. The overall AVS gross amount must be communicated to the personnel insurance companies, which will determine any adjustments to be paid.
In multi-currency accounting, similar to double-entry accounting, certain closing accounting operations are required before moving to the new year. These include adjustment entries, value adjustments, and reconciliations related to personnel contributions.
On the Year end closing operations page in double-entry accounting, both accounting and tax-related closing operations are listed.
Below, we will address the topics related to closing entries for exchange rate differences.
Year-end exchange rates and unrealized gains/losses
In order to obtain financial statements, foreign currency accounts must be converted to the base currency at the current or historical exchange rate. Exchange rates variations result in unrealized exchange rates gains or losses. These must be recorded with the following command from the Actions menu:
- Create transactions for exchange rate differences
- Please refer to this page for the entire subject of setting exchange rates and calculating unrealized gains and losses.
- Please note that the closing exchange rates must be entered in the Exchange rate table in rows without a date. These exchange rates are taken over by the program for the calculation of the opening balances of the New Year. If exchange rates with dates are entered, there will be differences in the opening balances of the New Year.
- If there are rows with dates in the Exchange Rates table (historical exchange rates), when closing the accounts, for calculating exchange rate differences, it is recommended not to activate the Use historical exchange rates (rows with dates) option. This ensures that the program uses the updated exchange rate found at the beginning of the exchange rates table, in the rows without dates (in the Rate column)
After the recording of the exchange rate differences, the balances in basic currency are updated according to the closing exchange rates entered in the Exchange rates table (rows without date). In the Chart of Accounts, the balances in the Balance column are equal to those in the Calculated Balance column.
Sending the file to the accountant for closures
If closures and/or checks are carried out by your trustee, you can simply send the file of your accounting created with Banana Accounting Plus via email or save the data on a USB stick.
- If your trustee uses Banana Accounting, you can simply transmit the AC2 file via email or through a USB flash drive. You can also save your file and digital documents in a shared folder with your trustee on Dropbox. You will no longer need to bring heavy binders of paper documentation to the trustee. Furthermore, the trustee will work quickly without having to search through paper documentation.
- If your trustee doesn't have Banana Accounting, you can create a PDF of the accounting data through the File > Create PDF folder menu and transmit the documentation via email. The trustee will indicate all the changes and additions to be recorded to properly close the accounting period.
Alternatively, your trustee can open your accounting file using the Free plan of Banana Accounting Plus, downloading it from our Download page. If your file has more than 70 transactions, your trustee won't be able to add new transactions or make changes, but they can still view all the data, obtain details of each account with a simple click on the account number, etc., and advise you on possible corrections or improvements.
Once the closing and verification entries are executed, it is recommended to lock the transactions
- Actions > Lock Transactions
The transactions rows will be numbered and will have a blockchain code that ensures their security.
End of year printouts
For end-of-year financial statement printouts, you can find the information by clicking on the following links:
PDF Folder
The Create PDF folder command allows you to have all the documents of the entire accounting exercise (account sheets, journal, VAT statements, monthly, quarterly, and annual reports...) in a single PDF file.
You can archive the accounting data by saving the accounting file and prints in PDF format. Optionally, make backup copies on an external disk drive.
On the Preparing documentation for the Audit page, we have published a series of notes and suggestions regarding the documentation to be sent to the auditor. The completeness of the documentation is a good basis for making the auditor's work more efficient and faster.
In Banana Accounting, the allocation of profit or loss occurs automatically at the beginning of the new year. For more information, please refer to the Create New Year page.
Normally, once the closure has been completed, there should be no recorded modifications. However, sometimes there is a need to make changes to the accounts, as in the following cases:
- Unrecorded exchange rate differences at closure
- Unrecorded missing transactions
- Errors in the transactions.
In these cases, it is recommended to proceed as follows:
- If you have already submitted the data to the authority, or if the accounts have already been audited and the balance sheet presented to shareholders or stakeholders definitively, do not make any changes to the accounts, as any modifications could be considered falsifications, with potential legal consequences.
- Make necessary adjustments in the following year, clearly describing the issue in a document that you will need to attach to the adjustment transactions.
- If you forgot to record exchange rate differences, follow the information on our website under Differences in opening balances.
- Obviously, depending on the situation, there may be tax consequences, so it is better to seek advice from your accountant.
- If the legal framework allows you to make changes to a closed year:
- Proceed with caution, limiting yourself to only the truly necessary modifications. If you forgot to record exchange rate differences, follow the information on our website under Create exchange rate differences.
- Review the accounts and perform all necessary checks to ensure that the changes do not cause any issues.
- After the modifications, open the file for the following year and update the opening balances using the Update opening balances command.
Printouts
All the printouts of the Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Statement, and the various Accounting Reports are available from the Reports menu. Each command has various options for customizing the various printouts.
To print the content of the tables, please refer to the Page setup section (last paragraph).
The printouts have the same features as those of the Double-entry accounting, but with the display of columns and values of foreign currencies, exchange rates and counter values in basic currency.
The principal printouts available:
Account card multi-currency accounting
Columns and views of the account card
In the Account card, there are three groups with of columns. In the headers of the Debit, Credit and Balance columns, the initials of the respective coins are indicated.
- Basic currency
Indicated are the opening balance, the transactions, and the balance in basic currency. - Account currency
The transactions in the Account currency are being indicated.
When the accounts are in Basic currency, these values are identical to those of the Basic currency. - Currency2
For every transaction, the amount in Currency2 is being indicated. The logic of for converting amounts depends on the account currency, see Converting to Currency 2 on the Multi-Currency File Properties page.
For the account card the amounts of the transactions are converted with the following logic:- For the opening or carry forward rows, the account balance is converted.
- For the transactions
- The Debit and Credit amounts in Currency 2 are converted.
- The balance of the account in Currency 2 is calculated by adding the amounts in Currency 2 resulting from the conversions.
It is possible that the final balance of the Currency 2 account is not equal to the balance of the currency account converted to Currency 2. See the Exchange rates issues page for possible rounding differences
-
Transaction currency
It is not visible if it is not equal to the account currency or not in Basic currency. If an account is registered in a currency different from the account currency, but equal to Currency2, the amounts in Currency2 will not be the original ones, but those converted from the basic currency.
Views of the Account cards
In the multi-currency account card there are several views, each of which displays certain columns at the same time. As you move from one view to another, the columns change.
You can change the arrangement of the columns and create additional views. More details about the views can be found at the following link: Tables setup.
Data editing
It is not possible to modify the data in the Account card. Double-click on the (underlined) row number to go back to the original corresponding row of the Transactions or Budget table. More details are available on the Account card page (paragraph Updating the Account card).
Info Window
In the lower part of the screen, the Info window, the values of the accounts related to the active transaction are being indicated.
- Account number
- Account description
- Transaction amount of the account in Basic currency
- Actual Account Balance in Basic currency
- Account's currency symbol
- Transaction amount of the account in the Account currency
- Actual Account Balance in Account currency
Enhanced balance sheet multi-currency accounting
The Enhanced Balance Sheet in the multi-currency accounting is done the same way as the one in double-entry accounting. Information is available at the following link: Enhanced Balance Sheet.
The difference consists in the fact that the foreign currency accounts report the amounts in foreign currency as well as in basic currency (amount converted).
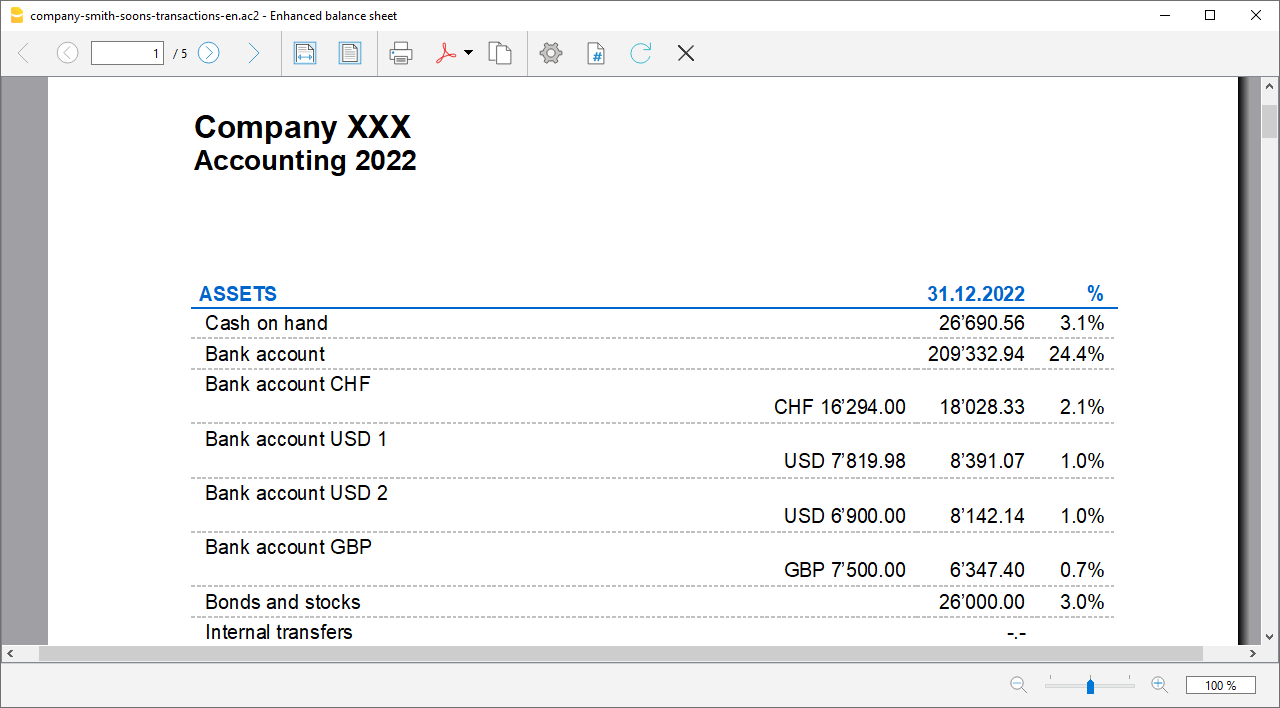
Enhanced balance sheet by groups multi-currency accounting
The Enhanced Balance Sheet by groups in multi-currency accounting is done the same way as the one in double-entry bookkeeping. Information is available at the following link: Enhanced Balance Sheet by groups.
Watch the video tutorial that shows how to create and print the Enhanced Balance Sheet with groups.
The difference consists in the fact that the foreign currency accounts report the amounts in foreign currency as well as in the basis currency (amount converted).
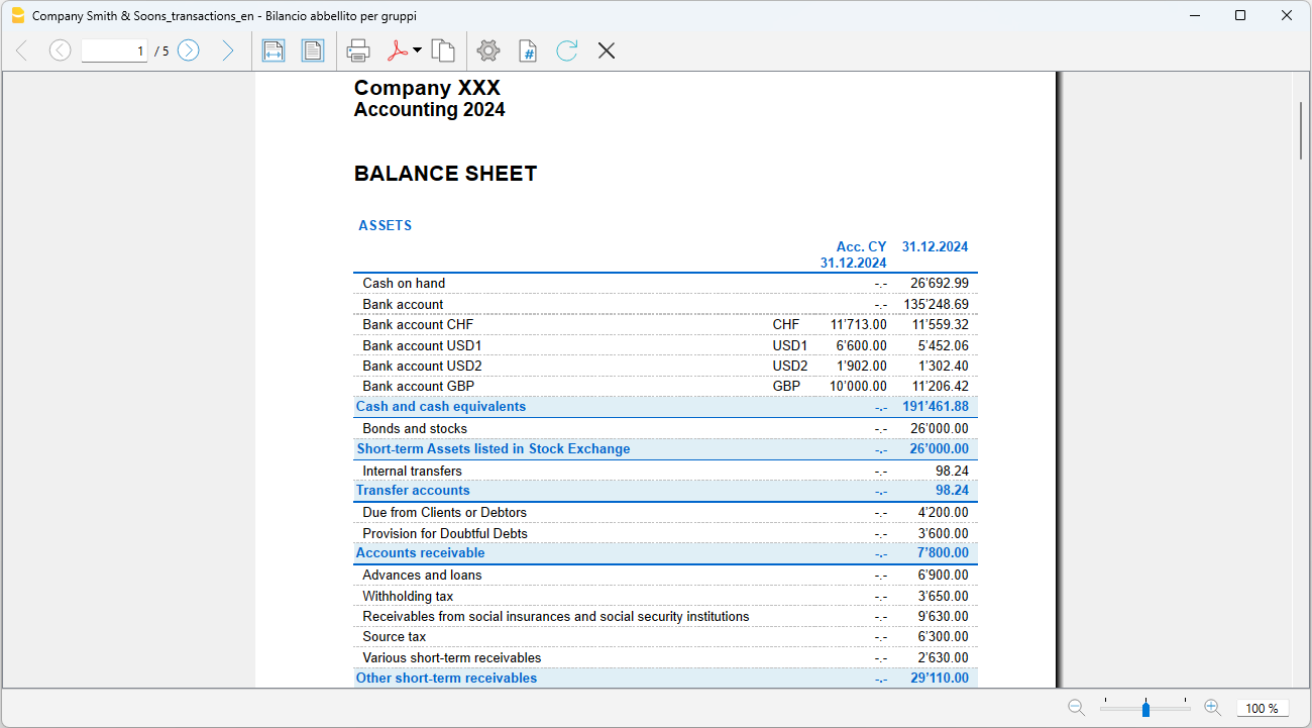
Accounting reports multi-currency accounting
Accounting Reports in multi-currency accounting are done the same way as the ones in double-entry bookkeeping. Information is available at the following links: Accounting report; External accounting report.
New Year | Multi-currency Accounting
Before moving on to the new year make sure you have carried out all the checks, verifications and closing entries as indicated on the following pages
- Year end closure of the Double-entry Accounting
- Year end closure of the Multi-currency accounting for exchange rate issues
All accounting information relating to the opening of the new financial year can be found on the page
In the following, we will limit ourselves to information on exchange rate issues in Multi-currency accounting.
Creation of a new accounting period
When switching to a new accounting year, the program automatically carries over the opening balances to the following year. More details are available on the page Create new year.
Also in the Multi-currency accounting, it is possible to decide to switch to the new year, even if the previous year has not been definitively closed (because entries have not yet been made, exchange differences have not yet been calculated, or the operating result has not been distributed).
It is important, however, that before closing the year, the exchange rate differences are calculated in the year that is about to close, from the menu Actions → Calculate exchange rate differences.
Then, in the new accounting period previously created, you can update the opening balances from the menu Actions → Update opening balances.
Differences in opening balances
In the event that there are differences in the opening balances in the new accounting period, we advise you to carry out all the checks and controls suggested on the Checks and verifications page.
If the differences are due to exchange rate differences not calculated in the previous accounting period, follow the instructions on the page Differences in the opening balances.
Print opening balances
To print the opening balances:
- To print the contents of the Table use the Print/Preview command, selecting the rows of the Balance sheet.
- It is also possible to use the Accounting Printouts and set the print only for the part of the Balance sheet and the opening column.
Differences in the opening balances | Multicurrency
In accountings that include foreign currency accounts, it is necessary to register exchange rate differences before closing the fiscal year.
To correctly record exchange rate differences, follow these steps:
- Update the Exchange Rates table, in the Exchange Rate column, with the official exchange rate as of 31st December, provided by the Public Administration.
- The closing exchange rate must appear in rows without a date.
- It is not possible to use a historical exchange rate (an exchange rate with a date); otherwise, exchange rate differences may arise.
If, when opening the new year (from the Actions menu > Create New Year), or when updating the opening balances (from the Actions menu > Update Opening Balances), the exchange rate differences are not recorded, the program will report a discrepancy in the opening balances in the new fiscal year.

In order to resolve this problem, there are two possibilities:
- If the preceding accounting year has not yet been audited, calculate the exchange rate differences for the previous year:
- Enter the official exchange rates as of 31st December into the Exchange Rates table, in the Exchange Rate column, in the rows without a date.
(or the closing exchange rates provided by the company’s statutes). - Via the Actions menu > Create transactions for exchange rate variation.
- Open the file for the New Year and Update opening balances
- If the previous year was closed and audited (and, if applicable, also reviewed), the new year's opening balances must be adjusted:
- Open the file of the new year
- Insert a new account Non-calculated exchange differences, in the assets or liabilities (Accounts table), as appropriate, or register the amount in account 1090 Transfer account (as in the example below)
- Enter the amount corresponding to the exchange rate difference in the Opening currency column

- In the accounting records of the new fiscal year, a balance related to exchange rate differences is generated in the Opening Currency column of the Accounts table, which must be adjusted.
To adjust the difference, proceed as follows:- In the Transactions table, on January 1st (or on the statutory opening date), record the amount of the exchange rate differences in the account Uncalculated Exchange Rate Differences, or as in the example, in account 1090 - Transfer Account, using as the counterpart the Exchange Rate Differences account (Gains and/or Losses on Exchange Rates) in the income statement.

After the transaction to arrange the exchange rate differences has been entered, the account that has been used should display a balance of zero, or equal to the amount corresponding to the balance prior to the transaction.
In the case of an exchange rate gain, the amount of the difference must be entered in a liabilities account, or in the assets, but with a minus sign in front of the amount.

This amount, which initially impacts the Income Statement of the new fiscal year, is then nullified during the first exchange rate update, which can be performed as needed during the year. If this is not the case and exchange rates are only updated at the end of the fiscal year, the position of the Gains and/or Losses on Exchange Rates account will still be correctly adjusted.
Accounting with cryptocurrencies
Banana Accounting allows you to manage any currency, including the Bitcoin, Ethereum and any other cryptocurrency, even the ICO (Initial Coin Offering), using any abbreviation and allowing for up to 27 decimals and freely settable exchange rates. Precise values and account statements are generated. In Banana Accounting, you will always have the exact values for each individual currency.
Any currency can be selected as the base currency, EUR, US$, Bitcoin and any currency can be managed.
Single or multiple currencies
When you are keeping accounts, you must first decide whether you are doing so in one single currency or if multiple currencies are required.
The Cash book and Income & Expense accounting work with one single currency, whereas Double-entry accounting allows for you to keep accounts in several different currencies.
The base currency is defined in the File prpoerties of the accounting (of the File menu). The program displays a list of predefined currencies, but you may indicate any other currency code.
For Double-entry accounting, amounts are indicated in the account currency as well as the base currency. Amount in the base currency can be added up and are therefore used for the preparation of the Balance Sheet, the Profit & Loss statement, as well as the different reports.
When selecting Multi-currency accounting, the currencies that you require can be be set up in the Exchange rates table, indicating the exchange rates between the different currencies. National or cryptocurrencies can be managed without restrictions and any code can be used.
Changing decimal points for the accounting
Decimal points are implemented when the accounting file is created, in order to avoid rounding up differences. Amounts are rounded up according the same method, thus avoiding differences that sometimes occur in Excel.
When starting a new accounting, it is advised to use an existing template, which is usually set up with 2 decimal points.
If you need to manage your accounting or accounts with a higher number of decimal points, you need to "re-create the file" with the following command
- Tools Menu → Convert to new file ...
The program will generate a copy of your file with the new Outline created for your new file, including the appropriate decimal points required. For Multi-currency accounting you will have to indicate:
- The decimal points in the base currency.
- The decimal points for accounts in foreign currencies.
Setting up decimal points for foreign currencies
When using multi-currency accounting in Double-entry accounting, rounding up needs to be indicated for amounts in foreign currencies.
Decimal points for foreign currency should generally not be inferior to those in use for the base currency.
When managing cryptocurrencies such as ETH, you must indicate 18 as a value in the conversion file.
The different currency codes must be indicated in the Exchange rates table, with the related opening and current exchange rates.
The currency code must be indicated for each account in the Accounts table of the Chart of Accounts.
In the Currency column, the amounts are therefore displayed therefore with the maximum number of decimals, also for the currencies that do not use as many decimals. If you want to have a smaller number of decimals, you can set it up in the format of the desired column. For example with "0.00000" will display only 6 decimals.
Currencies and decimal points
Currency codes are available and can be consulted in the relative Wikipedia page, with indication of decimal points commonly used.
- Currencies generally use 2 decimal points.
- Currencies with 0 decimal points are
- BIF Burundian Franc
- CLP Chilean peso
- DJF Djiboutian franc
- GNF Guinean franc
- ISK Icelandic króna
- JPY Japanese yen
- KRW South Korean won
- PYG Paraguayan guaraní
- RWF Rwandan franc
- UGX Ugandan shilling
- UYI Uruguay Peso en Unidades Indexadas
- VUV Vanuatu vatu
- XOF CFA franc BCEAO
- XPF CFP franc (franc Pacifique)
- Currencies with 3 decimal points are
- BHD Bahraini dinar
- IQD Iraqi dinar
- JOD Jordanian dinar
- KWD Kuwaiti dinar
- LYD Libyan dinar
- TND Tunisian dinar
- Currencies with 4 decimal points are
- UYW Unidad previsional
Cryptocurrencies
There is a multitude of cryptocurrencies, each carrying their own name and code.
There is no indication for their decimal points. For the best known they are
- BTC Bitcoin with 9 decimal points.
- ETH Ethereum with 18 decimal points.
Multiple other virtual currencies are based on the Ethereum blockchain and require 18 decimal points.
Indicate the appropriate decimal points for the required currency in the Outline create new file dialog (see image above).
Income & Expense accounting
The Income and Expense Accounting of Banana Accounting Plus manages the income and expenses of accounts and categories in a simple and intuitive way. Despite its simplicity, it guarantees professional results, because it uses functions and calculation engines such as double-entry bookkeeping. It is ideal for:
- Small businesses, to simplify the management of finances and have professional statements.
- Freelancers and the self-employed, to monitor their income and expenditure in a more intuitive and immediate way.
- Associations, Curatorships and other non-profit organisations, to keep accounts while working quickly, thanks to many functions that automate many work processes, resulting in clear and accurate statements.
- Auxiliary accounts for projects or real estate, to keep track of construction sites, projects, rents or other.
- Households, to keep track of expenses and income and manage the family budget
Getting Started with Income/Expense Accounting
For an easy and immediate start check our resources:
- ▶ Video: How to start an Income and Expense accounting
- Discover all the features of Income and Expense accounting
You can open the template that is closest to your needs and immediately create the file for your accounting. Enter the initial balances and you are already up and running. For more information visit the general page of How to start with Banana Accounting Plus.
The Transactions table
The Transactions table is the core of Income/Expense bookkeeping.
In the Transactions table you enter incoming and outgoing transactions. Entry is extremely easy and intuitive, even for those with no accounting knowledge.

Based on Income and Expenses: the table structure has columns where the data appears ordered and homogeneous. The columns and functions are customisable; rows can be highlighted and thanks to the innovative Filter function you can immediately find, edit and correct data.
There are pre-defined main columns in which to enter:
- The date of the transaction
- The document number, if any
- The incoming or outgoing amount
- The account to which the transaction refers (cash, bank, post office, customer or supplier).
- The category for the income or expense
Quick entry of Transactions: To speed up the entry of transactions, you can use various features: from data entry with autocomplete, to Recurring transactions, Importing bank transactions, or even setting up Rules for automatic completion of imported transactions. In no time, you will have complete accounting and can focus more on the productive activities of your business.
Categorization of income and expenses: Transactions are assigned to specific categories or classes of spending and earning. This helps to organize and analyze financial information more easily.
Accounting without discrepancies: The Balance column is an extremely useful feature; it allows you to instantly see any discrepancies. To use the Balance column, you need to make it visible through the Data > Columns setup menu.
Types of Transactions
As with any type of file, the following types of trasnactions are possible in Income/Expenses:
- Simple transactions, executed on a single line
- Compound transactions, executed on several lines
- Transactions with VAT, possible in Income / Expenses with VAT
Creating invoices
Even in Income / Expense Accounting, despite its simplicity, you can generate invoices to send to your customers. You can print invoices with a QR code (for Switzerland) or without (other countries).
It only takes a few steps to create your invoices:
- In the Accounts table, set up the list of your customers, and for each customer enter all data (address, country, language..).
- In the Transactions table, enter the invoice data. By also completing the data in the Account column (account no.) and the Category column (category no.), you can not only create and print the invoice, but at the same time you have already accounted for it.

Further Functions
The programme also allows you to add further data to your Transactions, so that the same data can also be used for:
- VAT management
- Customer and Supplier control
- Cost Centres and Segments to have reports for projects or sectors of activity.
- Budget
Reports and Printouts
After each transaction, the programme automatically updates all Account and Category balances.
You can obtain accurate and easy-to-understand reports, account and category sheets, journal and forecasts.
From the menu Reports > Enhanced Statement or Enhanced Statement with groups, get your reports in no time. Reports by period are also possible.
- The Enhanced statement displays all accounts and categories without any subgroups
- The Enhanced statement with groups display all accounts and categories also with subgroups

Printouts
The following printouts are possible from the Report menu:
Archiving data in PDF
At the end of the year, when all bookkeeping has been completed, corrected and audited, you can archive all accounting data with the command from the menu File > Create PDF Dossier .

Differences to double-entry bookkeeping
In double-entry bookkeeping, all accounts, both balance sheet and profit and loss account, are only found in the Accounts table. In Income/Expense accounting, to make it easier and more intuitive to use, the accounts are structured in two tables:
- Accounts table - list of asset accounts:
- Assets are shown in positive
- Debts are shown in negative
- Net worth is calculated as the difference between assets and debts.
- Categories table - list of expense and income accounts:
- Expenditure items are in negative
- Income items are in the positive
- Profit or loss is calculated as the difference between positive and negative values.
Transactions
All daily movements are entered in the Transactions table, both for double-entry bookkeeping and for Income/Expense bookkeeping. Between the two accounts, however, there is a substantial difference in the columns, namely:
- In the Income/Expense accounts there are two specific columns:
- Account - where asset accounts that have movements based on expenses incurred or income received are recorded.
- Category - where expense and income categories are recorded. It is also possible to have an account when bank and postal giro accounts are involved.
- In double-entry bookkeeping there are the following specific columns:
- Debit - where increases in assets and decreases in liabilities and expenses are recorded.
- Credit - where decreases in assets and increases in liabilities and revenues are recorded.
Information common to double-entry bookkeeping
On the pages of the Income and Expenses documentation you will find detailed and specific information. For all general functions, please refer to the double-entry accounting documentation. In particular:
- Add, rename or cancel an account
- Insert groups
- Check and recalculate accounting
- Lock transactions
- Create new year
Templates of Income/Expense Accounting
Below are the most commonly used templates:
- Individual Accounting | Income / Expense (Switzerland)
- Freelance Accounting | Income / Expense (Switzerland)
- Family Budget and Household Accounting | Income /Expense (Universal)
- Income & Expense Accounting for a Corporation (Universal)
Starting an Income/Expense accounting
The complete and professional accounting similar to Excel for those who do not have much accounting knowledge. You can always edit and get flawless results.
▶ Video: How to start an Income & Expense accounting file. Find out how to easily set up an Income & Expense accounting, adapt the Accounts and Categories tables, set a budget, enter the transactions and print reports.
Creating an accounting file, starting from a template
Banana Accounting Plus includes templates for all legal forms, divided by country and by category. They can be opened directly in the program, from the File menu, New... command, or they can be downloaded from our Templates page.
Here is how to start choosing a template directly from the program:
- File menu → New command
- Select the Region, the Category and the Accounting type
- From the list of the templates that appears, select the template that is closest to your own needs.
- Click on the Create button.
When entering a key word in the Search area, the program will display the templates that contain the entered key word.
It is equally possible to start from a blank file, by activating the Create Empty file option. In order to facilitate starting up and to avoid grouping errors, we however recommend that you always set out with existing template.
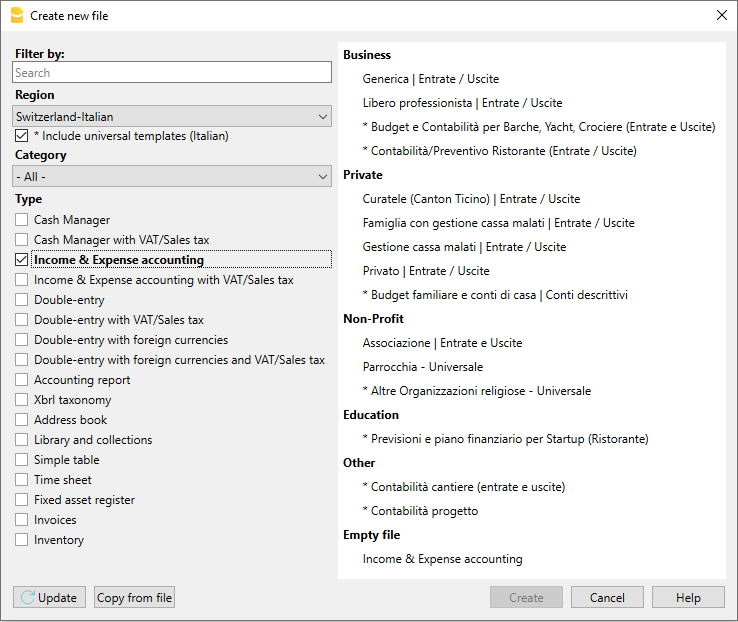
More information on how to create a new file is available on the Create New File page.
Setting up the File properties
Set your data in the File Properties (Base Data) and save the file as.
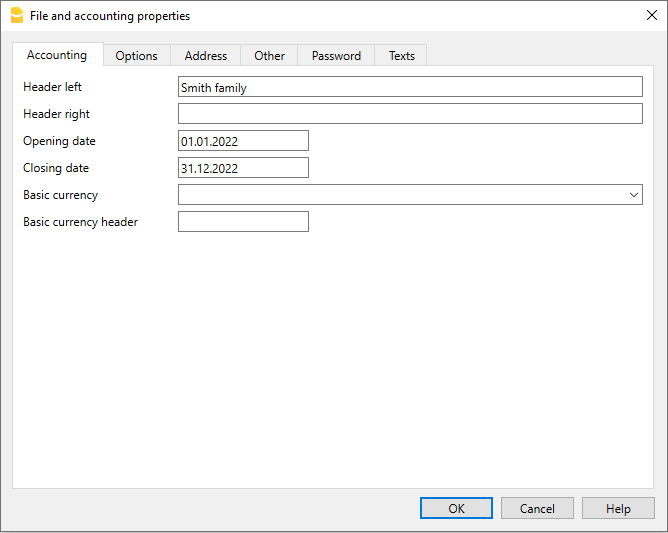
Save to disk
Via the File→ Save As command, save the data and also assign a name to the file. The typical save dialog of your operating system is displayed.
- It is advisable to use the name of the company followed by the year "Company-20xx.ac2" to distinguish it from other accounting files.
- You can keep as many accounting files as you need and each one will have its own name.
- You can choose the path or support you want (save on drive, USB or cloud).
If you also expect to have documents linked to the current year's accounts, it is suggested that you create a separate directory for each accounting year where all the files are to be grouped. Please also visit the Organizing your files page.
Customize the Accounts table
In the Accounts table, you can customize the estate accounts, according to your own needs:
- You can change the Account numbers
- You can change the Description
- In the Opening column you need to enter your opening balances
For Liabilities' accounts (f.ex. debts), the amount of the opening balance should be preceded by the minus (-) sign.
This operation needs to be executed only when using Banana Accounting for the first time, since from then on, every end of the year, when creating a New Year (menu Actions → Create New Year command), the opening balance will be automatically transferred.
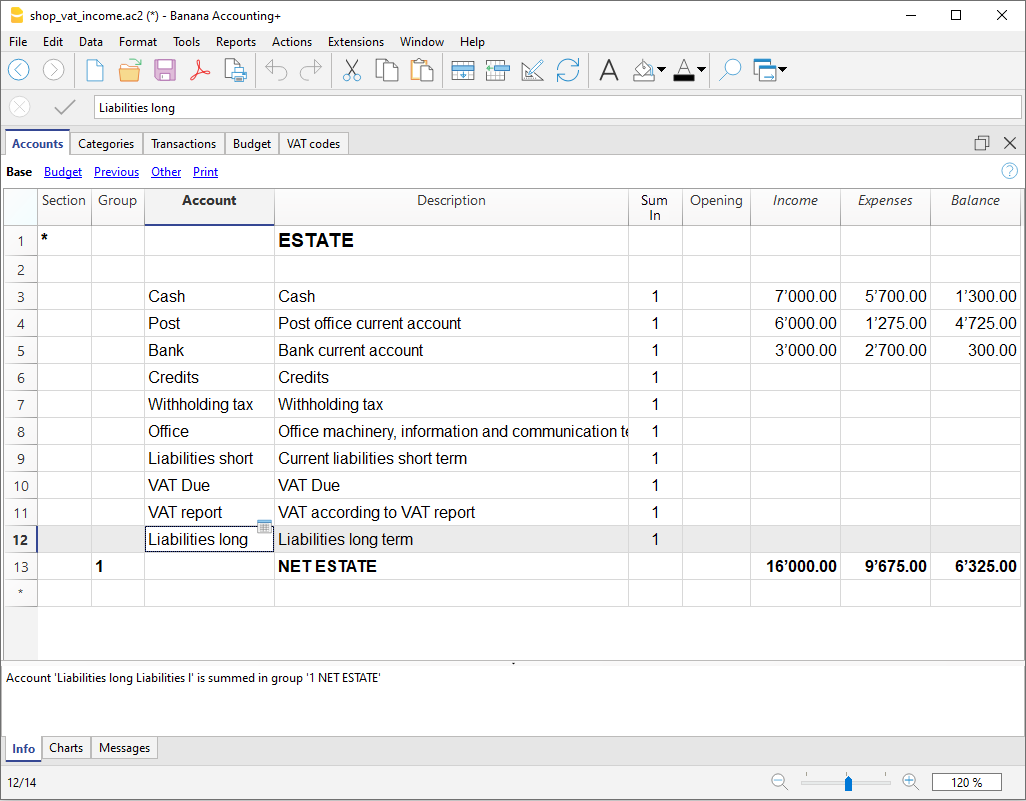
Customize the Categories table
In the Categories table, customize the income (earnings/revenue) and expense (expenses/costs) categories.
The Category numbers can be amended, as well as the Description.
At the start of the year, the categories don't and must not contain an opening balance, in order to determine the result of the accounting year.

Transactions table
In the Transactions table, the daily income and expense transactions are entered, indicating the account, for which the transaction was made and the category to which the income or expense is attributed.
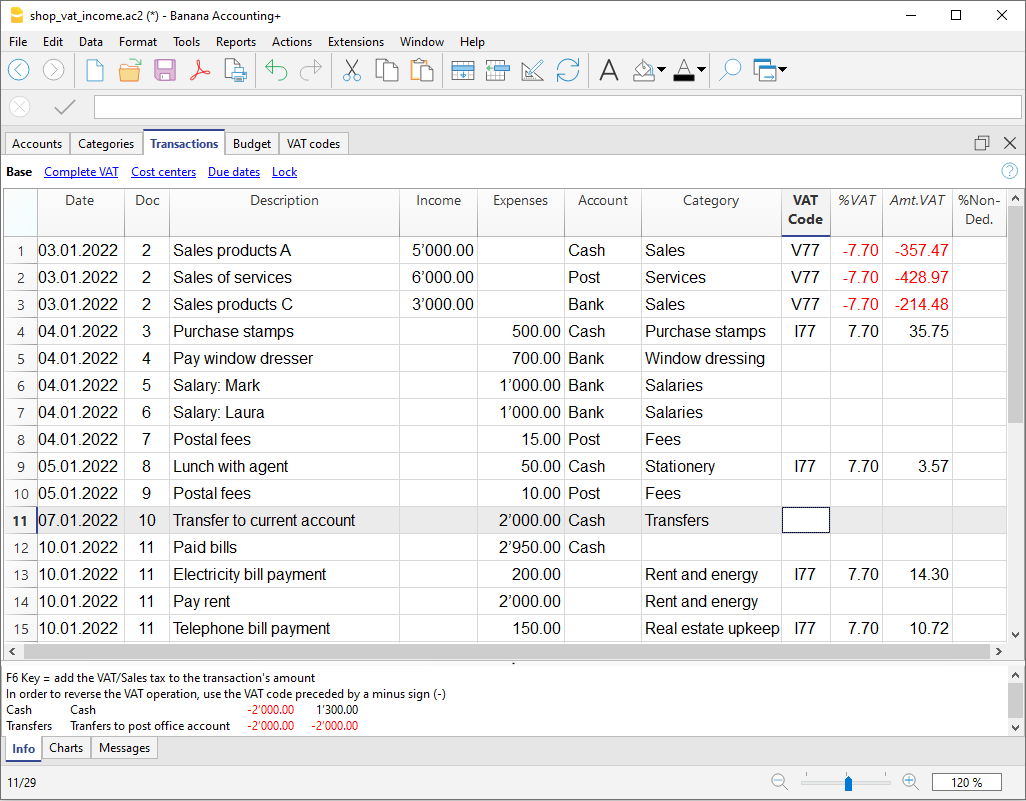
In the appropriate columns :
- Enter the Date
- Enter the Document number that is manually assigned to the paper document. This allows you to easily find documents, once the accounting transaction has been entered.
- Enter a Description
- In the Income column, enter the income amount
- In the Expenses column, enter the expense amount
- In the Account column enter the account number (it has to be an existing account in the Accounts table, ex. Bank)
- In the Category column enter the expense or income category (it has to be an existing category in the Category table).
Speeding up the recording of the transactions
In order to speed up the recording of your transactions, you can use:
- The Smart fill function that allows the automatic auto-complete of data that have already been entered at an earlier date.
- The Recurring transactions function (Actions menu), used to memorize recurring transactions into a separate table.
- Import of your bank or post office statements
Make visible the Balance column in the Transactions table
The new Balance column is a very useful feature: it allows you to immediately spot possible differences.
The Balance column is not visible by default: you can make it visible via the Data → Columns setup menu.
- Watch the Video: Using the Balance column to spot differences
- More information on the Balance column
Transactions with VAT
In order to enter transactions with VAT please proceed as follows:
- from the File menu, choose New command and choose Income /Expenses accounting with VAT/Sales taxes
- Choose one of the existing templates for your nation of the Income/expenses accounting with VAT type
In order to enter transactions with VAT, please refer to the Transactions page.

Transactions on multiple rows
Transactions on multiple rows, or Composed transactions are transactions involving more than two accounts and credits/debits on multiple accounts or categories (for example when you pay different invoices from the bank account). In this case you need to enter the transaction on multiple rows:
- In the first row enter the total amount of the income or expense and the account from which this amount is debited or credited
- In each subsequent row, enter the income or expense amount in the category column, and enter the appropriate category number.
Each individual amount is recorded on different row. When all the individual income and expenses rows are entered there shouldn't be any differences. - If you have made the Balance column visible, you will immediately see that as you proceed, the difference detected gradually decreases, until it is extinguished when you have finished compounding.

The Account card
The Account card allows you to have a complete list of entries relating to the same account or the same group.
- To open an account card you click once on the account number cell and then click once on the small blue arrow appearing in the upper right corner of the cell.
- To open multiple account cards you must select the Account cards command from Reports menu.
- To update the account cards, following changes in the Transactions table, you must click on the two circular arrows symbol, located at the top right of the account card.

The Category card
The Category card allows you to have a complete list of entries relating to the same category.
- To open a category card you click on the account number cell and then click once on the small blue arrow appearing in the upper right corner of the cell.
- To open multiple category cards you must select the Account cards command from Reports menu.
- To update the category cards, following changes in the Transactions table, you must click on the two circular arrows symbol, located at the top right of the category card.

Account cards per period
To open an account card with account balances at predefined dates, click on Reports in the menu, Account cards ... and click Period selected in the Period tab to insert your selected period. Visit the Period page for further information.
Print the Account cards
To print an Account card, open it from any table (Accounts or Transactions) and start printing from the File menu.
To print out several or all the Account cards, click Reports menu, select Account cards and select the Accounts you wish to print. The filter in the window allows you to select automatic selection of all accounts, cost centers, segments, groups etc. Visit the Account Cards page for further information.
Enhanced Statement
To view the Enhanced Statement and the Enhanced Statement with groups, choose the Reports menu and then the Enhanced statement or Enhanced statement with groups command. You can also obtain statements by period.
- The Enhanced statement displays all accounts and categories without any subgroups
- The Enhanced statement with groups displays all accounts and categories also with subgroups.

Archive data in PDF format
At the end of the year, when the accounting is done, corrected and revised, you can store all accounting data with the Create PDF dossier command from the File menu.
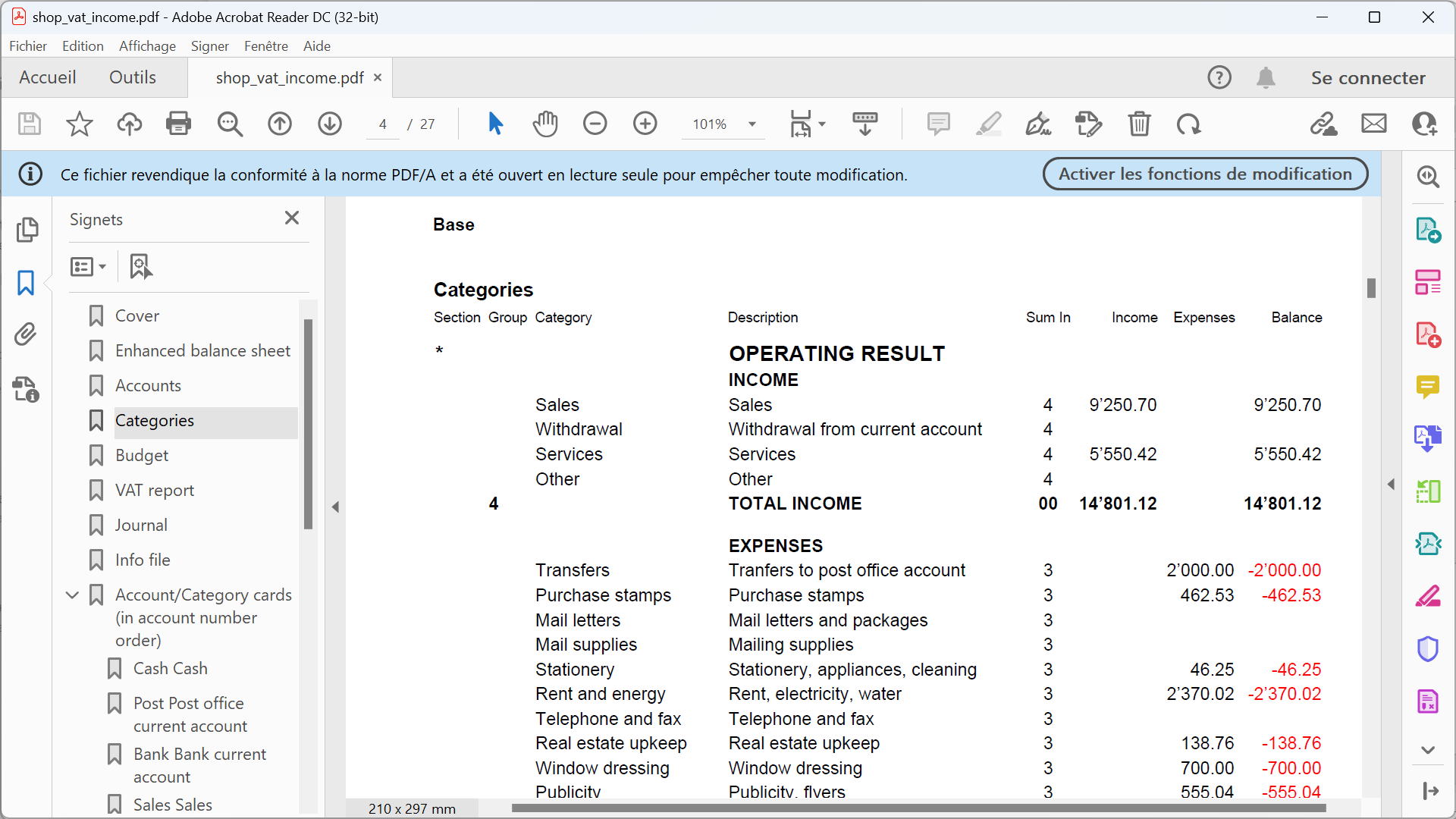
The Budget
Before starting your accounting year, you can create a budget with your assumed expenses and revenue, in order to have control over the financial and economic situation of your company.
The budget can be set in two different ways:
- From the Budget column of the Categories table. For each account the yearly budget is indicated.
In this case, when you process the budget from the Reports menu, Enhanced statement with groups command, the Budget column shows the amounts that relate to the entire year. - From the Budget table, that you need to manually activate using the Add new functionalities command from the Tools menu.
- In this table all estimates are entered as budget transactions, either income or expenses. If you activate this table, the Budget column of the Accounts table is automatically deactivate.
A detailed budget can be set in this case, that takes into account the possible variations during the year and in the different periods of the year
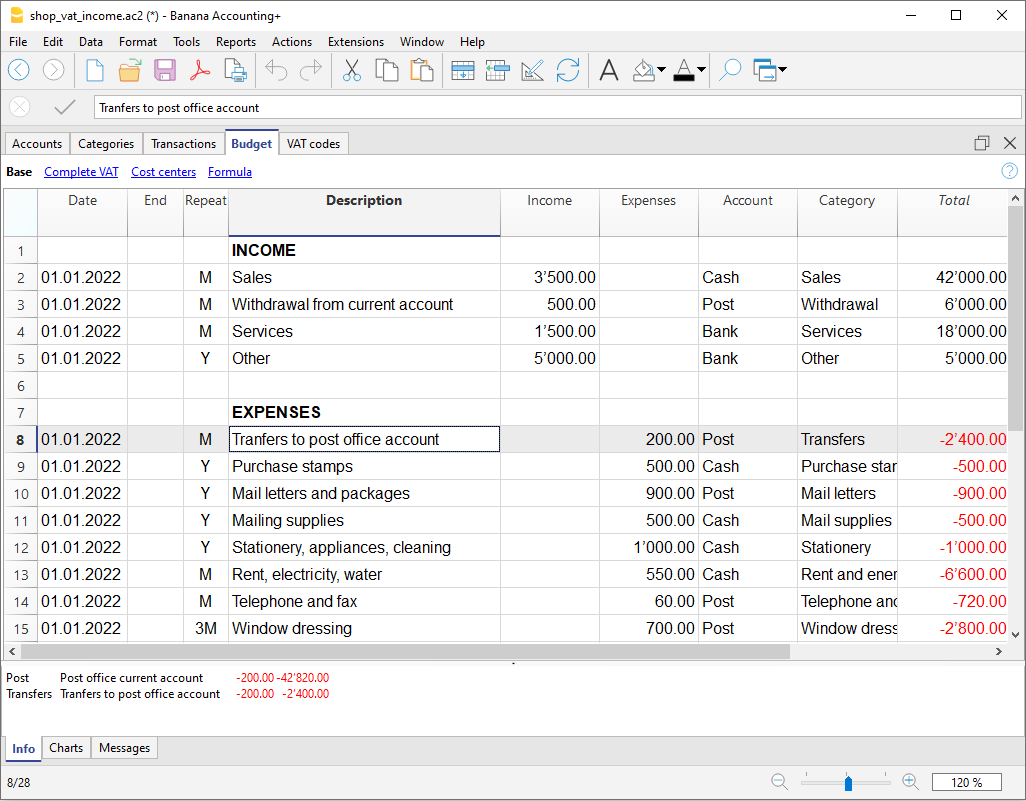
Opening Balances in Income & Expense Accounting
Opening balances when you start with Banana Accounting
When creating a new file for the first time with Banana Accounting, the opening balances must be entered manually in the Accounts table, Opening column.
- The positive amounts of the Balance Sheet (cash, bank, customers, furniture, etc.) must be entered normally in the Opening column.
- The negative amounts of the Balance Sheet (payables, loans, etc.) must be entered with a minus sign in front of the amount in the Opening column.
When you move to the new year, using the Create new year command, Banana accounting automatically reports all the opening balances in the Accounts table.

Starting with Banana Accounting during the year
If you start a new accounting, taking over the work already done with other programs, you have two possibilities:
- Start accounting from the start of the year, by entering the opening balances at the beginning of the year (Accounts table, Opening column) and the transactions (Transactions table) that have already been previously recorded with other programs (also see Transferring data from other software). Thus you will have all the accounting details a single file.
- Starting from the date when the accounting is resumed:
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
In addition to entering the opening balances of the balance sheets in the Accounts table, it is also necessary to enter the income (positive) and expenses (negative) balances in the Categories table. - Input the new entries in the Transactions table.
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
Balances of previous year
If you start a new accounting by taking over an existing accounting and you want the previous year's values to appear on the printouts, it is necessary to enter the previous year's balances in the Previous view, Previous Year column of the Accounts table:
- Enter the closing positive account balances of the previous year's Balance Sheet.
- Enter the closing negative account balances of the previous year's Balance Sheet (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).
- Enter the last year's closing balances of the Income.
- Enter the final balances of the previous year of Expenses (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).

Create new year
When you start the new year, the program automatically carries over the opening balances for the following year.
Consult the Create New Year lesson.
Print opening balances
To print the opening balances:
- To print the contents of the table, use the Print / Preview command, by selecting the rows of the Accounts table.
- You can also use the Accounting printouts and set the printout only for the Statement part and the opening column.
The Accounts table - Income & Expense accounting
The Accounts table presents the balance sheet, where you enter:
- The balance sheet accounts, including any accounts of customers, suppliers.
- The totalisation groups
In the following example, in the Accounts table, all accounts are grouped in Group 1 (Total Assets). The asset accounts are added to the liability accounts and the difference determines the Net Assets.
For more information on the grouping system, please refer to the Double-entry Accounting Groups page. - Opening balances.
The Accounts table displays account balances, columns of incoming and outgoing movements, and the budget. This provides an immediate and constantly updated view of the balance sheet situation. Assets are shown in positive, liabilities (debits) in negative.

The columns of the Accounts table
The main columns of the Accounts table are listed below. The display of columns changes according to the selected View.
Additional columns can be added, either system columns or own columns, via the menu Data > Columns setup.
Section
Enter an asterisk to signal a section change. For example, to distinguish Total Assets from Cost Centers.
Values must be entered in the Sections column for presenting the Enhanced Statement with groups.
Refer to the Sections page for further details and information.
Group
Values are entered that total the categories that have the same grouping in the Sum in column. They are fundamental for totals.
Account
Enter the number or initials of the account to be managed (cash, bank, post).
Description
Enter a description for the relative account. This description is automatically taken from the Account Description column of the Transactions table (if displayed).
Sum in (Gr)
Enter a value that identifies the category belonging to the same group.
The column heading 'Sum in', used in Banana Plus version, replaces the column heading 'GR', used in previous versions.
Opening
This is the column that shows the opening balances. The opening balance is only entered manually in this column the first time Banana accounting is used, or a new file is opened. At the start of the new year with automatic opening, the opening balances are automatically entered again.
Income
This locked column displays the balance of incoming transactions. The balance will be updated automatically after each registration.
Expenses
This locked column displays the balance of expenses. The balance will be updated automatically after each registration.
Balance
This locked column displays the balance resulting after income and expenses. The balance will be updated automatically after each registration.
Sections
The Sections in the accounts and / or categories table allow you to define a set of accounts and categories that you wish to print via the Report > Enhanced statement with groups command.
- The sections are indicated in the sections column of the accounts table and the categories table
- An * (asterisk) indicates the start of the section
- A ** (double asterisk) indicates the start of a subsection.
- A # indicates the start of the notes section
- One section ends when another begins
- Unlike double-entry accounting, numeric sections cannot be used
- If no section has been indicated, the first time you use the command, the program will insert it automatically
- In the "Balance Sheet" Accounts table
- In the "Operating result" Categories table
- It is useful to create separate sections if you have cost centers, segments or customer or supplier ledgers.
This way you can print out reports of what interests you only.
Customising the Accounts table
In the Accounts table you can customise the asset accounts according to your needs:
- You can change the account numbers
- You can change the description
- In the Opening column, enter the opening balance.
The opening balances of accounts payable must be entered with a minus sign in front of the amount.
This operation is only carried out the first time Banana Accounting Plus is used, since every time the programme creates a new year (menu Actions > Create new year) the opening balance is automatically updated.

Account Cards by Period
To view account cards with balances referring to a specific period, click on the menu Report > Account Cards and in the Period section activate Specified Period and enter the start and end date of the period. See the Period page for more information.
Printing Account Cards
To print an account card, simply view the card from any table (Accounts or Transactions) and launch the print from the File menu.
To print several or all account cards, click on the menu Report > Account/Category Cards and select the account cards to be printed. Using the filter in the window, all accounts, cost centres, segments, groups, etc. can be selected automatically. More information is available on the Account Card page.
Previous years' profit and loss account
In Income / Expense accounting, the totalisation line that groups income and expenses directly shows the net worth or equity, so there is no need to have a specific account.
If you wish to display the amount of the previous years‘ operating results, you must add a Previous Year Balance account. The allocation of the amount must be done manually in the Opening column (Accounts table) at the beginning of each year.
Income & Expense Categories
The Categories table presents the Income and Expenses status.
You can freely set:
- The Income and Expenses Categories.
- Possible cost and profit centers.
- The totalization groups.
For further information on the grouping system, refer to the Group page in double-entry accounting.
In the example below, there are three main groupings:
- Group 4 - Totals all the Categories that have grouping 4 in their Sum in column (total Income)
- Group 3 - Totals all the Categories that have grouping 3 in their Sum in column (total Expenses)
- Group 00 - Totals groups 4 and 3 (Total Income and Expenses), which determine the Result for the accounting period.

The columns of the Categories table
The main columns of the Categories table are listed below. The display of the columns changes according to the selected View.
You can add additional system columns as well as your own columns via Data > Columns setup.
Section
Enter an asterisk in the row that contains the title, to signal a section change, that will be displayed in the enhanced Statement with groups.
(the asterisk is inserted in the "Operating Result" title row in our example).
If different sections than Income and Expense are planned, such as Cost and Profit centers, another asterisk may be entered on the respective title row. Refer to the Sections page for further details and information.
Group
Enter an identifier (numerical or sign) identical to the one entered for each category in the Sum in column. The totals for each category belonging to the same grouping of the Sum in column will then be added up (in our example, Group 4 totals the Income Category and group 3 the Expenses category).
Category
The category number identifying the exit or entry is entered.
Description
Enter a description for the relative Income or Expense Category. This description is automatically taken from the Category Description column of the Transactions table (if displayed).
Sum in (Gr)
The code of a group is indicated so that the programme totals the amount of the line in the group.
The heading 'Sum in' has been adopted with the Banana Plus version.
The column name has remained Gr, to maintain compatibility with previous versions of the programme.
Each category has an identifier that is used to define in which group it is to be totalled (in the example, all income categories, in the Sum in column, have the grouping 4, because they are totalled in Group 4, Total Income).
Income
This locked column displays the balance of incoming transactions. The balance will be updated automatically after each registration.
Expenses
This locked column displays the balance of expenses. The balance will be updated automatically after each registration.
Balance
This locked column displays the balance resulting after income and expenses. The balance will be updated automatically after each registration.
Customizing the Categories Table
In the Categories table, you can customize the categories for income (earnings/revenues) and expenses (costs).
The category numbers can be changed, as well as the descriptions.
The categories should not have any opening balance at the beginning of the year, to determine the corresponding annual operating result.

The Category Card
The category card allows you to have a complete list of accounting transactions involving the same category.
- To open a category card click on the cell where the category number appears and again a click on the small blue symbol that appears at the top right of the cell.
- To open multiple category card you must select the Account card command from the Reports menu.
- To update category cards, as a result of changes in the Transactions table, click on the blue symbol, of the two circular arrows, located in the upper right corner of the category card.

Printing Category cards
To print a category cards, simply view the card from any table (Categories or Transactions) and launch print from the File menu.
To print several or all category cards, click on the Reports > Account cards menu and select the category cards you want to print. Using the filter in the window, you can perform an automatic selection of all accounts, cost centers, segments, groups, etc. More information is available on the Account card page.
Neue Gruppen erstellen
Alle von Banana Buchhaltung vorgeschlagenen Vorlagen sind auch in der Erstellung einer neuen Totalisierungsgruppe anpassbar.
Um eine neue Totalisierungsgruppe zu erstellen, geht man wie in unserem Beispiel vor:
Die Gruppe Liquidität wurde in die Tabelle Konten hinzugefügt.
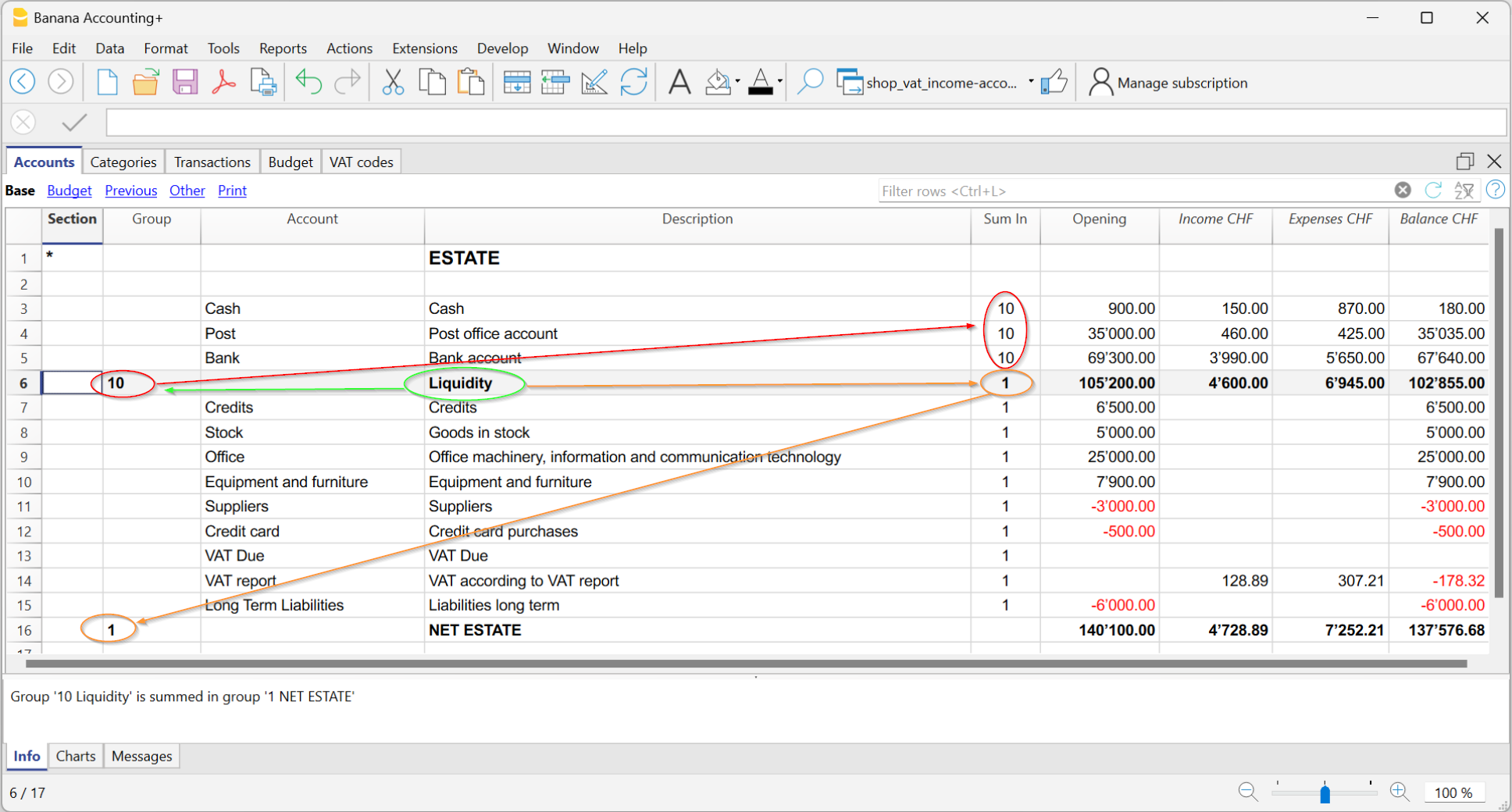
- Begeben Sie sich in die Tabelle Konten oder Kategorien und fügen Sie eine neue Zeile hinzu.
In unserem Beispiel wurde Zeile 6 (unterhalb der Zeile des Bankkontos) hinzugefügt. - In der Spalte Gruppe geben Sie die neue Totalisierungsgruppe ein.
In unserem Beispiel wurde die Gruppe 10 hinzugefügt, um die Konten der Liquidität zu summieren. - In der Spalte Summ. in geben Sie die Gruppe ein, die in der Spalte Gruppe definiert wurde.
In unserem Beispiel wurde in der Spalte Summ. in der Zeilen "Kasse", "Post" und "Bank" die Zahl 10 eingetragen, um die Gesamtbeträge jedes Kontos in der Zeile der Gruppe 10 ("Liquidität") zu erhalten. - In der Spalte Summ. in der Gruppe 10 Liquidität wird die Zahl 1 eingetragen, um den Gesamtbetrag in der Gruppe 1, die dem Nettovermögen entspricht, zu übertragen.
Transactions Income & Expense accounting
Income and Expense transactions are entered into the Transactions table, which is the central hub for accounting purposes. In this table, transactions are always visible and in perfect order, providing a clear overview and keeping everything under control. Additionally, all entered data can be modified and corrected at any time.
The columns of the Transactions table
The main columns of the Transactions table are listed below. The display of the columns changes according to the selected View.
You can add additional system columns as well as your own columns via Data > Columns setup.

Date
Enter the date of the incoming or outgoing transaction
Doc
A Doc number is entered. Usually, the document number identical to the paper document is assigned; this allows you to easily retrieve the documents after some time.
Description
Enter a description to identify the incoming or outgoing transaction.
Income
Enter the incoming amount.
Expenses
Enter the outgoing amount.
Account
Enter the estate accounts (cash, bank, post office, customers, suppliers ..)
- If it is an income the amount should be recorded as a positive on the account.
- If it is an expense the amount should be recorded as a negative on the account.
Category
Enter the reason for the income or expense; it can be an income or expense category, defined in the Categories table, or an account present in the Accounts table.
- Entering a category:
This is used to attribute income or expense to an item. The sign of the Category follows the sign of the account.- If it is an income, the amount should be recorded as a positive.
- If it is an expense, the amount should be recorded as a negative.
- Entering an account:
It is used to transfer amounts from one asset account to another (e.g., withdrawals, deposits, ...). On the account entered in the Category column the amount is then entered the opposite way. The transaction functions as in double-entry accounting:- If it is an income, the amount should be recorded as a negative.
- If it is an expense, the amount should be recorded as a positive.
Category Description
In this column, the description of the category, inserted in the Categories table, is automatically taken.
If in the Categories table the description of a category is modified, in order to visualize the new text in the Category Description column of the Transactions table, it is necessary to recalculate the accounting.
Entering Transactions
In the Transactions table, the incoming and outgoing movements between accounts and categories are recorded. There are different columns for entering transaction data:
- Date: the date of the entry.
- Doc.: the document number.
- Description: the description of the transaction.
- Income/Expenses: enter the amount coming in or going out.
- Account: enter one of the Estate accounts (cash, bank, post, clients, suppliers...).
- Category: the reason for the income or expense is entered, which could be a revenue or expense category or a contra account for asset movements.
After each entry, the amount is shown automatically in the account and category tab. In the category column, an account from a category or also an account from the Accounts table can be entered:
- If a category is entered in the Category column, the amount is recorded in the category as income and expense.
- If an account is entered in the Category column, the amount is recorded in reverse (with the sign reversed). If it is outgoing instead as positive. In this way, transactions can be made between two asset accounts (as in the case of a transfer).
- On the other hand, it is not possible to make transactions in and out of two categories with one entry.
It is necessary to use two lines of entry, without using the Account column, with the first line in and the second line out.
It is also possible to record compound transactions, exit from an account with several categories. In this case, several lines are used: on the first line the account without category is recorded and on the following lines the categories and without account are recorded.
The Income and Expense Accounting allows to manage operations in a similar way to the Double-entry accounting, except for movements between two Categories that require two entry rows.
Speeding up the recording of Transactions
In order to accelerate the recording of the Transactions, you can use the following functionalities:
- The Smart fill function that allows the automatic auto-complete of data that have already been entered at an earlier date.
- The Recurring transactions function, used to memorize recurring transactions into an appropriate table.
- Importing bank or postal account statements, to automatically import transactions from bank, postal or credit card statements.
Recording expenses or income
When recording a movement, the Account column should indicate:
- in the Account column, the account from which the amount enters or exits;
- in the Category column, the expense or income category.
In the Account/Category card, the amount will be recorded in positive if it is an income and in negative if it is an expense.
Transactions between asset accounts
In the Category column, it is also possible to enter an asset account, present in the Accounts table.
For example, to record a transaction into the cash account from a bank withdrawal, the entry is made as follows:
- Enter the incoming amount in the Income column.
- Enter the Cash account in the Account column.
- Enter the Bank account in the Category column.
In this case, the program will record the amount positively in the Cash account (which increases) and negatively in the Bank account (which decreases).
Thanks to this recording method, any direct movement between two asset accounts can be recorded on a single registration line, as in double-entry bookkeeping (see example in the image above, first transaction).
Transactions with multiple movements
When you need to record a transaction that is to be split across multiple accounts or categories, you must enter multiple rows of transactions.
Below we show an example (see registration Doc. 11).
Multiple bills are paid through the bank.

- Enter the same date and document number in all the rows that affect the same transaction. This allows you to easily locate a transaction with multiple entries.
- In the first row, enter the total amount in the Expenses column if it is a payment, or in the Income column if it is deposit.
- In the Account column, enter the liquidity account (account through which you pay or collect). The Category column in the first row remains empty.
- In the following rows, enter the amount of the invoice paid or collected on each row (the Expenses column or the Income column),
Each invoice will be entered on a separate row.
The Account column remains empty. - In the Category column, enter the category for each row to identify the entry or entry of the movement.
Examples of transactions with VAT
In order to manage transactions with VAT, it is necessary to have set up an Income / Expense template with VAT options.

Additional columns for VAT
Depending on the type of Income / Expense accounts setup (with or without VAT) there are additional columns where VAT data is entered.
VAT Code
Enter the VAT code referring to a sale or a cost. There must be a code in the VAT Codes table.
Refer to the Transactions with VAT page for explanations of VAT codes and further information.
Account and category card
In the account or category card, the presentation of the transactions is very similar to the ones of the Transactions table.
If you enter further transactions or make changes (always operated in the Transactions table), you can update the account/category card by clicking the Refresh icon on the right side of the screen.

Inserire le Registrazioni
Nella tabella Registrazioni si registrano i movimenti in entrata e uscita fra conti e categorie. Ci sono colonne diverse per inserire i dati delle operazioni da registrare:
- Data: la data della registrazione.
- Doc: numero di documento.
- Descrizione: la descrizione dell'operazione.
- Entrate/Uscite: l'importo in entrata o in uscita.
- Conto: viene inserito uno dei conti patrimoniali (cassa, banca, posta, clienti, fornitori....).
- Categoria: viene inserito il motivo dell'entrata o dell'uscita, ovvero una categoria di ricavo o spesa. Nella colonna Categoria è possibile inserire anche un conto presente nella tabella conti, come nel caso di una registrazione che riguarda dei movimenti patrimoniali (es. giroconto).
Dopo ogni registrazioni, l'importo viene riportato in automatico nelle schede conto e categoria.
Aspetti tecnici della colonna Categorie
La Contabilità entrate e uscite permette di gestire operazioni in modo simile a quella della contabilità in partita doppia, eccetto per movimenti fra due Categorie che richiedono due righe di registrazione.
Si possono anche registrare operazioni composte, uscita da un conto con più categorie. In questo caso si usano più righe: sulla prima riga si registra il conto senza categoria e nelle righe successive si registrano le categorie e senza conto.
Come registrare un'entrata e/o un'uscita
Quando registri un movimento deve indicare:
- Nella colonna Data indica la data del documento che registri.
- Nella colonna Doc. registra il numero del documento (non è obbligatorio)
- Nella colonna DocLink inserisci il percorso per collegarti e aprire il documento digitale.
- Nella colonna Descrizione, inserisci una descrizione.
- Nella colonna Conto, inserisci il conto presente nella tabella Conti (da dove l'importo entra o esce).
- Nella colonna Categoria inserisci la categoria di spesa o entrata.
Nelle schede conto e categoria l'importo sarà registrato in positivo se è un'entrata e in negativo se è un'uscita.
Movimenti fra conti patrimoniali
Quando un movimento interessa solo due conti patrimoniali, pertanto non vi è una categoria, nella colonna Categoria è possibile inserire anche un conto patrimoniale, presente nella tabella Conti. Nella tabella Conti invece non è possibile inserire una categoria.
Per esempio, per registrare un'entrata nella cassa da un prelevamento in banca, la registrazione si esegue nel modo seguente:
- Nella colonna Entrate si inserisce l'importo in entrata.
- Nella colonna Conto viene inserito il conto Cassa.
- Nella colonna Categoria viene inserito il conto Banca.
In questo caso, il programma andrà a registrare l'importo in positivo nel conto Cassa (che aumenta) e in negativo nel conto Banca (che diminuisce).
Grazie a questa modalità di registrazione si può registrare su una sola riga qualsiasi movimento diretto fra due conti patrimoniali.
Registrazione su più righe
Quando si deve registrare un'operazione che riguarda più conti e/o categorie, questa deve essere contabilizzata su più righe di registrazione.
Qui di seguito proponiamo un esempio (vedi registrazione Doc. 11).
Tramite cassa vengono pagate più fatture.
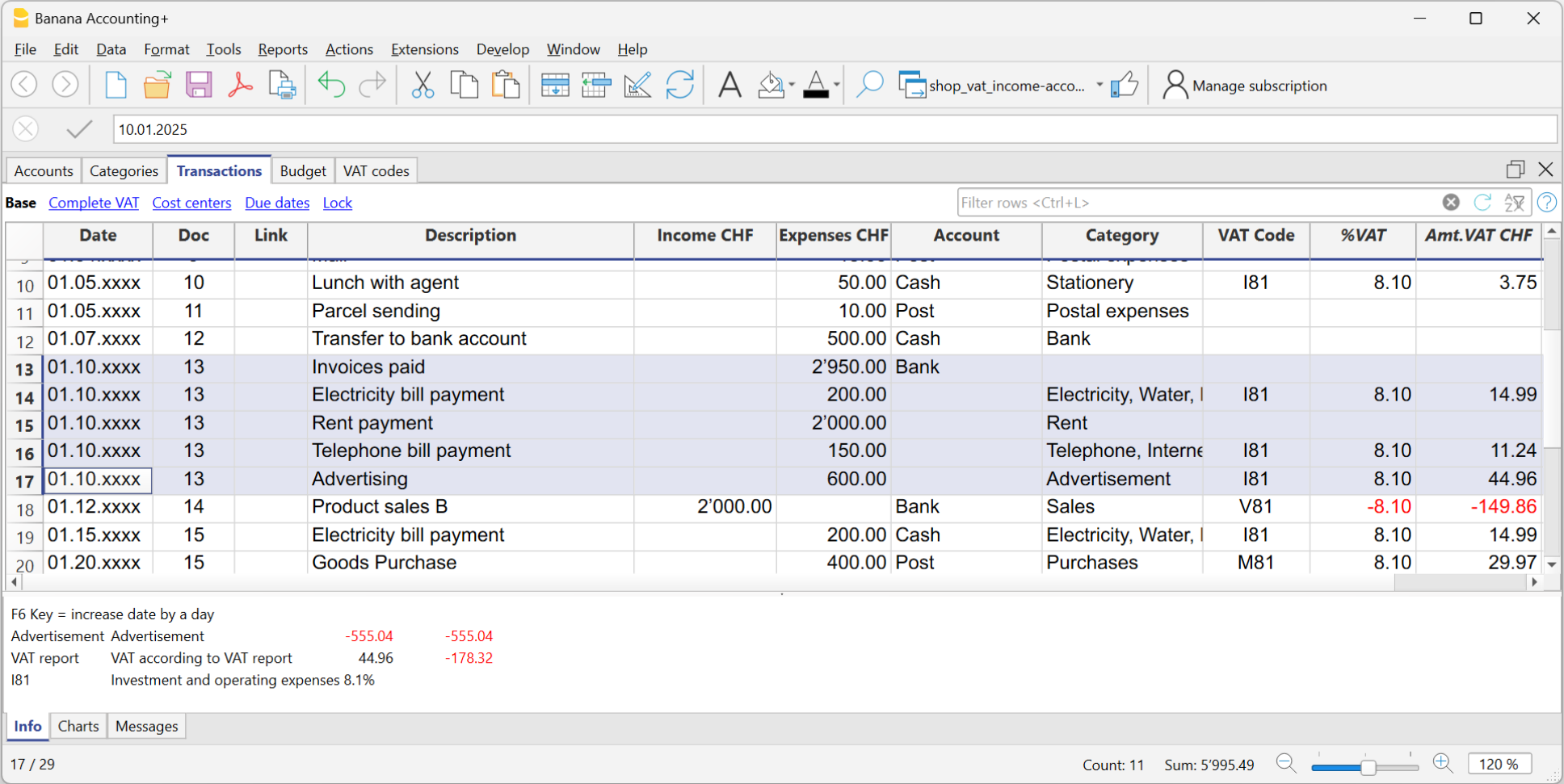
- Inserire la stessa data e lo stesso numero di documento in tutte le righe che interessano la stessa registrazione. Questo permette di individuare una registrazione che ha più movimenti.
- Nella prima riga inserire l'importo complessivo, nella colonna Uscite se si tratta di un pagamento, nella colonna Entrate se si tratta di un incasso.
- Nella colonna Conto, inserire il conto della liquidità (conto tramite il quale si paga o si incassa).
La colonna Categoria nella prima riga rimane vuota. - Nelle righe successive inserire su ogni riga l'importo della fattura pagata o incassata (rispettivamente colonna Uscite e colonna Entrate).
Ogni fattura verrà registrata su una riga.
La colonna Conto rimane vuota. - Nella colonna Categoria inserire per ogni riga la categoria per identificare la voce di uscita o di entrata del movimento.
Velocizza l'inserimento delle Registrazioni
Per velocizzare l'inserimento delle registrazioni si utilizzano le seguenti funzioni:
- Immissione dati con auto-completamento - consente la ripresa in automatico dei dati già inseriti in precedenza.
- Registrazioni ricorrenti - permette di memorizzare in un'apposita tabella le registrazioni ripetitive.
- Importazione dati dall'estratto bancario o postale - per importare in automatico i movimenti dall'estratto bancario, postale o carta di credito.
Scheda conto/categoria
Nella scheda conto o categoria, la presentazione dei movimenti è del tutto simile a quella della tabella Registrazioni.
Se si aggiungono nuove registrazioni o se si effettuano dei cambiamenti (sempre eseguiti nella tabella Registrazioni), è possibile aggiornare la scheda conto cliccando sul simbolo Aggiorna (freccia blu arrotondata, posizionata nella parte destra della finestra).

Transactions between two accounts
In Income / Expense accounting, a transaction is generally recorded with one account entered in the Account column and one category entered in the Category column.
- The accounts are those listed in the Accounts table.
- The categories are those listed in the Categories column.
It is also possible to record a transaction involving multiple accounts or categories, by entering one account or category per row, until the entry is complete.
When you need to record a transaction that involves two accounts, without using a category, you can use the Category column to enter the second account from the Accounts table.
An example could be the recording of a cash withdrawal from the postal account. The transaction should be entered as shown in the example below.

- Enter the Date and Description in the respective columns
- In the Income or Expense column, enter the amount
- In the Account column, enter the first account
- In the Category column, enter the second account
Transactions between two categories
In Income / Expense accounting, a transaction is generally recorded with one account, entered in the Account column, and one category, entered in the Category column.
It is also possible to record a transaction involving multiple accounts or multiple categories, by entering one row for each account or category, until the transaction is complete.
- The accounts to be used in the trasnsactions are those listed in the Accounts table.
- The categories to be used in the transactions are those listed in the Categories table.
When it is necessary to record a transaction between two categories, it is not possible to do so on a single row. A category cannot be entered in the Account column.
Therefore, the transaction between two categories must be recorded over two rows:

- On the first row:
- Enter the Date and Description in the respective columns
- Enter the amount in the Income or Expense column
- Leave the Account column empty
- Enter the first category in the Category column
- On the second row:
- Enter the Date and Description in the respective columns
You can also copy the data from the previous row - Enter the amount in the Income or Expense column.
If necessary, you can reverse the income or expense amount compared to the previous entry. - Leave the Account column empty
- Enter the second category in the Category column
- Enter the Date and Description in the respective columns
Registrazioni con IVA
Per poter gestire i movimenti con IVA, è necessario aver scelto un modello di Entrate / Uscite con le opzioni IVA.
Si tratta di modelli che hanno già definite le impostazioni e le funzioni per gestire l'IVA già definite:
- Nella tabella Conti sono presenti i conti IVA Rendiconto e IVA dovuta.
- Nelle Proprietà file, dati base, sezione IVA (menu File) è già impostato il conto IVA Rendiconto.
- Nella tabella Codici IVA sono presenti i codici IVA secondo le normative in vigore.
Come registrare i movimenti con IVA
Nella tabella Registrazioni sono presenti delle colonne specifiche dell'IVA. Nella vista Completo puoi avere una visione completa di tutte le colonne IVA.

Come dall'immagine presentata, per registrare dei movimenti con IVA devi inserire i dati nelle corrispondenti colonne:
- La Data del documento che registri.
- Il numero di Doc relativo al documento che registri.
- La Descrizione per identificare la registrazione in entrata o in uscita.
- L'importo in Entrata
- L'importo in Uscita.
- Il Conto patrimoniale (cassa, banca, posta, clienti, fornitori..).
- Se è un'entrata, sul conto l'importo verrà registrato in positivo.
- Se è un'uscita, sul conto l'importo verrà registrato in negativo.
- La Categoria di spesa o di entrata, oppure un conto presente nella tabella Conti. La categoria rappresenta il motivo per cui hai avuto un'entrata (es. Vendita) o un'uscita (es. spese affitto).
- Se è un'entrata, l'importo viene registrato in positivo.
- Se è un'uscita, l'importo viene registrato in negativo.
- Inserimento di un conto nella colonna Categorie:
Serve per registrare importi da un conto patrimoniale ad un altro (es. prelevamenti, versamenti, ...).- Se è un'entrata, l'importo viene registrato in negativo.
- Se è un'uscita, l'importo viene registrato in positivo.
- Nella colonna Codice IVA inserisci il codice relativo al movimento:
- Per una registrazione di vendita, inserisci il codice V81
- Per una registrazione di acquisto, legato all'attività principale della tua azienda, inserisci il codice M81
- Per una registrazione di acquisto, legato a investimenti o costi generali, inserisci il codice I81.
Automatizza l'inserimento del codice IVA
Nella tabella Registrazioni, quando registri un movimento con IVA, puoi automatizzare l'inserimento del codice IVA
Per registrare automaticamente il codice IVA devi proseguire con la seguente impostazione:
- Nella tabella Conti e Categorie visualizza la colonna Cod.IVA, dal menu > Dati > Disponi colonne > attiva Cod.IVA.
- Nella colonna Cod. IVA di tutti i conti e le categorie legati a delle operazioni con IVA, inserisci il codice
- Sui conti legati ad acquisti di beni patrimoniali inserisci I81.
- Sulle categorie di Vendita, inserisci V81
- Sulle categorie di acquisto inserisci M81 o I81.
Nella tabella Registrazioni, ogni volta che inserisci un conto o una categoria che hanno un codice IVA associato, il programma inserisce in automatico il codice IVA e tutti i dati relativi all'IVA.
Record credit card transactions
Credit card purchases are becoming increasingly common, not only in businesses but also in households. In order to have a better control of the expenses for credit card purchases, it is necessary to record the movements in your accounting. In this regard, it is necessary to verify that the Accounts table contains the credit card account, otherwise it should be added.
Record credit card transactions with advance payments
The credit card account is a debit account and is entered in the Account column.

In Income/Expense accounting, whenever advance payments are made on the credit card, you must record as follows:
- Enter the date, the description
- In the Expenses column, enter the expense amount
- In the Account column, enter the liquidity account (bank, post office).
- In the Category column, enter the credit card account.
When the credit card invoice arrives and the expenses are covered by the advance payments, it is necessary to record the credit card transactions to identify the costs incurred and write off the credit.
In this case you record on multiple rows:
- Enter the same date and the same Document No. for each transaction for all the rows that make up for the transaction.
- Enter the description indicating the type of expense.
- In the Expenses column enter the total amount paid by the credit card.
- In the Account column enter the credit card account.
- In the next rows to record each expense paid by credit card, record in the Expenses column the amount of the expense, and in the Category column, the category of the expense.
After all transactions have been recorded, check your credit card balance (open your credit card account card).
Registrazione sul conto privato
Il conto privato è un conto finanziario, utilizzato nella contabilità per registrare quelle transazioni che non riguardano direttamente l'azienda, ma movimenti relativi alla sfera privata del titolare. Questo conto tiene traccia dei prelievi e degli apporti del titolare a scopi privati; pertanto serve per tenere separate le finanze aziendali da quelle personali, evitando confusione nella contabilità aziendale.
Prelievi dall'azienda del privato
Se il titolare utilizza fondi aziendali per spese personali, l'importo viene addebitato sul conto privato. Gli importi prelevati dal privato figurano nella tabella Conti, nella colonna delle Entrate del conto Privato perché si riferiscono ad un credito dell'azienda nei confronti del titolare. Nella colonna Saldo del conto privato, l'importo è positivo.
Versamenti nell'azienda del privato
Se il titolare effettua dei versamenti di fondi privati su conti aziendali, l'importo viene accreditato sul conto privato. Gli importi versati dal privato figurano nella tabella Conti, nella colonna delle Uscite del conto Privato, perché si riferiscono ad un debito dell'azienda nei confronti del titolare. Nella colonna Saldo del conto privato, l'importo è negativo.
Saldo del Conto Privato/socio
- Saldo positivo: indica che il titolare ha un debito verso l'azienda.
- Saldo negativo: indica che il titolare ha un credito verso l'azienda.
Credit card December invoice paid the following year
The December credit card invoice is usually received in January of the following year, and consequently, the payment is also made in January.
All expenses listed in the December credit card invoice belong to the previous year; therefore, they must be recorded in the accounting of the previous year.
Recording the December Credit Card Invoice
To record it correctly, it is necessary to have the liability account Costs to be Paid in the Accounts table, which is a transitional account. If it is not present, it must be added.
In the Transactions table, enter:
- Date and any document number in the respective Date and Doc. columns.
- Description
- Total credit card amount in the Expenses column
- Costs to be Paid account in the Account column
- Expense category in the Category column. If the invoice includes multiple expenses, record each expense on a separate row.
Recording the payment of the December credit card invoice in the following year
In the following year, when the new year is created, the balance of the Costs to be Paid account is displayed as an opening balance in the Accounts table.
When the credit card invoice is paid, the Costs to be Paid account is cleared.
To record the payment of the credit card invoice, enter:
- Date, any document number
- Description
- Total amount of the credit card invoice in the Expenses column
- Liquidity account from which the invoice is paid in the Account column
- The Costs to be Paid category in the Category column.
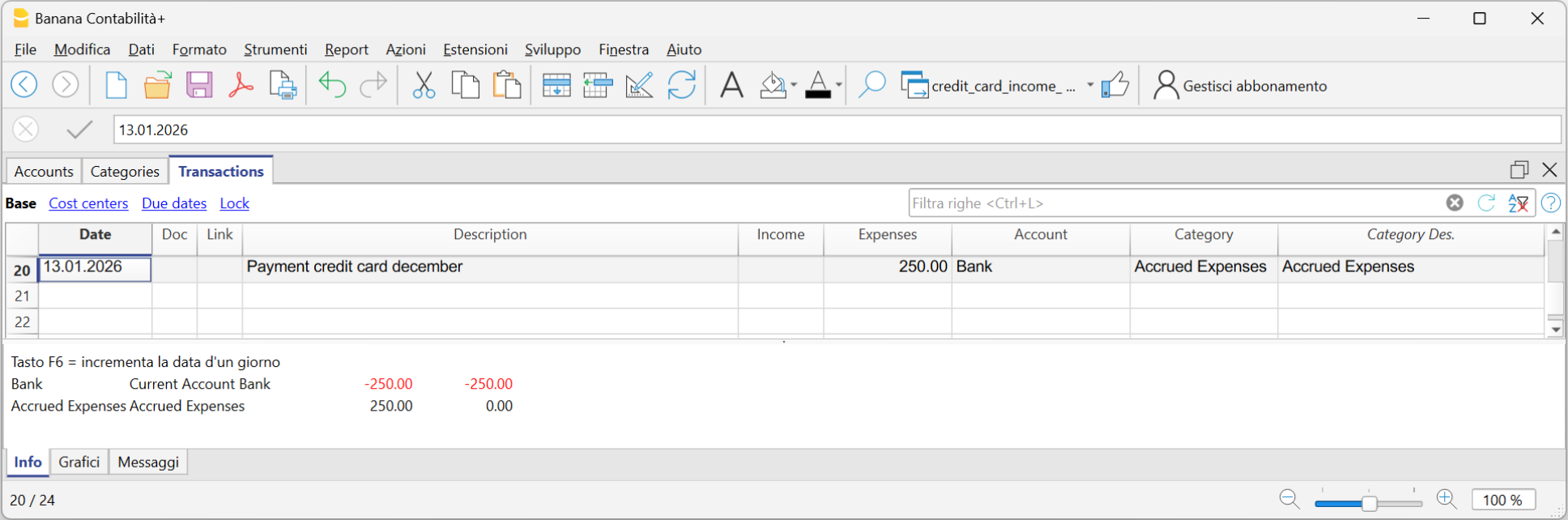
Velocizzare le Registrazioni
Velocizza le Registrazioni
Per velocizzare l'inserimento delle registrazioni puoi utilizzare diverse funzioni:
- Immissione dati con autocompletamento - appena digiti la descrizione, nella finestra in basso appaiono le registrazioni già immesse con la stessa descrizione; premendo il tasto F6, hai la ripresa della registrazione, basta cambiare l'importo, se questo è diverso dalla registrazione precedente.
- Registrazioni ricorrenti - puoi memorizzare le registrazioni che si ripetono durante l'anno (es. affitti, abbonamenti, ecc) nella tabella Registrazioni ricorrenti e riprenderli all'occorrenza nella tabella Registrazioni, digitando semplicemente un ID identificativo nella colonna Doc, con cui sono stati memorizzati.
- Importazione dei movimenti bancari - scarica il file fornito dalla tua banca e importa i movimenti direttamente nella tabella Registrazioni. Hai tutti i movimenti con data, descrizione, conto e importo, devi solo inserire la categoria di spesa o di entrata.
- Impostazione di Regole per l'importazione automatica - imposta le Regole ad ogni movimento che importi e in un batter d'occhio hai la contabilità completa, senza inserimenti manuali di contropartita, codice IVA e centri di costo; avrai più tempo da dedicare all'attività produttiva della tua azienda.
Budget transactions
The budget in the Income / Expenses accounting can be set in two different ways:
- Budget Column
- Budget Table set via the Tools menu > Add/Remove functionalities
Budget Column
In the Budget column, in the Budget view, the amounts are entered on an annual basis. If the Budget column is used, the Budget table should not be used.
Budget Table
Financial planning is performed in the Budget table.
Forecasts are entered as if they were normal transactions, as in the Transactions table.
Quantity and Prices can also be entered as well as Calculation Formulas.
For further information on the budget refer to Budget table.
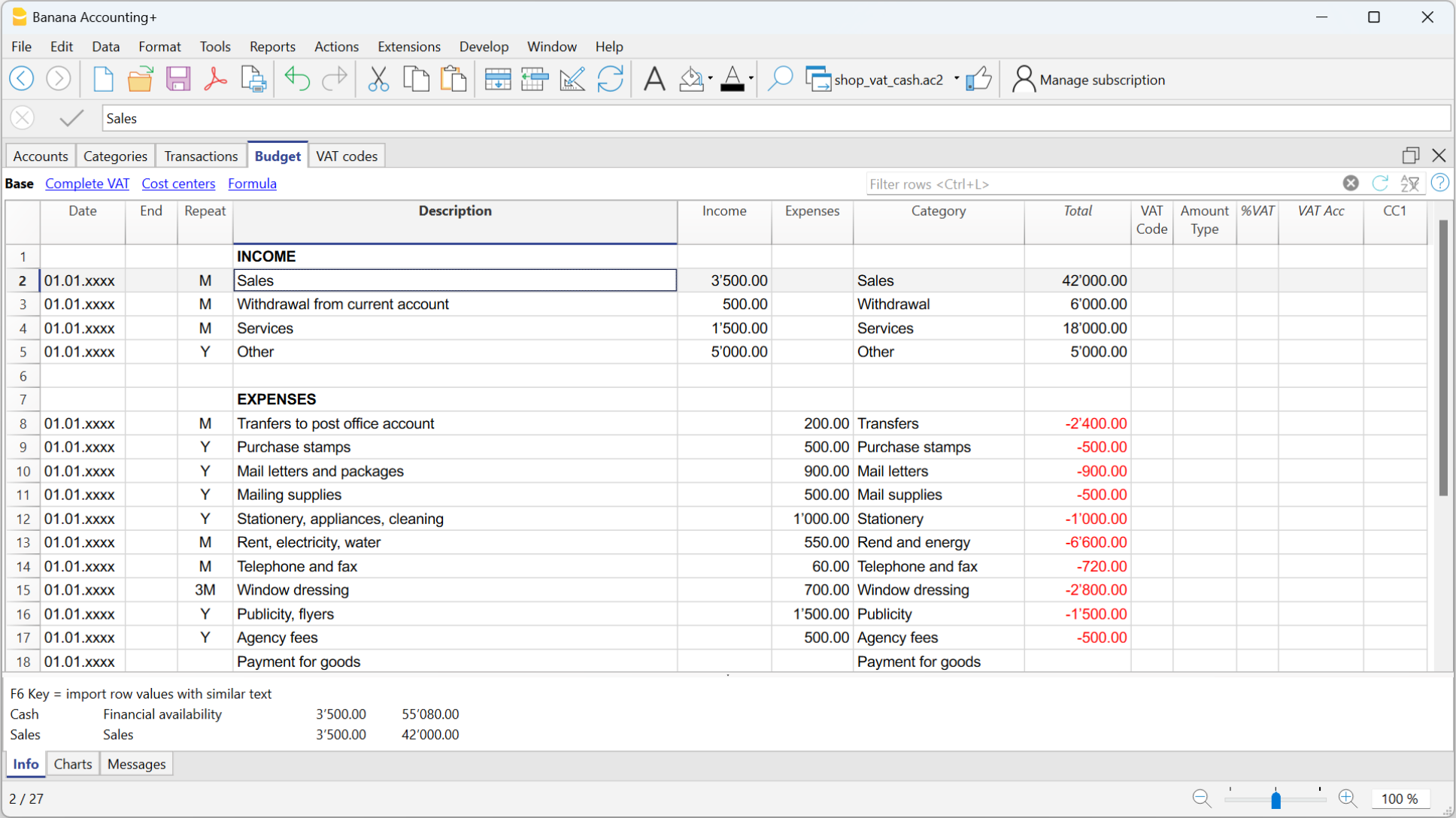
Printouts
Instant information
Account balances, income and expense are on ready display in the Accounts and Category tables.
After each entry of a transaction, balances are adjusted automatically and there is no need to run a report to to have the situation under control, as you can simply display the Accounts or Categories tables.
To print the content of the tables, please refer to the Page setup section (last paragraph).
Advanced printouts
All printing is run from the Reports menu, where the different functions for printing are located:
- Journal by period command. You can display and print the whole table or just a specified period.
- Account/Category or group cards command. You may select all cards or define your selection.
Define the required period in the Period tab and click the required print settings in the Options tab. Print settings can be saved in the Customization tab so they can be resumed without them to be having defined again. - Enhanced statement command. You may also print a defined period and various options and customizations may be included.
- Enhanced statement with groups command. You may also print a defined period and various options and customizations may be included.
- Accounting Report command. The report with the required options are displayed in the Accounts table. Reports by period are possible, also with the comparison of previous periods or years; each period may contain subdivisions and the customization can be saved.
Account/Categories card - Income / Expenses
The account or category card corresponds to the ledger and allows you to have a complete list of the accounting entries concerning the same account, the same category, a cost center, a segment or a group.
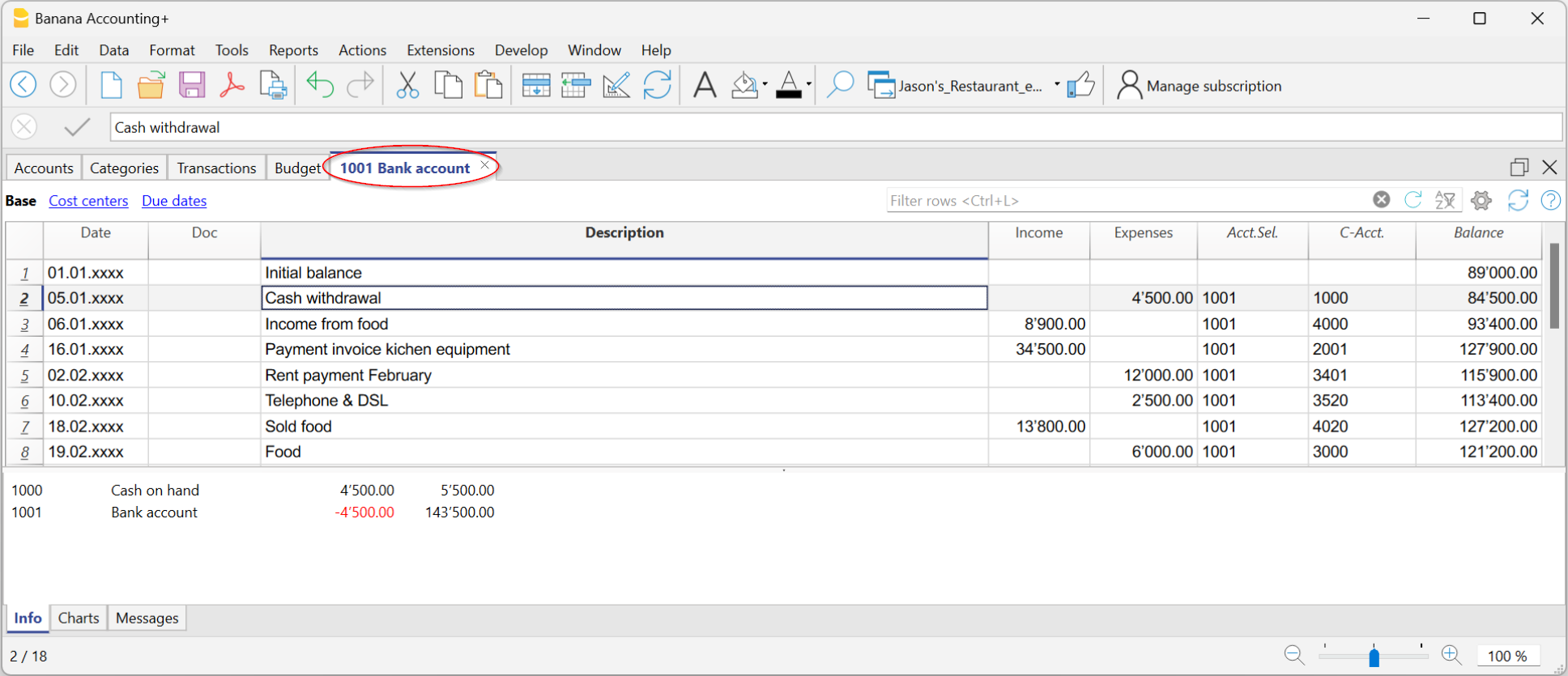
Open the account card
There are two ways to open and print an account or category card.
First method
This method is recommended when you want to view and print all or several account / category cards.
- Click Report > Account/Category Cards from the menu

A dialog box appears with the following sections:
For detailed information on the sections, click on the corresponding links.
Second method
This method can be used when you need to open only one card at a time within the tables.
- Click on the small icon that appears when you select the cell that contains the account, category or group number.

Update the account card
The account or category card is temporary and is calculated at the time of the request. If transactions are changed or added in the Transactions table, the account card is not updated simultaneously.
To update the account card, following changes, it is necessary to use the Account/Category card command again, or if the account card is still open, click on the symbol shown in the image below.
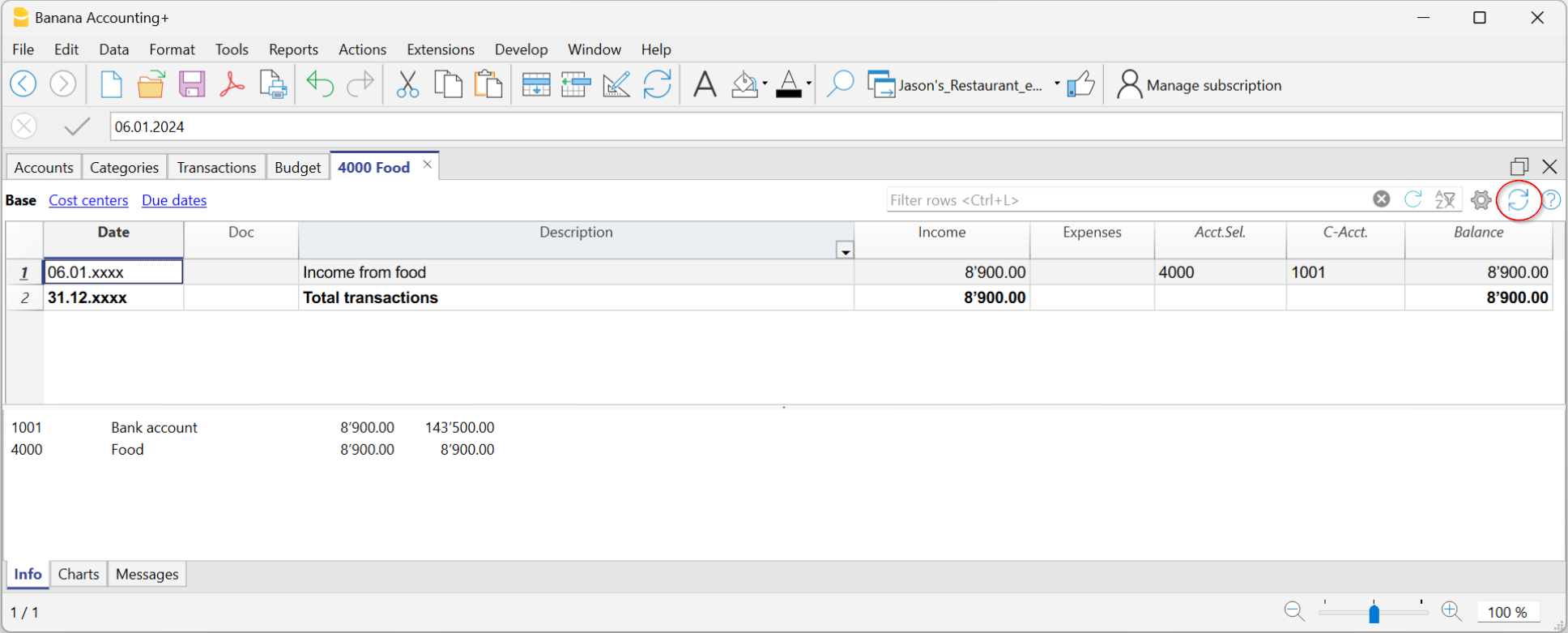
Note
In the account, category or group card it is not possible to change the data. Within the account card, by double clicking on the row number, the program switches to the corresponding row of the Transactions table or of the Budget.
The Selected Account column
In the Selected Account column, which can be made visible, starting from any account card, via Data > Columns setup, the account on which the transaction took place is displayed.
When you get an account card of one or more accounts, categories, groups and segments, you see exactly which account is used.
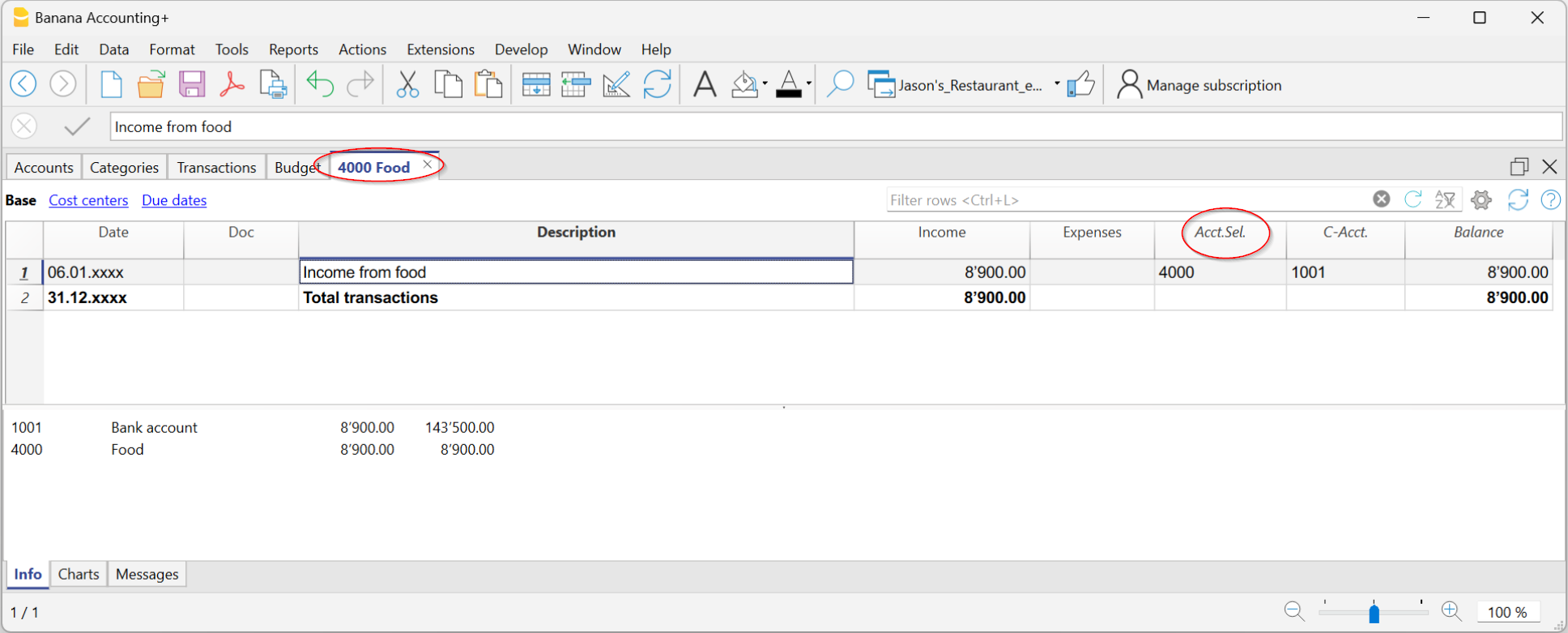
The Counterpart Column
The C-Acct. column is displayed on the account or category card, indicating the offset account that completes the posting.

Cards of groups or classes
In the account tab of a group or class, all the transactions of those accounts belonging to the selected group or class are regrouped.
The accounts or categories of the group or class can be viewed by making the Selected Account column visible with Columns setup via the Data menu.

Print the ledger (account cards)
To print an account card:
- display the card from any table (Accounts or Transactions) and launch the printout from the File menu.
To print multiple account cards:
- Report menu > Account cards
- Using the Filter it is possible to automatically select all the account cards to be printed or partially (eg only accounts, cost centers or segments).
- In the various sections Period, Options, Customization desired functions are activated (eg period, one account per page ....).
- Confirm with OK, after setting the desired options.
- The selected account cards will appear on the screen. To print, click on the File > Print menu.
Print Account Cards by Period
To view account cards with balances for a specific period:
- Report menu > Account cards
- in the Period section activate Specified, and enter the start and end date of the period.
See the Period section page for more information.
Print the Budget account card
If the budget transactions have been entered in the Budget table, it is possible to have the account or group cards of the budget:
- Reports menu > Account / Category cards > activate Budget transactions.

Accounts and Categories settings in the Enhanced statement with groups
In the dialogue box, you can set how to print accounts and categories

Insert a logo in the account cards
As from Banana 9, it is possible to insert a logo also in the printing of the account cards.
After creating the account card detail, proceed as follows:
- Reports menu > Account cards
- File menu > Print preview.
- In the dialog box that opens, under Logo, indicate your logo (instead of none).
More detailed information is available on the Logo setup.
Save the setups
If you happen to regularly print the cards of certain accounts, for example all those of sales, it is useful to create a special customization:
- Report menu > Account cards > Customization section
- Click on the New button
- Indicate the name in the description, for example "Sales Accounts"
- Select the accounts you want to print
- From the File > Page setup menu you can determine the margins and other page settings.
Whenever you need to print the accounts, select the customization you created.
Journal - Income / Expense accounting
The entries in the Income / Expense application, as in all Banana Accounting applications, are inserted in the Transactions table. If you want to print the Journal (list of all transactions), you can proceed in two different ways:
- From the Transactions table:
- select from the File menu → Page Setup (in order to set up all the print options)
- return to the File menu → Print.
- From the menu Reports → Journal by period.
Journal per period
Banana Accounting, via the menu Reports → Journal by period, offers the possibility to print the Journal with the movements of the entire period or of the period selected by entering the start and end date of the period.

The information on the Period section is identical to that of the Period section of the common functions.

In the Column for sorting section, you can choose the base on which type of date to sort and print the journal.
Enhanced Statement (Balance sheet and profit & loss statement)
In the Income/Expense accounting, the Balance Sheet and Income Statement are represented by the Enhanced Statement and Enhanced Statement with Groups. This terminology is used because they have a much simpler and different structure compared to the classic balance sheet and income statement in double-entry accounting.
The Enhanced Statement provides a summary of the financial and economic situation for the fiscal year.
- The Enhanced Statement is calculated and displayed from the Report menu > Enhanced Statement command.
- The embellished report displayed in preview, can be saved in PDF, HTML, MS Excel and Copy to clipboard format.
- It is possible to calculate, view and print the report at the end of the year, or for a specific period.
See also Print Example.

Page header
Rows 1-4
These rows allow the definition of the Statement's headers.
Logo
It is possible to insert the logo in the header of all pages of the report.
If one or more logos have been added in the menu File→ Logo setup, you can select one from the list.
If no logo has been added, the Edit button can be used to add the logo.
Column header
Initial date
Insert the initial date of the current accounting.
Final date
Insert the final date of the accounting.
Previous year
Insert the final date of the previous year's accounting.
Cover page
Cover page
Activating this function prints the cover page.
Logo
You can insert the logo on the cover page of the report.
If you have added one or more logos in the menu File→ Logo setup, you can select one from the list. If no logo has been added, the Edit button can be used to add the logo.
Print pages
Checking the boxes defines the options to be printed in the report:
Accounts
The accounts will be printed.
Initial page
The initial page of the document with the file headers will be printed.
Categories
The categories will be printed.
End of page after accounts
The accounts and the categories will be printed on two different pages..
Include in printout
By selecting the boxes, you choose the options that must appear in the printout.
Some of these options are not available (e.g. Budget balances) if a specific period is selected in the Period section.
Other Tabs
The explanations for the other tabs are available at the following pages:

Enhanced statement with groups ( Balance sheet and profit and loss statements)
This feature allows the user to obtain the Enhanced statement with groups, with all the options that are available in the Double-entry accounting.
The Enhanced statement with groups (Reports menu) makes it possible to:
- Include all the groups that are present in the Accounts and Categories tables in the printout,
- Exclude groups or accounts individually
- Select a subdivision by period
(for example, in the first semester, one can select to have a subdivision by month or per quarter) - Select a subdivision by segment.

Accounting report
The Accounting Report displays the Accounts or Categories table based on the options selected in the dialog. The columns present the amounts of accounts and categories divided and grouped by:
- Period - With a start and end date or covering the entire period.
- Breakdown - The specified period is divided into months, quarters, semesters, or years.
- This command displays the amounts of accounts according to a certain grouping, for a specified period or per subdivision.
Transactions without date are being considered as opening transactions and will not appear in the printouts of the Profit & Loss Statement.

Display
You select the desired grouping scheme:
- Accounts - the Report will show a list of all accounts with the following columns: opening balance, income, expenses and account balance
- Categories - the Report will show a list of all categories with the following columns: opening balance, income, expenses and account balance.
Options
You select the accounts to be included or excluded:
- Exclude accounts - only the categories will be printed
- Include accounts with no transactions - accounts with no transactions will be printed as well
- Include accounts with 0 balance - accounts with zero balance will be printed as well
- Exclude groups without accounts - groups of accounts with zero balance will not be printed.
Other Sections
The explanations for the other tabs are available at the following pages:
Note: To print the balance sheet and income statement, refer to the pages:
VAT Report (for files with VAT option only)

Information on the VAT Report is available on the VAT report page.
Year end closures
Closures in accounting refer to all the control operations, adjustments, and temporal delimitations carried out at the end of the year before preparing the financial statements.
Technical aspects and new year
With Banana Accounting, each fiscal year has its own separate file. Technically, there is no concept of an accounting closure:
- When a new year begins, a new file is created using the Create New Year command
- You can continue working simultaneously on both the new year's file and the previous year's file. Once the closure operations are completed, the updated balances are carried over to the new year's file using the Update Opening Balances command.
Use the Filter for quick verifications and corrections
To perform checks quickly, especially at the end of the year, we recommend using the Filter function. This feature allows you to filter all transactions based on a word, phrase, account, or a set of elements. The advantage of this function is that you can correct or modify transactions directly on the rows displayed by the filter, without having to scroll through the entire Transactions table to find matching entries.
For more details, please refer to the page:
- Filter Rows (available only with the Advanced plan).
Accounting check command
Banana Accounting allows you to record transactions quickly and even leave operations pending without interrupting your workflow.
The Actions > Check Accounting command performs a series of verifications, similar to re-entering the data from scratch. When errors or discrepancies are detected, they are flagged for your attention.
It is recommended to use the Check Accounting command regularly and whenever there are discrepancies or error notifications, significant changes (such as initial exchange rates, VAT codes), and especially before closing the accounts.
Verification of accounting balance correspondence
The first verification is undoubtedly to ensure that the accounting balance of the accounts matches reality. The cash account balance must correspond with the actual cash status. The balances of bank accounts, credit cards, loans, or assets must match those of the bank statements. The same applies to all other accounts that have provisions, VAT, suppliers, etc.
If there is a discrepancy, you need to identify the reason and complete either the initial balance or the transactions.
Differences in the transactions table
In the Transactions table (Info window at the bottom), ensure that no discrepancies are reported. In addition to the functions available in the Check Accounting command, Banana Accounting Plus includes the Balance column in the Transactions table, which allows you to identify all rows where discrepancies occur. A quick scroll through the column is sufficient to immediately spot accounting differences and correct them, preventing errors from being carried over to the new year.
Differences between bank statement balances and accounting balances (CheckBalance function)
This check is essential for the accuracy of your accounting records. We recommend performing the balance verification, #CheckBalance, not only at the end of the fiscal year but also periodically at the end of each month. This helps prevent any mismatched balances from being incorrectly carried over from month to month.
Information on balance verification transactions is available on the Balance Verification transactions page.
Once the verification entries have been performed, it is recommended to lock the transactions.
- Actions > Lock transactions
The transactions rows will be numbered and will have a blockchain code to ensure their security.
The Create PDF Dossier command allows you to compile all the documents of the entire fiscal year (account statements, journal, VAT reports, monthly, quarterly, and annual reports, etc.) into a single PDF file.
You can archive your accounting data by saving the accounting file and prints in PDF format. Additionally, consider making backup copies on an external hard drive.
Registrazioni di chiusura
Aspetti contabili
A fine esercizio, prima di passare al nuovo anno, ci sono delle operazioni contabili di chiusura da eseguire. Si tratta di registrazioni di assestamento, rettifiche di valore e conguagli relativi ai contributi del personale. Qui di seguito ricordiamo le principali:
Importare i movimenti degli stipendi nel file della contabilità
Questa operazione è prevista solo nel caso in cui gli stipendi vengano gestiti con un gestionale specifico che permette di importare i movimenti nel file di Banana Contabilità Plus.
L'importazione si esegue dal menu Azioni > Importa in contabilità > Importa movimenti con intestazione colonne.
Ricordarsi di inserire la registrazione della quota tredicesima di dicembre, se questa non viene creata dal gestionale stipendi.
Assestamento conto Delcredere
Le aziende che registrano sul fatturato, se prevedono delle perdite presunte, devono assestare il conto Delcredere.
Ammortamenti
Al 31.12 bisogna rilevare il deprezzamento dei beni mobili e immobili e valutare eventuale l'ammortamento accelerato per quei beni soggetti a una rapida obsolescenza.
Puoi utilizzare il nostro applicativo Registro beni ammortizzabili che crea in automatico le registrazioni di ammortamento e puoi riprenderli nel file della contabilità.
Assestamento magazzino
L'applicativo Magazzino permette di avere dei conteggi precisi sia per pezzi sia per valore, aiutandoti a determinare più velocemente l'assestamento del tuo magazzino.
Rilevare le fatture dei clienti e dei fornitori aperti al 31.12
Per facilitare la procedura, con la funzione delle fatture aperte per cliente e fatture aperte per fornitore puoi rapidamente rilevare i valori al 31.12.
Consumo proprio
Se nell'azienda vi è l'uso di un'auto aziendale, registrare il consumo proprio con il codice IVA appropriato.
Chiusure e dichiarazione IVA
Prima di inoltrare la dichiarazione IVA, consigliamo di utilizzare il comando Controlla Contabilità.
- Verificare che il conto IVA in automatico dopo aver stornato il saldo nel conto IVA dovuta (IVA da pagare all'AFC) sia a zero. Nel conto IVA dovuta deve risultare l'importo da versare o l'importo a credito da ricevere.
- Prima di inoltrare l'ultima dichiarazione IVA, visualizzare nuovamente i rendiconti IVA degli altri trimestri per controllare che gli importi versati all'AFC siano ancora corrispondenti a quelli visualizzati.
- Utilizzare il comando del Riassunto IVA per visualizzare i vari report e creare una stampa in PDF per l'archiviazione dei dati. In caso di controlli fiscali saranno utili.
Assestare il conto Imposte alla fonte
Nel caso nell'azienda ci siano dei dipendenti soggetti alle imposte alla fonte, dopo aver conteggiato e registrato gli stipendi di dicembre, in base al conteggio inviato all'Ufficio imposte alla Fonte, registrare l'assestamento.
Rimborsi per quadri superiori
Se previsti, nello stipendio di dicembre includere l'importo previsto dalle autorità fiscali come rimborso forfettario.
Assestamento conto Privato
Verificare il saldo del conto privato. In caso di rapporti di debito/credito fra l’azienda e il/i proprietario/i (o persone vicine) registrare gli interessi attivi o passivi secondo quanto previsto dal contratto di prestito o secondo le direttive fiscali vigenti.
Assestamento conto Imposte e tasse
Verificare che gli acconti pagati durante l'anno si riferiscano all'anno in corso. I pagamenti di imposte che concernono anni precedenti, bisogna registrarli a chiusura dei relativi accantonamenti che risultano nel conto “Imposte dirette” (patrimoniale). Se il saldo degli accantonamenti non è sufficiente o è eccessivo, la differenza deve essere registrata come costo/ricavo straordinario o relativo a periodi precedenti.
Registrazione conguagli AVS/AD/IPG/AD
- Durante l'anno, nel conto dei contributi AVS, solitamente vengono registrati gli acconti pagati alla Cassa Cantonale di Compensazione AVS (in Dare) e le quote trattenute sugli stipendi ai dipendenti (Avere).
- Se durante l’anno gli assegni familiari pagati ai dipendenti sono stati registrati in un conto dedicato, per esempio nel conto “Contributi assegni familiari”, per riconciliare la contabilità con il conteggio di chiusura AVS e registrare il relativo assestamento si può girare il saldo di questo conto sul conto Contributi AVS/AD.
Registrare i conguagli previdenziali Lainf, Lainf complementare, LPP
Con la registrazione degli ultimi stipendi di dicembre e il pagamento delle tredicesime, occorre stampare la lista degli stipendi con l'indicazione di tutti gli stipendi lordi. Il lordo complessivo AVS devi comunicarlo alle assicurazioni del personale, che determineranno eventuali conguagli da pagare.
Inviare il file al commercialista per le chiusure
Se le chiusure e/o le verifiche vengono eseguite dal tuo fiduciario, basta inviare il file della tua contabilità creato con Banana Contabilità Plus per email oppure salvare i dati su una chiavetta USB.
- Se il tuo fiduciario ha Banana Contabilità, basta trasmettere il file ac2 per email o tramite chiavetta usb. Puoi anche salvare il tuo file e i documenti digitali in una cartella condivisa con il tuo fiduciario su Dropbox. Non dovrai più portare dal fiduciario pesanti classeurs per la documentazione cartacea. Inoltre, il fiduciario lavorerà velocemente senza dover andare a cercare nella documentazione cartacea.
- Se non possiede Banana Contabilità puoi creare un PDF dei dati contabili, tramite il menu File > Crea dossier PDF e trasmettere per email la documentazione. Il fiduciario ti indicherà tutte le modifiche e aggiunte da registrare per chiudere correttamente l'esercizio contabile.
In alternativa, il tuo fiduciario può aprire il file della tua contabilità usando il piano Free di Banana Contabilità Plus, scaricandolo dalla nostra pagina di Download. Se il tuo file ha più di 70 registrazioni non potrà aggiungere registrazioni o fare modifiche, ma potrà comunque vedere tutti i dati, ottenere il dettaglio di ogni conto con un semplice click sopra il numero di conto, ecc. e consigliarti su possibili correzioni o miglioramenti.
Create a new year | Income and expense Accounting
The Create New Year command prepares a file for the new year based on the accounting file that is being closed. The command does not modify the current file, so it can be executed without any effect.
Logics of the transition to the New Year
With Banana Accounting you have a separate file for each year. When the new year starts, the operational logic is as follows:
- With the Actions > Create New Year command, the Program creates a new file for the year, using the same chart of accounts, settings and balances of the current year that is about to close.
- Once the new year file is created, save it with a new name.
- The operation of creating the new file can be repeated if you decide not to save the file.
- You can work on both files at the same time:
- In the new one, the transactions of the new year will be entered. It will also be possible to make changes to the chart of accounts, VAT or other, without affecting the previous one.
- In the previous year's file, the operations will continue to be entered in order to complete the year and carry out the typical closing operations, verification of balances, printing of reports etc.
- In the New Year's file, with the command Actions > Update Opening Balances, the changes that were made in the previous year's file are resumed. This operation should be done at the latest when there are no more changes in the previous year.
Once the New Year's file has been created, those who have subscribed to the Professional Plan of Banana Accounting Plus, will see the message Advanced Plan in demonstration mode. This message will appear in the Info window at the bottom of the screen and it will only disappear when reaching 70 transaction rows in the Transactions table.
Checking and closing previous year's accounts
Before updating opening balances, to avoid any differences between closing and opening balances for the following year, it is important to ensure that you have performed all checks, verification operations, and all closing accounting transactions.
In Banana Accounting Plus, under the Advanced plan, the Filter function is available. This feature is particularly useful during the closing phase to quickly search for rows with the same texts or values, based on the key entered for the filter (e.g., word, account, amount, etc.). With this function, it is possible to make corrections directly on the filtered rows, without having to scroll through the entire Transactions table—especially at year-end when the number of transactions is high.
Unlike Double-entry accounting, when the Income and Expense accounting period is closed, there is no profit or loss to be allocated. The difference between the Income and Expense categories in the new accounting period is shown as an increase or decrease in the estate.
Operations performed by the Create new year command
The Create new year command performs the following operations, taking into account the parameters set by the user:
- Creates a new file (with no name) with the chart of accounts and all the settings identical to your current file, but without transactions.
- Copies the data from the Balance column of your current file to the Opening column of the new file (only for the selected classes)
- Copies, for all the accounts of the Report, the data from the Balance column of your current file to the Previous Year column of the new file.
- Updates the File and accounting Properties of the file:
- Sets the start and end dates, adding 1 year to the existing ones.
- In the Options section, sets the previous year's file name and enables the option to use the previous year's transactions for autocompletion.
- If there are data in the Budget table, it carries over the operation rows in the new year taking into account the settings.
In the Income/Expenses accounting method, there is no need to allocate the profit or loss for the year, as the total equity in the Accounts table already represents the net equity or owner's equity.
However, if this allocation is required, a specific account must be set up in the Accounts table. For more details, please refer to the section Profit or Loss Accounts from Previous Years.
Update opening balances | Income & Expense accounting
The Update Opening Balances command takes data from the previous year's file and updates the opening balances for the current year.
When do you need to use the Update Opening balances command?
The Update Opening Balances command is required in the following cases:
- You have created the New Year with the Create New Year command, but you still made changes to the previous year's file (additional transactions, new accounts, ..).
- Changes were made in the previous year (added or changed transactions, added accounts...).
Check the previous year accounting
In order to avoid differences between the previous year closing balances and the New Year and opening balances, it is important, before using the Update opening balance command, to make sure that you have carried out all the checks, verification operations and all the closing accounting entries as indicated in the Year end closure of the Double-entry accounting page.
The Update Opening balances dialog window
In order to access this dialog, use the Actions menu > Update opening balances command.
You need to enter the path to where the previous year's file is located:
- The program will suggest the name of the saved file
- If the file's name or the location path is changed you the Browse button

Operations carried out by this command
The command resumes the data from the previous year, without changing its contents. This command can therefore be repeated without any impact on the previous year's file.
The command performs the same operations as in Create New Year , except those referring to the creation of the file.
Change of the Chart of Accounts of the previous year
If after creating the New Year you add accounts to the previous year and carry over the balances, the program may indicate an error. In this case, you should:
- Enter the new accounts in the new year's file as well.
- Repeat the Update Opening balances operation
You can import changes with the Import Accounts command.
Cash Manager
The Cash Manager (or Cash Book) is an application of Banana Accounting Plus, to manage the cash or any other account. It is free and unlimited because it is included in the Free plan of Banana Accounting Plus. It is ideal for:
- Families - to keep track of expenses and income and plan a family budget.
- Children and Students - to learn how to manage their first expenses and be aware of their savings.
- Companies and Associations - to budget and manage cash income and expenditure, keep the first note and manage cash in a separate file from accounting.
Check out our resources for an easy and immediate start:
Getting Started with the Cash Manager
For a quick and easy start, choose one of our Cash Manager templates and save it as a name. For more information visit the generic page of How to get started with Banana Accounting Plus.
In the Transactions table you are immediately operational and can enter incoming and outgoing transactions. Entry is extremely easy and intuitive, even for those with no accounting knowledge.

The Transactions Table
The Transactions table is at the heart of the Cash Manager's bookkeeping.
It allows you:
- Clarity and order of the columns: thanks to the table layout you always have an immediate and complete overview of the data entered.
There are main columns, already predefined, in which you can enter:- The date of the transaction
- Any document number
- The incoming or outgoing amount
- The category for the entry or exit
- To insert digital attachments: in the Transactions table, you can also make the DocLink column visible, which allows you to add the receipt or invoice to each movement in PDF format, ensuring the immediate availability of the documents in case of future audits or to transmit them to the accountant.
- To always make corrections: if there are errors, you can easily correct them, ensuring correct and accurate results every time.
Speeding up the transaction registration
Banana Accounting Plus offers several functions to speed up the data entry process, such as:
- Auto-completion. In the Description column, by typing the first few characters, the programme automatically suggests similar movements that have already been entered previously and, by pressing F6, completes the current movement with the selected data.
- Recurring Transactions. It is possible to store recurring transactions in a special table, taken from the menu Actions > Recurring Transactions, and to resume them with a single click, saving time and simplifying work.
Reports and Printouts
After each transaction, the programme automatically updates all account balances in the Category table and in the account. You can easily print statements and reports for easy monitoring of income and expenditure and the status of available cash in the cash account.
Professional and accurate reports at the touch of a button:
From the menu Reports > Enhanced statement or Enhanced statement with groups, get your reports in no time. Reports by period are also possible.
- The Enhanced statement displays all accounts and categories without any subgroups.
- The Enhanced statement with groups displays all accounts and categories also with subgroups.
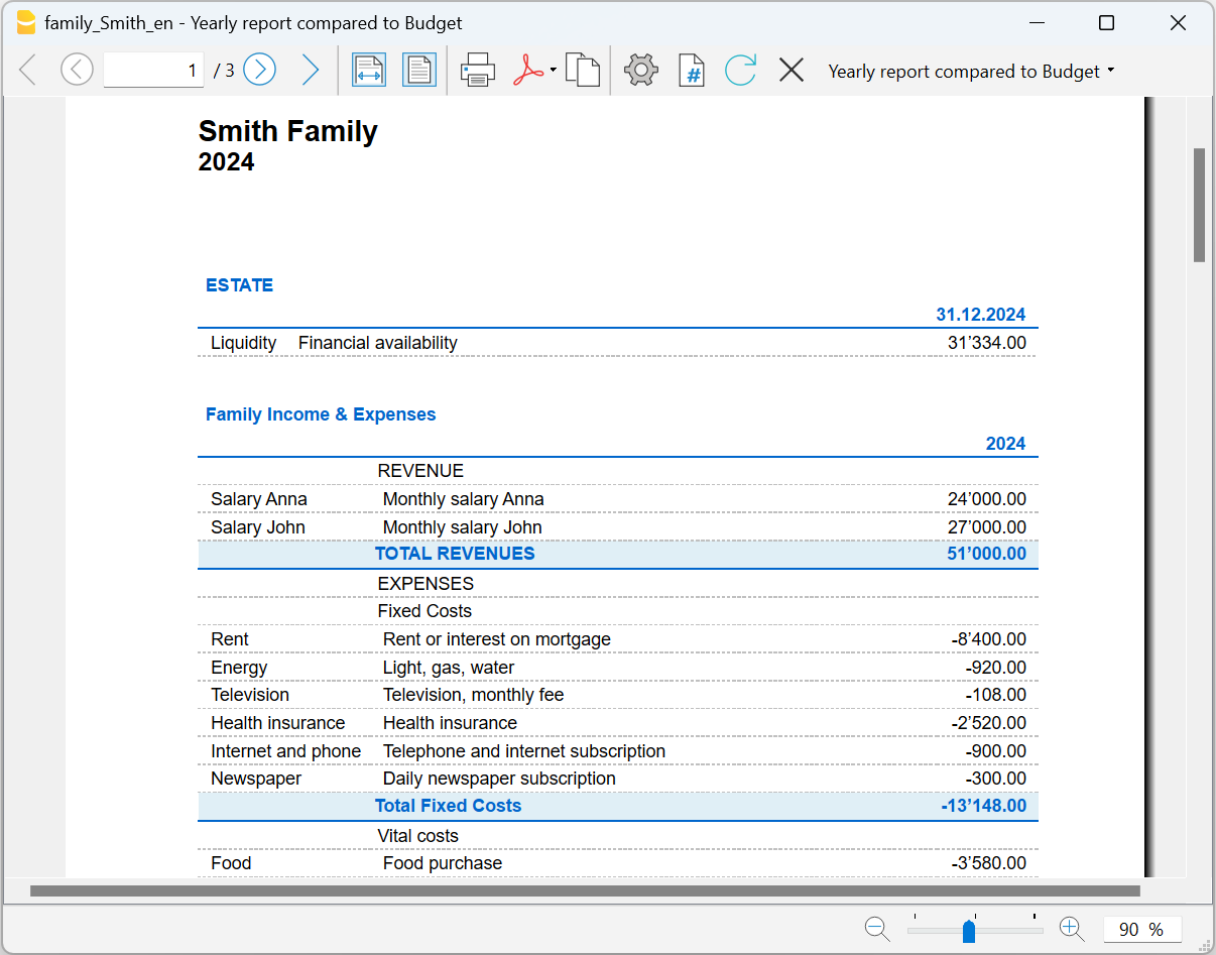
PDF data archiving
All accounting data, over a period of years, must be available at all times, both for tax purposes and for any internal requirements.
Simple and comprehensive archiving. From the menu File > Create Pdf dossier, you can easily archive all accounting data in a single PDF document. This allows you to store the entire accounting for the year in an orderly and complete manner, making it easier to access and consult the data in the future.
Topics common to other applications
- Add, cancel an account
- Rename an account
- Insert groups
- Cost and profit centers
- Segments
- The Balance column
Printouts
How to Start a Cash Manager
▶ Video: How to start a Cash Manager (Cash book) file. Learn how to enter and monitor the movements of your money of your cash account.
Creating an accounting file, starting from a template
Here is how to start choosing a template directly from the program:
- File menu → New command
- Select the Region, the category and the accounting type (with or without VAT).
- From the list of the templates that appears, select the template that is closest to your own needs.
- Click on the Create button.
You can search for a template by entering a keyword in the Search box; the program displays the templates containing the keyword entered.
It is equally possible to start from a blank file, by activating the Create blank file option. In any case, in order to facilitate the start and avoid grouping errors, we recommend that you always start from an existing template

Further information is available on the Create New File page.
Setting up the File properties
Set up your own data from the File and Accounting properties command and save with your own file name.
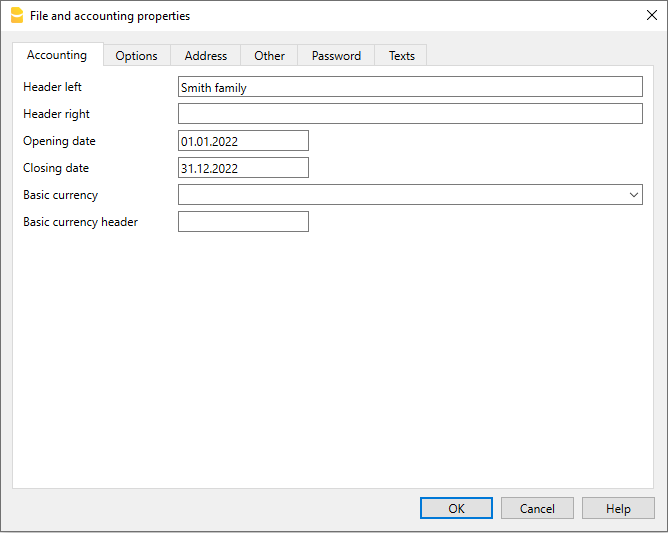
Save to disk
Via the File→ Save As command, save the data and also assign a name to the file. The typical save dialog of your operating system is displayed.
- It is advisable to use the name of the company followed by the year "Company-20xx.ac2" to distinguish it from other accounting files.
- You can keep as many accounting files as you need and each one will have its own name.
- You can choose the path or support you want (save on drive, USB or cloud).
If you also expect to have documents linked to the current year's accounts, it is suggested that you create a separate directory for each accounting year where all the files are to be grouped. Please also visit the Organizing your files page.
Entering the opening balance of the account
Enter the account you wish to manage in the Accounts table of the Cash Manager and the initial amount in the Opening column. At the start of a new year, using the menu Actions → Create New Year ... command will automatically generate the opening balances to be carried over.
Only one account can be entered: if you need to manage more than one you need to use the Income / Expenses accounting.
Customising the Categories table
In the Categories table, customize the income and expense categories, according to your own needs. It is possible to:
- Change the category numbers
- Change the description
- Add or delete categories
- Add or delete subgroups
All balances of the categories will determine the result of the accounting year (profit or loss) and must therefore not contain any balances at the start of the year.
Add new categories
If new categories need to be added in an already existing group, proceed as follows:
- Add an empty row (Edit menu → Add rows ) before the Total of the Group
- Enter the category number or code in the Category column
- Enter the category description
- In the Sum in column add the same grouping code or number as the other categories belonging to the Group Total
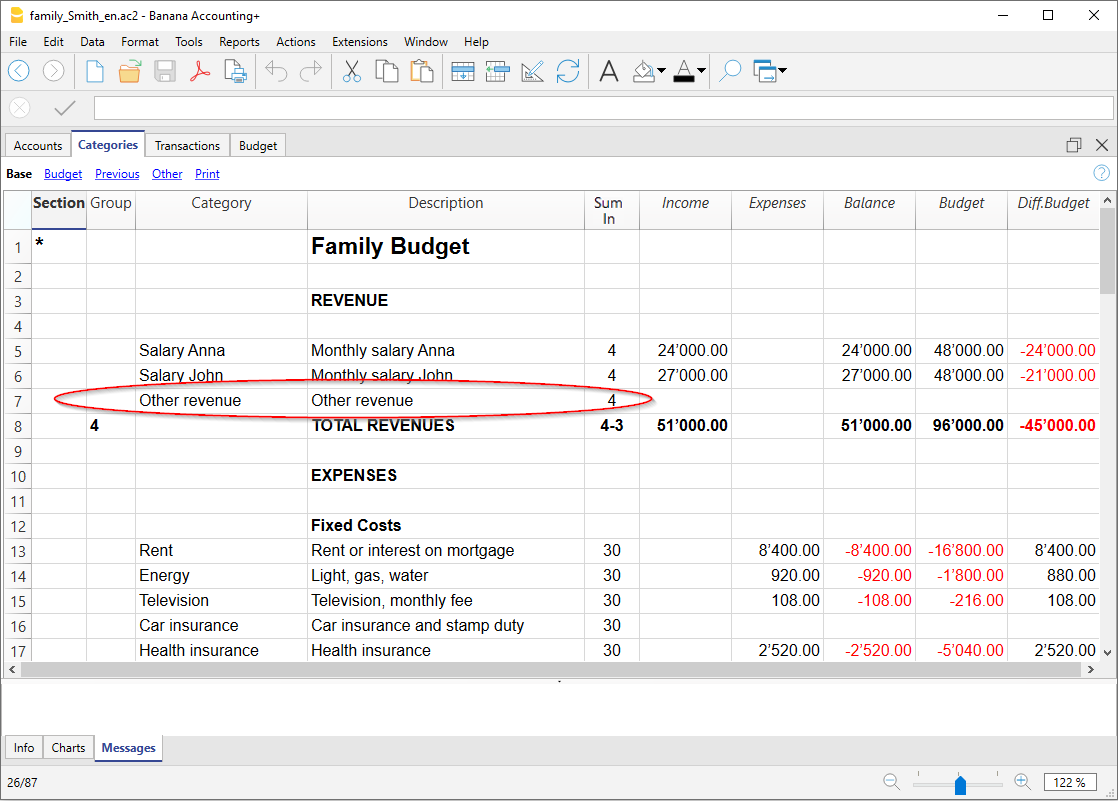
Add subgroups
To add new subgroups, proceed as follows:
- Add an empty row (Edit menu → Add rows ... command) where you wish to add a new subgroup
- In the last empty row, in the Group column, enter a number or code for the totalisation group (in our example 31 - Other income)
- Enter the description that identifies the new subgroup
- In the Sum in column, enter the totalisation group (in our example 3 - Total sales).
Delete categories or subgroups
Select the categories or subgroups you wish to delete and proceed with in the Edit menu → Delete rows ... command.
Transactions
In the Transactions table, income and expense transactions are entered, indicating the category to which the income or expense is attributed.
Speeding up the recording of the transactions
In order to speed up the recording of your transactions, you can use:
- The Smart fill function that allows the automatic auto-complete of data that have already been entered at an earlier date.
- The Recurring transactions function (Actions menu), used to memorize recurring transactions into a separate table.
- Import of your bank or postal account statement.
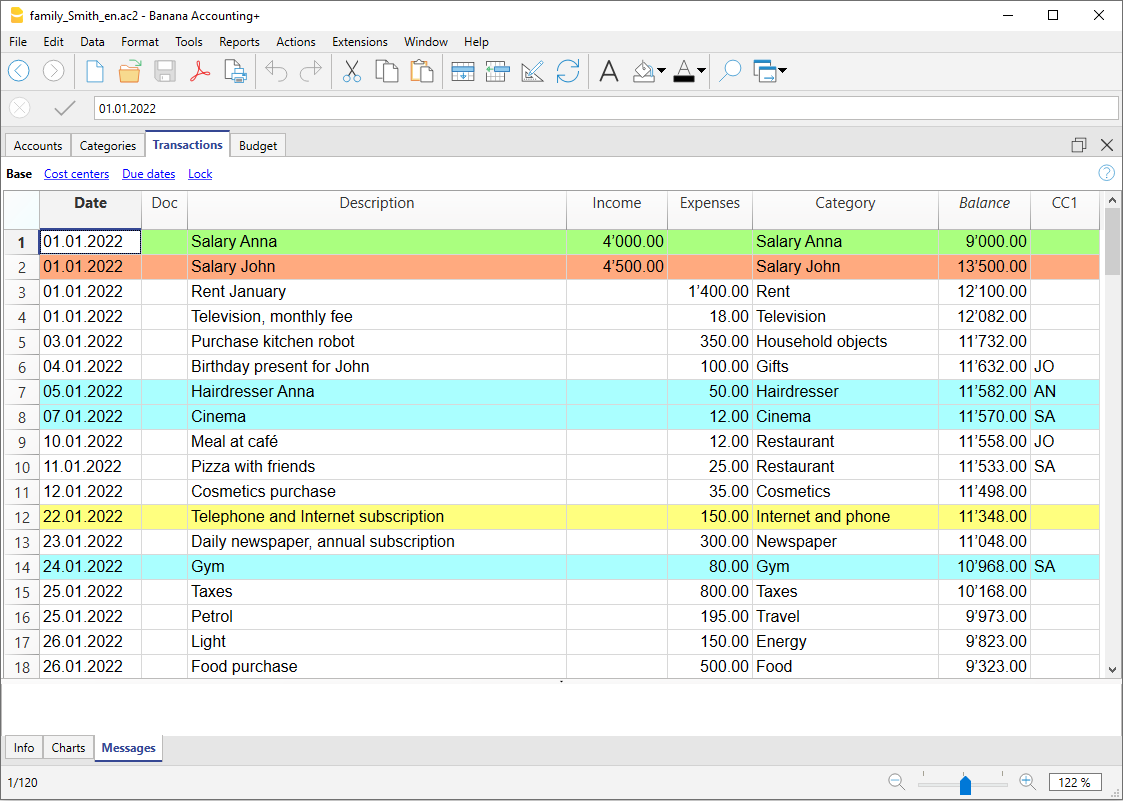
Make visible the Balance column in the Transactions table
The new Balance column is a very useful feature: it allows you to immediately spot possible differences.
The Balance column is not visible by default: you can make it visible via the Data → Columns setup menu.
- Watch the Video: Using the Balance column to spot differences
- More information on the Balance column
Transactions with VAT
In order to enter transactions with VAT please proceed as follows:
- from the File menu, choose New command and choose as Type the Cash Manager with VAT/Sales tax
- Choose one of the existing templates for your nation.
In order to enter transactions with VAT, please refer to the Transactions page.
The Category or Group card
The Category or Group card allows you to have a complete list of accounting entries relating to the same category or group.
- To open an category or group card you click once on the account number cell and then click once on the small blue arrow appearing in the upper right corner of the cell.
- To open multiple category or group cards you must select the Account cards command from Reports menu.
- To update the category or group cards, following changes in the Transactions table, you must click on the two circular arrows symbol, located at the top right corner of the account card.
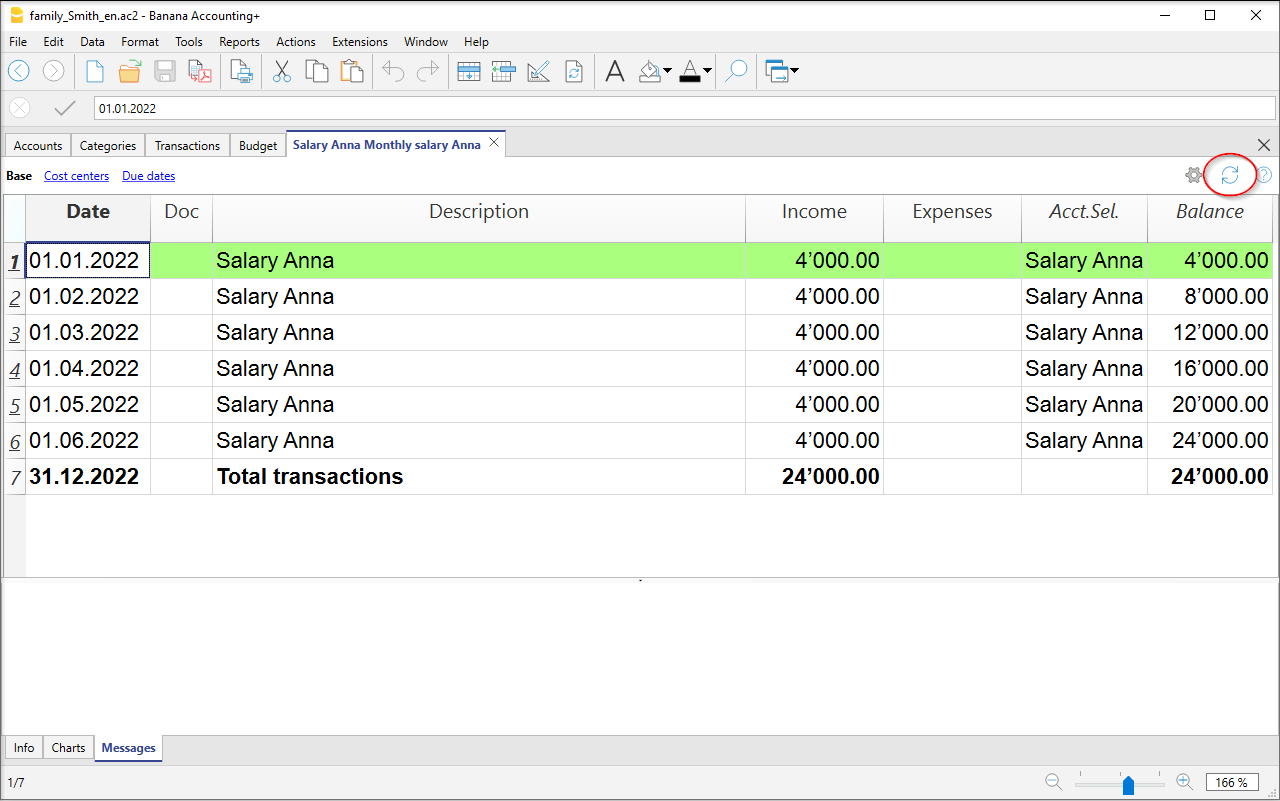
Account cards per period
To open an category cards with account balances referring to a predefined period, click on the Reports menu, Account/Category cards ...command and click Period selected in the Period tab to insert your selected period. Visit the Period page for further information.
Print the Category card
To print a Category card, open it from any table (Accounts or Transactions) and start printing from the File menu.
To print out several or all the Account/category cards , click Reports menu, select Account/category cards and select the accounts/categories you wish to print. The filter in the window allows you to select automatic selection of all categories, cost centers, segments, groups etc ... Visit the Account Cards page for further information.
Enhanced Statement
To view the Enhanced Statement and the Enhanced Statement with groups, choose the Report menu → Enhanced statement or Enhanced statement with groups command. You can also obtain statements by period.
- The Enhanced statement displays all accounts and categories without any subgroups
- The Enhanced statement with groups displays all accounts and categories also with subgroups
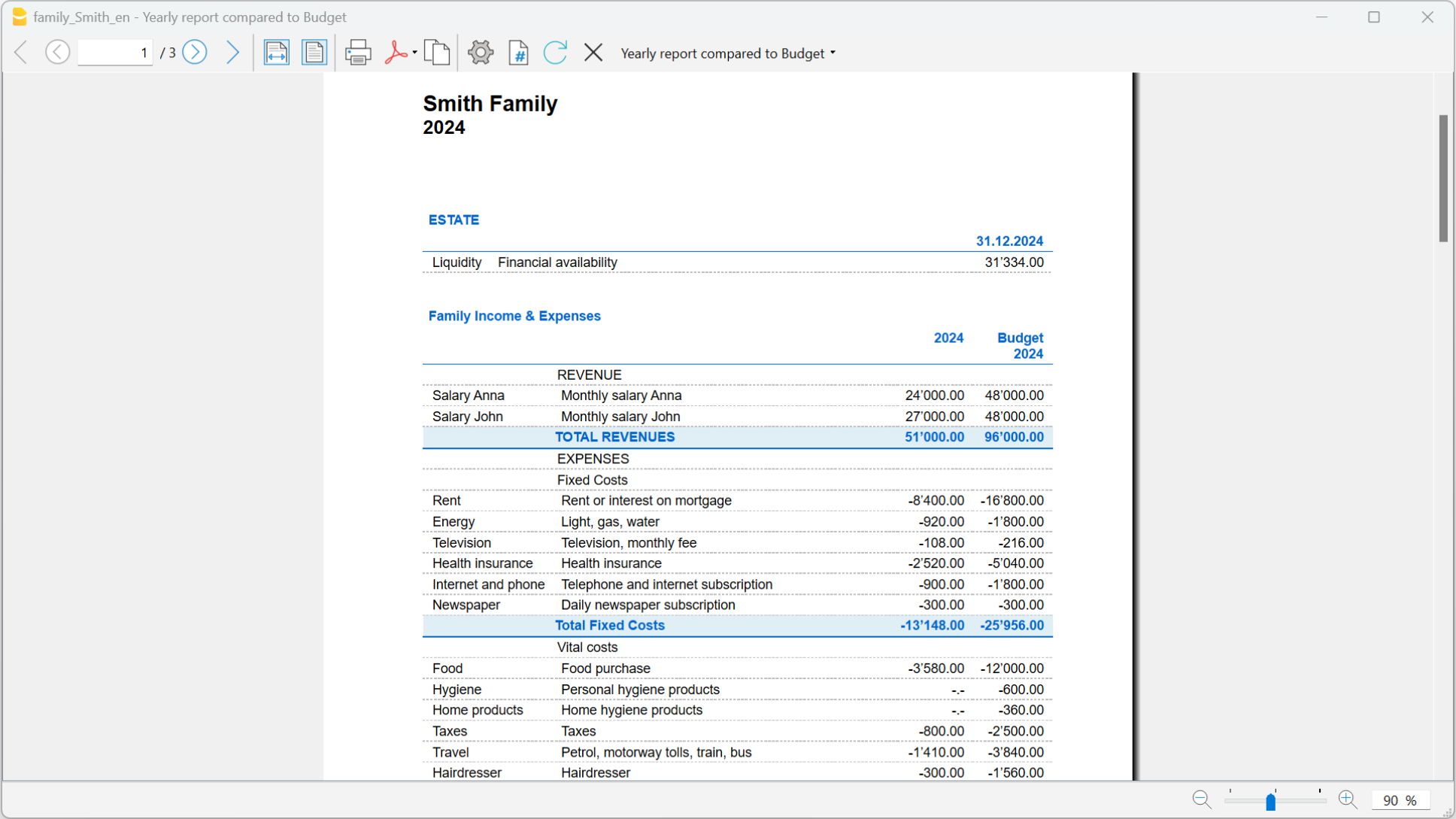
Archive data in PDF format
At the end of the year, when the accounting is done, corrected and revised, you can store all accounting data with the Create PDF dossier command from the File menu.

The Budget
Before starting your accounting year, you can create a budget with your assumed expenses and revenue, in order to have control over the financial and economic situation of your company.
The budget can be set in two different ways:
- From the Budget column of the Categories table. For each account the yearly budget is indicated.
In this case, when you process the Budget from the Reports menu, Enhanced statement with groups command, the Budget column shows the amounts that relate to the entire year. - From the Budget table, that you need to manually activate using the Tools menu → Add new functionalities → Add Budget table command.
In this table all estimates are entered as budget transactions, either income or expenses. If you activate this table, the Budget column of the Accounts table is automatically deactivated.
In the Budget table you can setup a detailed budget that takes into account possible variations during the year and in different periods of the year.
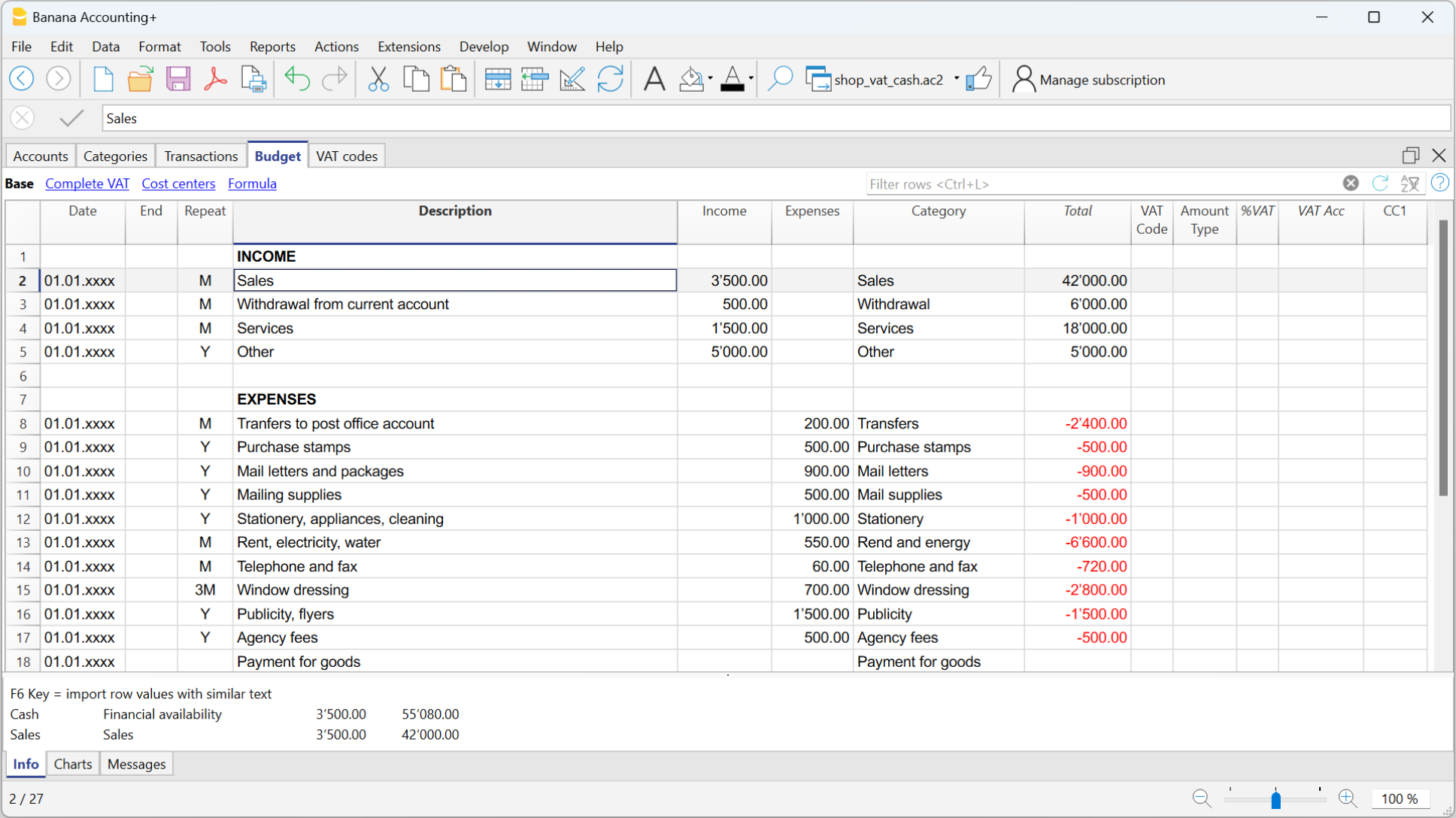
Cash Manager Accounts Table
The Cash Manager Accounts table contains only one account and no other accounts can be added.

The columns of the Accounts table:
The main columns of the Categories table are listed below. The display of columns changes according to the selected View.
Additional columns can be added either system or own columns via the menu Data > Columns setup.
Group
This column remains empty.
Account
Enter the number or initials of the account to be managed (cash, bank, post office).
Description
Enter a description relating to the account entered.
Opening
You need to enter the opening balance only the first time you use a new file or when using Banana accounting for the first time. At the beginning of the new year with automatic opening, the account balance is automatically updated.
Income
The column is protected and shows the balance of income transactions. The balance is updated automatically after each transaction.
Expenses
The column is protected and shows the balance of outgoing expenses. After each transaction the balance is updated automatically.
Balance
The column is protected and shows the total balance between income and expenses. After each transaction the balance is updated automatically.
Cash Manager Categories table
The Categories table presents the Income and Expenses situation.
The Categories table
In the Categories column, for each income and expense, the respective categories are set.
In addition to the Categories column, there are columns to set:
- Sections
- The Totalization groups.
For further information on the grouping system, refer to the Grouping system. - Any Cost and Profit centers.
In the example there are three main groupings:
- Group 4 - Totals all the Categories that have grouping 4 in their Sum in column (total Income)
- Group 3 - Totals all the Categories that have grouping 3 in their Sum in column (total Expenses)
- Group 00 - Totals groups 3 and 4 (Total Income and Expenses), which determine the Result for the accounting period.

The columns of the Categories table
The main columns of the Categories table are listed below. The display of the columns changes according to the selected View.
You can add additional system columns as well as your own columns via Data > Columns setup.
Section
An asterisk is inserted in the row where a title is entered, which will then be taken over in the Enhanced Statement with groups
(in our example the asterisk is inserted on the line of the title Operating result).
If other sections are provided in addition to income and expenses, such as cost and profit centers, another asterisk can be inserted in the Sections column, again on the title row. More details are available on the Sections page.
Group
Enter an identifier (numerical or sign) identical to the one entered for each category in the Sum in column. The totals for each category belonging to the same grouping of the Sum in column will then be added up (in our example, Group 4 totals the Income Category and group 3 the Expenses category).
Category
Enter the Category number that will identify the type of expense or income.
Description
A description is entered to identify the income or expenses category. This description is automatically taken from the Category Description column of the Records table (if displayed).
Sum in (Gr)
The code of a group is indicated so that the programme totals the amount of the line in the group.
The heading ‘Sum in’ has been adopted with the Banana Plus version.
The column name has remained Gr, to maintain compatibility with previous versions of the programme.
Each category has an identifier that is used to define in which group it is to be totalled (in the example, all revenue categories, in the Sum in column, have the grouping 4, because they are totalled in Group 4, Total Revenue).
Income
The column is protected and shows the balance of income transactions. The balance is updated automatically after each transaction.
Expenses
The column is protected and shows the balance of outgoing expenses. After each transaction the balance is updated automatically.
Balance
The column is protected and shows the total balance between income and expenses. After each transaction the balance is updated automatically.
Customising the Categories table
You may customise the entry and exit categories in the Categories table according to your needs. You can:
- Change category numbers
- Change description
- Delete or add categories
- Insert or delete subgroups
All category balances determine the operating result (profit or loss) and must therefore have no balance at the beginning of the year.
Adding new Categories
If you need to add new categories to an existing group, proceed as follows:
- Insert empty rows (menu Edit > Insert Rows) before the Totalisation Group row
- Enter the category number or abbreviation in the Category column
- Enter a description to identify the category
- Enter in the Sum in column , the same grouping number as the other categories, belonging to the same Totalisation Group.

Adding Subgroups
To add new subgroups, proceed as follows:
- Insert empty rows (menu Edit > Insert rows) in the area where you wish to insert the new subgroup
- In the last empty row enter a number or abbreviation for the totalisation in the Group column (in the example "34 - Total Optional Costs")
- Enter a description to identify the new subgroup
- Enter in the Sum in column the Totalisation Group (in the example "3 - Total Costs").

Deleting categories and subgroups
To delete categories or subgroups, select the rows with the categories and subgroup to be deleted and issue the command Delete rows from the Edit menu.
Opening Balances | Cash Manager
You only need to enter the Initial Balance the first time you use Banana Accounting Plus.
Opening balances when you start with Banana Accounting
When creating a new file for the first time with Banana Accounting, the opening balances must be entered manually in the Accounts table, Opening column.
When you move to the new year, using the Actions > Create new year command, Banana accounting reports all the opening balances automatically.
It is not possible to enter more than one account; for this you must use the Income/Expense Accounting.

Start with Banana Accounting during the year
If you start a new accounting, taking over the work already done with other programs, you have two possibilities:
- Start accounting from the start of the year, by entering the opening balances at the beginning of the year (Accounts table, Opening column) and the transactions (Transactions table) that have already been previously recorded with other programs (also see Transferring data from other software). Thus you will have all the accounting details a single file.
- Starting from the date when the accounting is resumed:
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
In addition to entering the opening balances of the Cash in the Accounts table, it is also necessary to enter the income (positive) and expenses (negative) balances in the Categories table. - Input the new entries in the Transactions table.
- Enter the opening balances (Accounts table, Opening column), taking over the values of the other accounting.
Balances of the previous year
If you start a new accounting by taking over an existing accounting and you want the previous year's values to appear on the printouts, it is necessary to enter the previous year's balances in Accounts and Categories > Previous view > Previous Year column:
- Enter the closing balances of the previous year's Cash (Accounts table).
- Enter the closing balances of the previous year's Expenses (Categories table).
- Enter the final balances of the previous year of Revenues (insert the minus sign in front of the amount).

Create new year
When you start the new year, the program automatically carries over the opening balances for the following year.
Consult the Create New Year lesson.
Print opening balances
To print the opening balances:
- To print the contents of the table, use the File > Print / Preview command, by selecting the rows of the Balance Sheet.
- You can also use the Accounting printouts and set the printout only for the Statement part and the opening column.
Budget table of the Cash Manager
Financial planning is carried out in the Budget table.
Before starting a financial year, you can budget expenses and estimate income to keep the economic and financial situation under control.
The budget can be set in two different ways:
- In the Categories table, under the Budget column. For each category, the annual budget amount is indicated.
In this case, when you generate the Budget from the Report menu using the command Enhanced Statement with groups, the Budget column shows the amounts that refer to the entire year. - In the Budget table, which can be activated from the Tools menu > Add/Remove functionalities > Add Budget Table.
In this table, all budgeted expenses and incomes are recorded with transactions. If this table is activated, the Budget column in the Accounts table is automatically disabled. In this case, you can set a detailed budget that takes into account possible variations during the year and in different periods of the year.

Create new year
It is possible to transition to the new year automatically in the following ways:
- Open the file of the year that has just ended and from the Actions menu > Create new year.
- Confirm the basic file Properties.
- Save the file with a new name.
- The account, carrying over the initial balance.
- The categories are carried over without bringing an initial balance, as they start from zero, to determine the operating result of the new year.
Transactions table of the Cash Manager
The transactions of the Cash Manager are entered in the Transactions table.

There are specific columns to enter:
- the date
- the document number
- the description
- the income or expense amount
- the category relevant to the income or expense in the Category table
- should the transaction be subject to VAT tax, enter the VAT code in the VAT code column.
The VAT codes are listed in the VAT codes table.
Speeding up the recording of the Transactions
In order to accelerate the recording of the transactions, you can use:
- the Smart fill function that allows the automatic auto complete of data that have already been entered at an earlier date.
- the Recurring transactions function (Actions menu), used to memorize recurring transactions into an appropriate table.
Examples of transactions without VAT
Examples of transactions with VAT
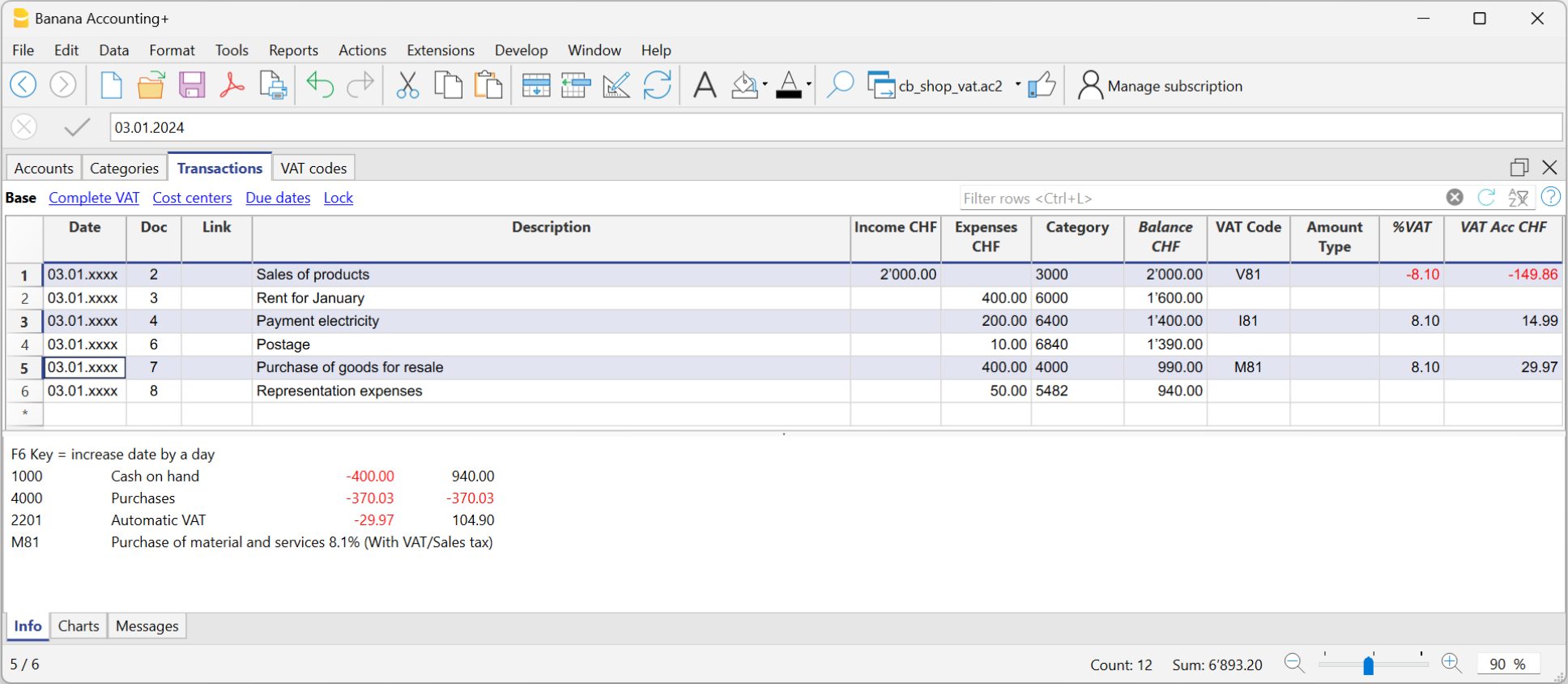
Category card
To display the transactions of a category, click once on the small blue arrow appearing in the upper right corner of the cell.
The display of entries in the Categories table is similar to the one in the Transactions table.
When new transactions are added or changes are made (i.e. in the Transactions table), it is possible to update the tab of a category by clicking on the Update symbol (blue symbol, of two circular arrows, located in the right part of the window).

Printouts
Instant information
In the Accounts and Categories tables, the balances of the accounts and the categories of income and expenses are displayed immediately. After each individual entry, the balances are updated automatically, and there is no need to generate reports to keep the situation under control; you simply need to position yourself in the Accounts and Categories table.
To print the content of the tables, please refer to the Page setup section (last paragraph).
Advanced printouts
All printing is run from the Reports menu, where the different functions for printing are located:
- Journal - command to define the period. You can display and print the whole table or just a specified period.
- Account/Category cards - Account cards / Categories. You may select all cards or define your selection.
Define the required period in the Period tab and click the required settings in the Options tab. Print settings can be saved in the Customization tab so they can be resumed without them to be having defined again.
- Enhanced statement - Enhanced statement command. You may also print a defined period and various options and customizations may be included.
- Enhanced statement with groups - Enhanced statement with groups command. You may also print a defined period and various options and customization may be included.
- Accounting report - Account report command. The required options are displayed in the Accounts table. Reports are possible for current, previous periods or previous years; each period may contain subdivisions and the customizations can be saved.
Example of printout of Enhanced statement with groups

Cash Manager account / category card
The account or category card corresponds to the ledger and allows you to have a complete list of the accounting entries concerning the same account, the same category, a cost center, a segment or a group.
Open the account card
There are two ways to open and print an account or category card.
First method
This method is recommended when you want to view and print all or several account/category cards.
- Via the Reports > Account / Category Cards menu

A dialog box with the following sections appears:
For detailed information on the sections, click on the corresponding links.
Second method
This method can be used when you need to open only one card at a time within the tables.
- Click on the small icon that appears when you select the cell that contains the account, category or group number.

Update the account card
The account or category card is temporary and is calculated at the time of the request. If transactions are changed or added in the Transactions table, the account card is not updated simultaneously.
To update the account card, following changes, it is necessary to use the Account / category card command again, or if the account card is still open, click on the symbol shown in the image below ![]() .
.

Note
It is not possible to change the data in the account, category or group card. Within the account card, by double clicking on the row number, the program switches to the corresponding row of the Transactions table or of the Estimate.
The Account Selection column
In the Account selected column, which can be made visible, starting from any account card, via the Data > Columns setup menu, the account on which the transaction took place will be displayed.
When you get an account card of one or more accounts, categories, groups and segments, you see exactly which account is used.

Cards of groups or classes
In the account card of a group or class, all the transactions of those accounts belonging to the selected group or class are regrouped.
The accounts or categories of the group or class can be viewed by making the Account Selected column visible.

Budget Account card
Once the budget transactions have been entered in the Budget table, it is possible to have the account or group cards of the budget:
- Reports menu > Account / category cards > activate Budget transaction.

Print the ledger (account cards)
To print the cards:
- Reports menu > Account cards
- Through the Filter it is possible to automatically select all the account cards to be printed or partially (eg only accounts, cost centers or segments).
- In the various sections Period, Options, Customization the desired functions are activated (eg period, one account per page ....).
- Confirm with OK after setting the desired options.
The selected account cards will be displayed on screen. To print, click on the File → Print menu.
Insert a logo in the account cards
As per Banana 9 version, it is possible to insert a logo also in the printout of the account cards.
After creation of the account card detail, proceed as follows:
- Reports menu > Account cards
- File menu > Print preview.
- In the dialog box that opens, under Logo, indicate your logo (instead of none).
More detailed information is available on the Logo setup page.
Save the settings
If you happen to regularly print the cards of certain accounts, for example all those of sales, it is useful to create a relevant customization:
- Report menu > Account cards > Customization section
click on the New button - Indicate the name in the description, for example "Sales Accounts"
- Select the accounts you want to print
- From the File > Page setup menu you can determine the margins and other page settings.
Whenever you need to print the accounts, select the customization you created.
Journal Cash Manager
Journal
As in all Banana Accounting applications, transactions are entered in the Transactions table. If you want to print the Journal (list of all transactions), you can proceed in several different ways:
- Position yourself in the Transactions table and click on the Print preview icon; then click on the Print icon
- From the Transactions table and select from the File menu > Print preview > Print icon.
- From the menu Reports menu > Journal by period ...
Journal by period
Banana Accounting, through the menu Report > Journal by period, offers the possibility to print the Journal with the movements of the entire period or of the selected period, by entering the start and end date of the period.

The information on the Period section is available on the Period page of the common functions.
In the Sort column tab, you can select the base on which type of date to order and print the journal.
Enhanced Statement
The information on the Enhanced Statement is identical to that of the Enhanced Statement of Income / Expenses.
Enhanced Statement with groups
The information on the Enhanced Statement with groups is identical to that of the Enhanced Statement of Income / Expenses.
Accounting report
The information in the Cash Manager Accounting Report is identical to that of the Income / Expenses Accounting Report.
VAT/sales tax report (only with VAT option)

Information on the VAT Report is available on the web page VAT/Sales tax report.