In this article
In the Exchange Rates table, the basic currency (accounting currency) and foreign currencies with all their related parameters are entered.
Before setting up the Exchange Rates table, it is necessary to set up in the Accounts table, foreign currency accounts with their respective codes; you also need to define the basic currency in the File menu > File and accounting properties.
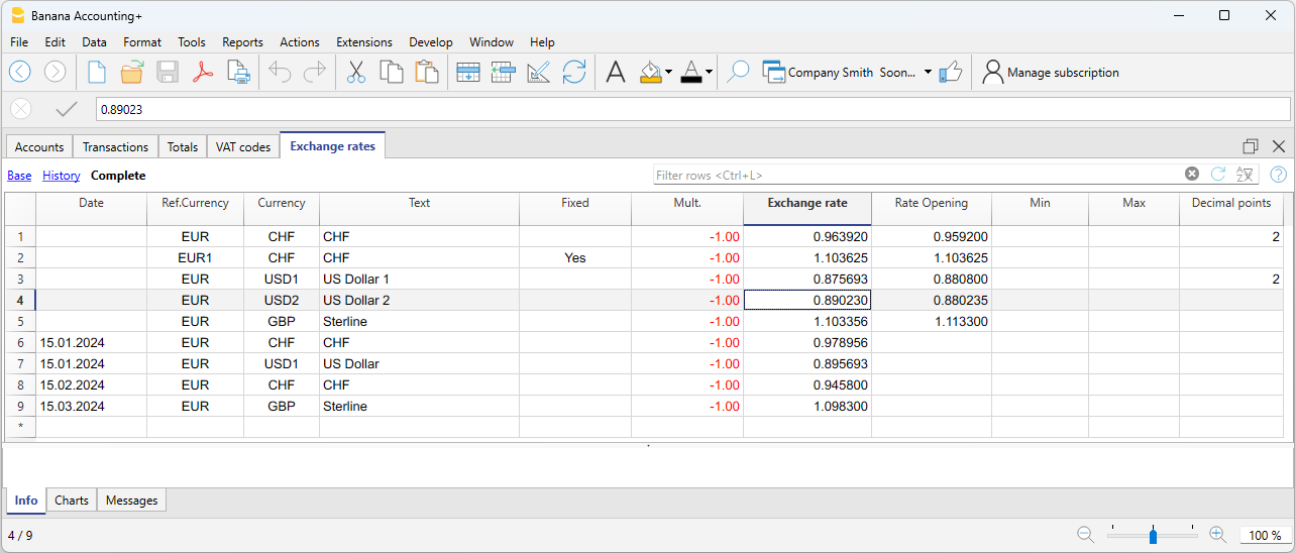
Exchange rates with and without date
There are two types of exchange rates:
- Exchange rates without date
For each currency used there must be an exchange rate line without date.
The exchange rate rows without a date are used as reference rates to convert foreign currencies into the basic currency according to the current exchange rate. They are used:- When there is no historical exchange rate (exchange rates with dates).
- At year end, to define official closing rates and calculate exchange rate differences (end of the accounting period).
During the closing process, it is mandatory to use exchange rate rows without a date in order to calculate exchange rate differences.
- Current exchange rate and closing exchange rate
- It is the exchange rate entered in the Exchange rate column; it is the current exchange rate or the closing exchange rate.
- This exchange rate is automatically used in the transactions, when there is no historical exchange (exchange rows with date).
If you modify the exchange rate in the Exchange rates table, the exchange rates and amounts previously used in the journal rows are not changed. - It is used for the calculation of the balance column calculated in the accounts table and for the conversion to Currency 2.
- Every time transactions in foreign currency are recorded, the resulting exchange rate differences are displayed in the Calculated Balance column of the Accounts table (Balances view). These differences are the foundation for calculating exchange rate differences and for the conversion into Currency 2.
- Closing exchange rate
- It is used as an exchange rate for exchange rate differences postings.
- It becomes the opening exchange rate when creating a new year.
- Opening exchange rate
It's the exchange rate entered in the Rate Opening column and it is used in the following cases:- When first creating a multi-currency file in Banana Accounting Plus
- When creating the new fiscal year, the opening exchange rate is automatically taken from the previous year's closing rate (in the Exchange Rate column).
The opening exchange rate is automatically used in the Accounts table to convert the opening amounts in foreign currency into the opening amounts in the basic currency of your accounting file.
If you need to edit the opening exchange rate, you must use the Recalculate accounting command.
- Current exchange rate and closing exchange rate
- Exchange rates with date (historical exchange rates)
When dates are entered in the Exchange Rates table, and foreign currency transactions are recorded in the Transactions table based on a date specified in the Exchange Rates table, the program selects the exchange rate with the date equal to or closest to but not exceeding the date of the transaction entry.
The program uses the historical exchange rate in these cases:- When entering transactions at a specific date and in the Exchange rates table there is an historical exchange rate.
- When creating exchange rate differences and specifying to use historical exchange rate.
In exchange rates with a date (historical exchange rates), no opening exchange rate should be indicated (Opening Rate column).
Columns of the Exchange rates table
All the columns available for the Exchange rates table are visible in the Complete view.
Date
Rows without a date are used as reference exchange rates by the program. Rows with a date are used as historical exchange rates.
Ref. Currency
It is the starting currency (basic currency) for the exchange (EUR in the example).
Currency
This is the destination currency (foreign currency). It's value is converted into the Reference currency.
Text
A text to indicate the foreign currency description
Fixed
True or false. If there is a fixed exchange rate, enter Yes in this column. In this case, for the foreign currency with a fixed exchange rate, the same rate is used consistently until it is modified. Typically, a fixed exchange rate is applied when there are accounts whose value should not undergo continuous fluctuations, such as real estate investments.
Mult. (Multiplier)
The multiplier is usually 1, 100 or 1000 and is used to obtain the effective exchange rate. The multiplier is used for currencies which have a very low unit value in order to avoid having to insert exchange rates with many zeros. In our templates, the negative multiplication (-1) is used in the Multiplier column of the Exchange rates table.
In this case:
- In the Ref. (Reference) Currency column, the base currency of the accounting system is entered
- In the Currency column, the foreign currency is entered.
When in the Ref. Currency and Currency columns the abbreviations of the currencies are reversed, the Multiplier 1 (positive exchange rate) must be entered in the column.
If transactions have already been made with the same currency, do not change the multiplier, otherwise the programme will report errors in the entries due to incorrect exchange rates.
Exchange rate
It is the current or closing exchange rate of the currency against the reference currency.
This is also used to calculate exchange rate differences. Before calculating exchange rate differences, it is necessary to update the rate in this column according to the official closing rate.
The exchange rate and the multiplier are being applied according to the following formulas
- With multiplier > 0
Currency amount = Ref. currency amount* (exchange rate / |mult.|)
- With multiplier < 0
Ref. currency amount = Currency amount * (exchange rate / |mult.|)
Opening Exchange rate
This is the exchange rate at the moment the accounting is opened. To be indicated only on a row without date.
- It is used to convert the opening amount of the foreign currencies into the opening amount of the accounting’s basic currency.
- Should be corresponding to the closing exchange rate of the preceding year.
When transitioning to the new fiscal year, the opening exchange rate is automatically updated based on the closing exchange rate from the previous year entered in the Exchange Rate column (Exchange rates table).
If the closing exchange rates are not equal to the opening exchange rates, the Assets and Liabilities might result into different totals; see Differences in the Opening Balances. - The opening exchange rate should never be changed in the course of the year, otherwise exchange rate differences are being created in the total of the opening balances.
- The opening exchange rate should not have a date.
Minimum
The minimum exchange rate accepted. If an inferior exchange rate is used for the transactions, there will be a warning.
Maximum
This column shows the maximum exchange rate accepted. If a superior exchange rate is used for the transactions, there will be a warning.
Decimal Points
The number of decimal points to be used when rounding the amounts of the foreign currency.
Modifications in the Exchange rate table
The current exchange rates for foreign currencies can be modified in the Exchange rates table, specifically in the Exchange rate column for rows without a date. In this scenario, when a transaction with an account in a foreign currency is entered in the Transactions table, the program automatically uses the exchange rate set in the Exchange rates table. If a change is made to an exchange rate in the Exchange rates table, there are no repercussions on previously entered transactions; the new exchange rate is applied to future transactions.
It is also possible to manually modify the exchange rate directly in the Transactions table by entering the desired rate in the Exchange rate column. This modification does not affect the exchange rate present in the Exchange rates table.
- Modification of the Opening exchange rate
If the opening exchange rate is modified, the next time you recalculate the accounting, the balances in basic currency of the accounts will be recalculated with the new exchange rate. Therefore, if you have opening balances, pay attention when modifying the Opening exchange rates.
If you modify the opening exchange rates and there are opening balances, it is important to recalculate the accounting. - Modification of the multiplier
- When changing the multiplier of a currency already used in the Transactions table, the program will report a warning as soon as the accounting is being recalculated. The transaction amount and the correct amount in the basic currency will have to be reentered.
- When the accounting is being recalculated, the opening balances in basic currency will be recalculated as a result.
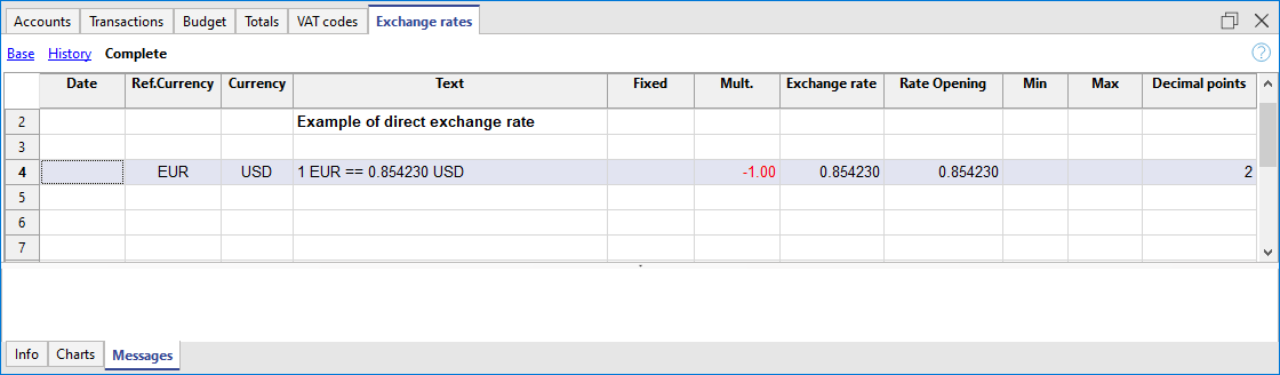
Direct exchange rates
Direct exchange rates are those where the basic currency and the foreign currency are indicated on the same row.
In the example below, the direct exchange rate is EUR → USD.
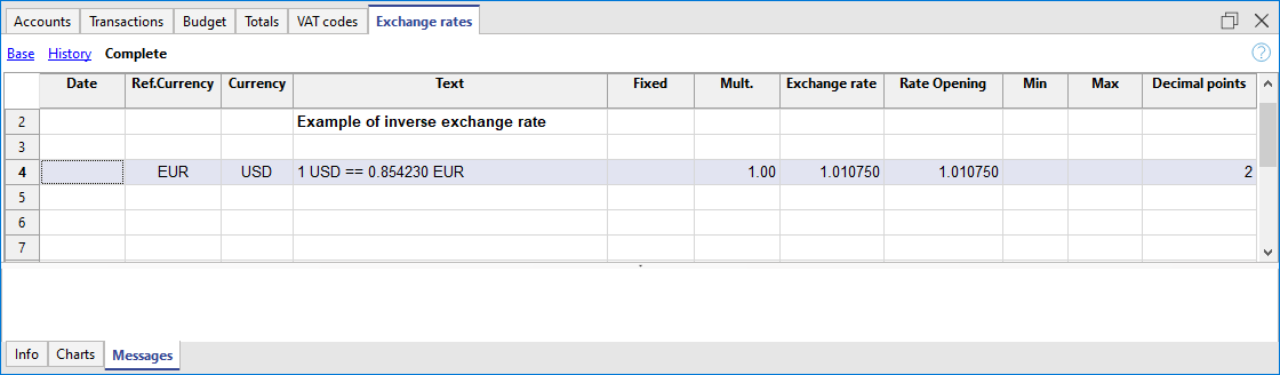
Indirect exchange rates
Indirect exchange rates are those where a direct exchange between two currencies is not being indicated (not recommended).
The exchange rate is deducted by the program based on other combinations of entered exchange rates
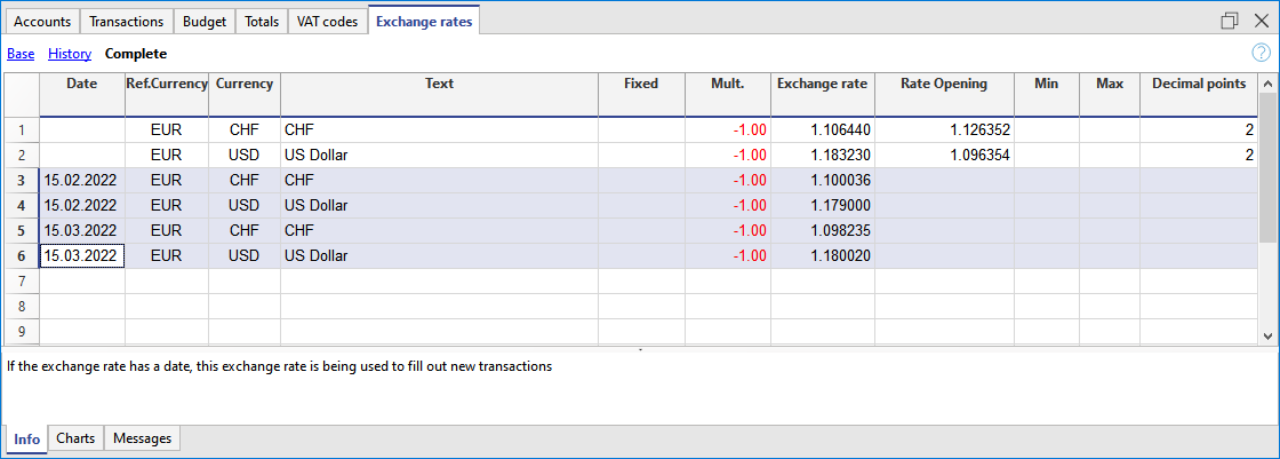
Historical exchange rates
As explained above, if an exchange has a date, the program considers it to be a historical exchange rate.
In the cases indicated here, the program chooses the exchange rate with a date equal to or less than the date of the transaction row.
- When entering transactions, if there is a historical exchange rate, it is proposed and used as the default exchange rate.
- When the exchange rate differences transactions are created and the option to use the historical exchange rate is activated.
- In rows with a date, the opening exchange is not used.
If you import several historical exchange rates at the end of your accounting period, that is, when you have already entered accounting transactions, simply manually delete the transactions exchange rates (Exchange rate column, Transactions table) to make sure that the program uses the imported exchange rates instead of those entered in the transactions.
Monthly average exchange rate
When entering a monthly average exchange rate, this must be inserted manually in the Exchange rate table, in a row without date. In the Transactions table, for foreign currency accounts, the average exchange rate will always be included until it is updated again in the Exchange rate table.
For the monthly average exchange rate, we recommend consulting the page of the exchange rates proposed by the Swiss Confederation, available in Italian, French or German.