全球: 商业会计
无增值税的商业会计模板
商店会计
商店会计 feiSimple Accounting for a Shop
Simple Accounting for a Shop michael房地产管理的收益&费用核算
房地产管理的收益&费用核算 cathie公司的收益&费用记账模板
公司的收益&费用记账模板 cathieComptabilité multidevise pour PME
Comptabilité multidevise pour PMEModèle idéal pour la gestion de la comptabilité des sociétés anonymes. Le plan comptable est structuré selon le schéma PME et présente les registres clients/fournisseurs. Il y a des comptes en devises étrangères et des centres de coûts.
Comptabilité pour sociétés anonymes
Comptabilité pour sociétés anonymes caterinaComptabilité pour sociétés de personnes morales avec les registres clients/fournisseurs
Comptabilité pour sociétés de personnes morales avec les registres clients/fournisseursModèle idéal pour la gestion de la comptabilité des sociétés anonymes. Le plan comptable est structuré conformément au régime des PME. Il y a des centres de coûts.
Comptabilité pour sociétés de personnes morales avec les registres clients/fournisseurs
Comptabilité pour sociétés de personnes morales avec les registres clients/fournisseursModèle idéal pour la gestion de la comptabilité de personnes morales. Le plan comptable est structuré conformément au régime des PME. Il y a des centres de coûts et la gestion des clients et fournisseurs.
Comptabilité pour Entreprise jusqu'à 500'000 CHF chiffre d'affaires
Comptabilité pour Entreprise jusqu'à 500'000 CHF chiffre d'affairesPlan comptable structuré pour gérer une entreprise dont le chiffre d'affaires annuel n'excède pas 500'000 CHF. Avec TVA et des centres de coûts.
公司会计 (含中英文报表)
公司会计 (含中英文报表) feiComptabilité pour Entreprises Individuelles
Comptabilité pour Entreprises IndividuellesPour gérer les comptes d'une petite entreprise individuelle. Le plan comptable est structuré avec des groupes et sousgroupes et centres de coût.
Comptabilité pour Entreprises individuelles
Comptabilité pour Entreprises individuellesPour gérer les comptes d'une petite entreprise individuelle avec TVA et centres de coût.
公司的复式记账模板
公司的复式记账模板 cathieYacht, Boats, Cruises Income & Expense Accounting Log Book with Budget and Cash Plan
Yacht, Boats, Cruises Income & Expense Accounting Log Book with Budget and Cash PlanTrack yacht or sailboat expenses and revenues. No need of accounting experience.
Easy to use Accounting software for Yacht. Predefined account file with chart of account, with comprehensive list of expenses (Engine, Crew, Administrative, Guests) and Revenues, that can be easily adapted for your specific needs.
This accounting template provides.
- Predefined account chart with Expenses (Engine, Crew, Administrative, Guests) and Revenues that can be easily adapted for your specific needs.
- Cost and revenues subdivision also by cruise.
Buchhaltung für ein Restaurant | Beschreibende Konten
Buchhaltung für ein Restaurant | Beschreibende KontenBudget für ein Restaurant erstellen
In jedem Gastronomiebetrieb ist es entscheidend, im Laufe des Jahres fundierte Entscheidungen über die wirtschaftliche und finanzielle Situation treffen zu können – idealerweise frühzeitig, bevor Probleme entstehen. Deshalb bietet Banana Buchhaltung in seinen Vorlagen die praktische Funktion "Budget", mit der Sie den Finanzplan (Budget) für Ihr Restaurant einfach und strukturiert erstellen können.
Wir führen Sie Schritt für Schritt durch die Budgeterstellung. Folgen Sie einfach den nachstehenden Anleitungen – schnell, unkompliziert und praxisnah. So können Sie sich voll und ganz auf das konzentrieren, was wirklich zählt: die erfolgreiche Führung Ihres Betriebs und die Zufriedenheit Ihrer Gäste.
1. Einnahmen eingeben
Zuerst müssen die fixen Einnahmen erfasst werden. Zur Orientierung können Sie sich dabei an den Einnahmen des Vorjahres orientieren. In der Regel setzen sich die Einnahmen aus folgenden Bereichen zusammen:
- Lebensmittelverkäufen
- Getränkeverkäufen
Gerade bei Restaurants ist es sinnvoll, die Umsätze für Speisen und Getränke monatsweise aufzuteilen, da diese je nach Feiertagen und Jahreszeiten stark schwanken können. Selbstverständlich können Sie die Verkaufspositionen individuell anpassen – z.B. nach Art der Speisen oder Getränke noch weiter untergliedern.
Darüber hinaus gibt es möglicherweise Einnahmen, die nicht direkt mit dem Tagesgeschäft Ihres Betriebs zusammenhängen, zum Beispiel:
- Mieteinnahmen aus Immobilien
- Zinserträge aus Bank- oder Postkonten
Eine Anleitung, wie Sie die Budgetdaten im Banana-Programm technisch eingeben, finden Sie auf unserer Webseite unter Tabelle Budget.
2. Fixe und variable Ausgaben eingeben
Listen Sie alle Ausgaben auf, die im Laufe des Jahres zu erwarten sind. Auch hier können Sie sich an den Ausgaben des Vorjahres orientieren und überlegen, ob es Änderungen geben wird – und die Beträge entsprechend anpassen.
Zu den wichtigsten Ausgabeposten zählen:
- Waren- und Rohstoffeinkauf (z.b. Lebensmittel und Getränke)
- Löhne und Gehälter
- Ausrüstung und Ausstattung
- Sozialversicherungsbeiträge
- Versicherungen (z.B. für Personal, Maschinen, Sachwerte)
- Miete, Hypotheken, Zinsen
- Steuern und Abgaben
- Energie- und Betriebskosten (Strom, Wasser, Gas)
- Telefon- und Internetkosten
- Reinigungsdienste
- Werbung und Marketing
Besonders bei Lebensmitteln und Getränken lohnt es sich, die Ausgaben auf Monatsbasis aufzuteilen – denn je nach Saison oder Feiertagen können die Kosten stark schwanken.
3. Einnahmen und Ausgaben überprüfen
Nachdem Sie alle erwarteten Einnahmen und Ausgaben aufgelistet haben, ist es an der Zeit, diese miteinander zu vergleichen. Ziel ist es zu prüfen, ob der angestrebte Gewinn – also Ihr Hauptziel – realistisch erreichbar ist.
Für diesen Vergleich benötigen Sie einen Budgetbericht. Wenn Sie mit einer Banana-Buchhaltungsvorlage arbeiten, öffnen Sie im Menü Berichte den Befehl Formatierte Bilanz nach Gruppen und wählen dort den gewünschten Jahresbudget-Bericht aus – dieser ist in diesem Fall besonders aussagekräftig.
Die Analyse des Budgetberichts verschafft Ihnen einen umfassenden Überblick über Ihre voraussichtliche Liquidität, Ihre Schulden (Verbindlichkeiten) und Ihr Gesamtvermögen – basierend auf den geplanten Einnahmen und Ausgaben.
Diese Übersicht hilft Ihnen zu erkennen, ob Sie bestimmte Einnahmen oder Ausgaben möglicherweise überschätzt oder unterschätzt haben.
Sollte sich ein möglicher Verlust abzeichnen, empfiehlt es sich, umgehend Sparmassnahmen zu ergreifen: Überdenken Sie Ihre geplanten Ausgaben – und passen Sie die Beträge gegebenenfalls an, um Ihre finanziellen Ziele abzusichern.
4. Überprüfung mit der Bilanz zum Jahresende
Am Ende des Jahres, wenn alle Buchungen erfasst wurden, können Sie einen Bericht erstellen, der Ihnen den Endbestand aller Konten anzeigt und diesen mit den budgetierten Werten vergleicht. So prüfen Sie zuverlässig, ob Ihre zu Jahresbeginn erstellte Planung realistisch war – und ob Sie den damals angestrebten Gewinn tatsächlich erreicht haben.
Um den Vergleich zwischen den geplanten Werten und den tatsächlichen Endsalden zu erstellen, gehen Sie ins Menü Berichte, wählen Formatierte Bilanz nach Gruppen und klicken dort auf Jährlicher Ausdruck mit Budgetvergleich.
Bei grösseren Abweichungen können Sie analysieren, bei welchen Einnahmen oder Ausgaben Ihre ursprünglichen Schätzungen ungenau waren – und diese Beträge im Budget für das neue Jahr entsprechend anpassen.

含外汇的公司复式记账模板
含外汇的公司复式记账模板 cathiePayPal Templates | Double-entry
PayPal Templates | Double-entryPayPal import transaction
Banana has an import filter that allows you to directly import the PayPal transactions data in your accounting file.
The attached files are predefined with the accounts so that you can start immediately using it.
There are two template example files you can download and open in Banana:
Files suitable for
These template files are especially suitable in case you have only one PayPal preferred currency.
The imported transactions will automatically be imported to the currency account, so that you can separately see all transactions.
If in PayPal you keep balances in different currencies, it will be more suitable to use a PayPal accounting in Multicurrency.
Even if you use another accounting software, you will find that is very efficient to keep a separate accounting in Banana and keep your PayPal accounting in it. Instead of recording all transactions in your accounting solution, you can keep a separated accounting in Banana and once a month or when needed, only record the summary movement for the period in your accounting solution .
Further adapting the file
The file can easily be adapted to suit your needs.
Adding new accounts and new currencies
-
In the Accounts table, add new accounts for other currencies or for different Income or Expense types.
Changing to another Basic currency
This file can easily be converted into one with another Basic currency.
- Change the Basic currency in the File properties.
Add VAT/Sales Tax, change language or convert into another type
Use Convert to new file to add more options or change the accounting file settings.
Contabilità Ristorante (Multi-Moneta)
Contabilità Ristorante (Multi-Moneta)Come fare il preventivo per un ristorante
Segui passo per passo la nostra guida alla pagina Come fare il preventivo per un ristorante che ti insegna come creare e gestire un budget familiare.
PayPal Templates | Multi-currency accounting
PayPal Templates | Multi-currency accountingPayPal import transactions
Banana has an import filter that allows you to directly import the PayPal transaction data into your accounting files.
The attached files are predefined with the accounts so that you can immediately start using it.
There are two template example files that you can download and open in Banana:
- Multi currency accounting with EUR as a Basic Currency
- Multi currency accounting with USD as a Basic Currency
Files suitable for
These example files are especially suitable in case you have PayPal transactions in different currencies and especially if you have set up your PayPal account to use and keep different currencies (see also PayPal template for Double-entry accounting) .
The imported transactions will automatically be imported to the currency account, so that you can see all transactions separately and have a balance in the currency.
Even if you use another accounting software, you will find that is very efficient to keep a separate accounting in Banana and keep your PayPal accounting in it. Instead of recording all transctions in your accounting solution, you can keep a separated accounting in Banana and once a month or when needed, only record the summary movement for the period in your accounting solution .
Further adapting the file
The file can easily be adapted to suit your needs.
Adding new accounts and new currencies
-
In the Accounts table, add new accounts for other currencies or for different Income or Expense types.
-
Add new currencies in the Exchange rates Table
Changing to another basic currency
This file can easily be converted into one with another Basic Currency
- Change the Basic currency in the Accounting properties.
- Adapt the Exchange Rates table with the appropriate currencies and exchange rates.
- In the Accounts table, change the currency for the accounts that need to be in Basic currency.
Add VAT/Sales Tax, change language or convert into another type
Use the Convert to new file command to add more options or change the accounting file settings.
含增值税的商业会计模板
商店会计
商店会计 fei含增值税公司的复式记账模板
含增值税公司的复式记账模板 cathieLibro de caja para un Comercio con IVA (con transacciones)
Libro de caja para un Comercio con IVA (con transacciones) barbara含外汇和增值税的公司复式记账模板
含外汇和增值税的公司复式记账模板 cathie公司 (含中英文报表)
公司 (含中英文报表)使用Banana财务会计软件,做专业的复式记账会计,一键生成资产负债表,损益表。多语言多汇率,使用中文做账一键点击生成外文报表。
创建您的文件
- 从该模板开始,创建一个新文件(模板编号+10680),使用在文中所解释的任何一种方式。
- 文件菜单→文件和账户属性命令,设置公司名称,会计期间及本位币。
- 文件菜单→另存为命令保存文件。以公司名称和年份作为文件名很有用。
例如“公司-2020.ac2”
文件和账户属性
- 账套
此标签可以编辑账套的信息,账套名称,开账日期和结账日期,以及记账本位币。 - 选项
此标签可以激活会计发生业务所需的功能。 - 地址
此标签中可以填入该会计账套的公司或个人信息,这些信息会做为本公司信息显示在给客户开具的发票中。 - 外汇
此标签中选择汇兑损益的会计科目代码。 - 增值税
此标签中选择应交增值税的会计科目代码。 - 其它
此标签中选择做账的语言和出报表的语言。 - 密码
此标签中设置账套密码。 - 文字
此标签中可以输入额外的信息,比如会计的名字。
编辑账户表
账户表格内显示有资产负债表及损益表的账户。
- 资产负债表显示所有资产账户的余额,即资产和负债。资产与负债之间的差额决定了个人资本。
- 损益表显示所有收入和费用的账户,它们的差额决定会计年度的损益状况。
所有的账户都可以根据您的需求进行客制化的编辑。例如,可以更改账号或摘要,可以在期初列内输入初始的余额,可以添加账户并且删除那些不需要的账户。
创建您的预算
在预算表格内,您可以输入指定年份的预估收入和费用。
- 列出每月费用和收入
例如,在办公室的租金中输入日期,重复,摘要,费用,借方账户,贷方账户和金额。
也可以会月收入执行相同的操作,并输入预估的收入。
输入会计发生业务
在会计发生业务表格中,输入实际的会计发生业务。
- 日期
- 摘要
- 借方账户
输入相对应的账户科目 - 贷方账户
输入相对应的账户科目 - 金额
对所有的会计发生业务执行同样的操作。
导入银行对账单
为了加快这些操作的进程,您可以导入银行对账单的数据并将其链接到数字收据。可以使用报表菜单→导入到账套命令。
报告和预算的比较
在输入会计发生业务后,程序将自动更新账户余额,您可以立即将其与预算余额进行比较。可随时查看并比较过去,现在和未来的会计数据。
外贸公司 (含中英文报表)
外贸公司 (含中英文报表) fei全球商业计划模板
针对自由职业者和小公司的现金流计划,预算和管理
针对自由职业者和小公司的现金流计划,预算和管理使用Banana财务会计软件创建现金流量预算,就像使用Excel创建现金流量预算一样,但是更快,更安全,而且全部免费。借助现成的模板,您可以立即开始,只需输入数据即可。
您事先知道有多少流动性资金,流动性会持续多长时间,何时会面对费用的支出以及稳定的收入。您可以模拟费用减少,并查看它对流动性和盈利能力的影响,了解未来的销售量以及您的资金是否足够。
根据我们的操作指南,可以帮助您进行现金流量预算并解决财务问题。如果在细节上遵循操作,您一定会取得成功,因为您可以对费用进行修改和更正,轻松更新预算。
创建您的文件
- 从该模板开始,创建一个新文件(模板编号+11047),使用在文中所解释的任何一种方式。
- 文件菜单→文件和账户属性命令,设置公司名称,会计期间及本位币。
- 文件菜单→另存为命令保存文件。以公司名称和年份作为文件名很有用。
例如“公司-2022.ac2”
调整账户和科目表
在创建自己的现金流量之前,您需要快速调整账户和科目以适应您的特定需求。
账户表
账户表仅显示现金账户,或者更确切地说,显示的是您所拥有的流动性。您可以通过更改账户名称、摘要和期初余额对其进行自定义。

科目表
该表格包含收入和费用类别以及资本变动。您可以通过添加新项目,更改科目名称,更改顺序并删除不需要的科目来编辑这些科目。您随时可以查看每个科目的更新余额。

通过有用的资本流入 & 资本流出部分,您可以登记:
- 贷款注入及偿还
- 所有者的注入及支出
- 固定资产的购入及销售
要随时了解当前的现金流量 (当您开始输入日常会计发生业务), 您只需查看净现金变动行中的值。通过这种方式,您一眼就能知道资金是流入还是流出,以及确切的金额。

创建您的现金流量预算
Banana财务会计软件有意义的创新之处在于,它可以创建现金流量预算以控制流动性并为您的业务做出及时的决策。
因此,我们现在建议您创建自己的现金流量预算。转到预算表:该表格包含了您一年内所有的现金流入及流出。
要正确创建预算,请按照以下简单步骤操作:
- 输入营业收入
- 输入营业费用
- 输入资本注入
- 输入资本支出
输入营业收入
首先列出所有的营业收入及其金额。现金销售是主要的收入,但是其它收入取决于您的经营活动。
营业收入可能包括:
- 现金销售
- 杂项现金收入
- 客户信用账户中的收款
- 利息
要在预算表中插入一笔会计发生业务,您必须输入日期(您预期会有这笔收入的日期),期末(如果需要),重复(该收入重复的频率,例如每周,每月或每年),摘要,收入列中金额和收入的科目。
在模板中,您可以看到已经存在的预算会计发生业务示例,可以根据您的需求轻松修改或清除。您也可以输入新的一笔业务。
为了使估算金额尽可能的精确,请查看去年的金额,并在需要更谨慎时采用四舍五入。
提示:
- 只基于有保障的收入
- 根据收入的重复次数汇总金额(每周,每月,每年,...)

输入经营费用
现在是该列出所有经营费用的时候了。正如您对收入所做的那样,在这里您必须通过查看去年的金额来估算费用,当需要更加谨慎时,可以将其四舍五入。在一年的年初做一个大概的预测,总是比对费用的增加感到意外要好得多。
经营成本可能包括:
- 工资
- 薪资
- 房租
- 保险费
- 广告及促销
- 公共事业
- 差旅费
- 通讯费
- 银行费用
- 利息
- …
提示:
- 根据费用的重复性将它们分组 (每周,每月,每年,...)

输入资本注入 & 输出
这个部分对于净现金流量预测是非常有用的,而不仅仅是一个经营预测。您必须输入预期的资本注入及输出发生业务,固定资产的投资及撤资。
资本可能包括:
- 贷款注入
- 所有者现金注入
- 销售固定资产
资本输出可能包括:
- 贷款偿还
- 支付给所有者的现金
- 购买固定资产

控制您的现金流量预测
重要的是通过您的预测,可以立即知道业务是否产生了正的现金流量。您好奇吗?生成的预测报告会给您答案!
要做这个检查非常容易:只需到点击报表菜单 → 按组生成报表,然后在出现的列表中选择第一年预算报告。点击确定 查看预测报告。
任何活动的目标肯定是拥有正的现金流量 ,因为只有这样才能使其生存,或者更确切地说是能够向供应商付款,偿还债务,...检查净现金变动项目(在报告底部)并确保您获得正的结果(流入)。 如果是这样,您会很高兴,因为您的业务经营得很好!
另一方面,如果您的净现金流量(流出)为负,则意味着您的企业很难管理流动性。 在这种情况下,您需要做的首先是重新检查估计的收入和支出,是否有任何调整或需要纠正的错误,可以改善现金流量。 如果您仍然有负的现金流量,则需要考虑从明年或预测期开始时,采取措施改善流动性管理。 您极有可能将不得不尝试减少运营费用。

除年度预测外,始终在报表菜单 → 按组生成报表中 ,有更详细地控制流动性趋势(例如,其在一年中的表现),您可以选择每季度和四年的报告,或者创建您自己的报告。


输入发生业务
在现金流量预测得到控制的情况下,您可以开始登记各种实际发生的流动性发生业务,并不时将其与期望值进行比较。
登记流动性发生业务
每日发生业务必须插入到发生业务表中 。 进行登记的过程与预算表中的预测过程相同(唯一的区别是没有重复列)。 该表中还有一些示例可以删除和编辑。

用账户明细查看动向
当您逐步输入发生业务记录时,检查现金帐户或特定费用科目随时间变化的情况可能会很有用。 为此,您可以查看相应的账户/科目明细。
例如,通过选择现金账户明细,您将获得其所有活动的摘要。 通过单击底部的图表选项,您可以更直接地查看该账户的表现。
提示:每月至少检查一次现金账户,可以立即查看进展情况并将其与过去几个月进行比较。

检查余额和预算之间的差额
为了更好地控制表现,您可以转到账户或科目表,选择预算视图,然后查看预算差额列,该列向您显示实际余额与预算值之间的差额。这样,您便有了一个额外的指标,可以了解是否在预算方面做得很好,并可以做出更好的决策。

将预测与当前报告进行比较
在一年中,您可以随时将当前状况与预测进行比较,了解是否花费更多,以便提前做出决策。在年底,您可以把实际报告和预测进行最终比较,以查看您是否已实现预期的净现金流量。
从账户菜单 → 按组生成报表 → 与预测比较的年度报表。

如果您希望有一个更精确和更有针对性的视图,可以创建按月细分的报告,其中还包括每个月的余额和预算值之间的差额。 这可以让您了解您流动性困难最大的月份和收入最多的月份。

到年底了,所以现在您必须重新计划下一个,创建一个新的现金流量预测,与您到目前为止所做的完全一样。 不要停止,只有这样,您才能看到您的现金流量越来越好!
创业公司的财务计划 | 收益&费用会计核算
创业公司的财务计划 | 收益&费用会计核算请注意:这个财务计划的模板是以酒吧或餐馆的管理为例的,因为这是被大众所熟知的商业活动,因此非常适合何用来了解Banana财务会计软件的运作原理。此模板也可用于其它类型的活动 (初创公司),为其做财务和流动性的规划。
初创公司预算和财务计划的完整示例教程
初创公司预算和财务计划的完整示例教程模板文件
无论您是打算开展新业务还是制定业务计划,流动性预测管理是至关重要的。特别是在新的业务开始时,可能很容易让您陷入财务困境。
Banana财务会计软件为您提供设置财务计划和流动性预测的可能性,允许每天进行高度准确的监控。允许您将会计预测到未来,并在您的分类账中管理未来的几年的财务核算。
请注意:这个财务计划的模板是以酒吧或餐馆的管理为例的,因为这是被大众所熟知的商业活动,因此非常适合何用来了解Banana财务会计软件的运作原理。此模板也可用于其它类型的活动 (初创公司),为其做财务和流动性的规划。
卢克餐厅的财务计划和流动性管理
本节将解释如何根据复式记账模式为一项新的创业活动制定财务计划。
更多信息请参考预算及财务预测的好处和特点部分。
卢克计划在2022年开设一家餐厅,并正在准备一份财务计划,包括所有必要的细节。
- 他的项目融资包括正当途径和从第三方贷款。
- 2022年1月,他租用经营场所,重新装修并布置,开始了他的商业活动。
- 财务计划成立时间为2022年1月至2025年12月。
下面我们会向您展示使用Banana财务会计软件,轻松制定月度计划的例子:

经济预测和流动性管理
这个模板将帮助您了解Banana财务会计软件中财务计划的不同功能。一些功能,如公式,将在更高级的情况下使用。在Banana财务会计+中,只有在高级计划中才有可能输入公式。现在就更新!
- 预算发生业务的应用
- 重复性发生业务
- 使用数量和单价
- 使用公式
- 使用变量
- 计算资产和负债账户的利息
- 结转账户余额
- 结转发生业务记录
- 一个会计年度按季度划分的预算,包括经营结果和流动性预测
- 几个会计年度的预算,包括经营结果和流动性预测
文件和账户属性
开账日期为2022年1月1日,结账日期为2022年12月31日。
这也是用于预算中总计列的计算周期。

会计科目表
此示例旨在解释您的预算预测表的功能。
- 会计科目表,精简,便于使用。
- 账户的综合名称是用来说明Banana会计软件的使用。
- 期初基本货币。活动是从头开始的,所以没有期初余额。
- 预算基本货币。这是会计期末的总体预算。 请注意,这代表了预算期末的资产负债表和损益表。


创建您自己的会计科目表
账户表定义了支出、收入和投资等要素。如果您想对费用进行更详细的细分,您需要添加其它账户。
与其从一个非常简单的会计科目表开始,然后再添加科目和组别,建议从一个更有结构的会计科目表开始。Banana会计软件提供有不同的会计科目表模板,建议选择和调整一个最接近您需求的模板,然后添加预算标签。
预算表
预算表 (请参阅列说明) 内输入与计划相关的记录。
财务计划可通过复式记账输入在预算表中。预算表提供了更多附加的列,极大地便于编制财务计划。
- 重复
例如,如果您指定M=每月,则会生成所有后续月份的数据。
如果单元格为空,则操作仅执行一次。 - 期末
与重复相结合,设置经营活动发生的最后日期。 - 总金额
当前年度记录的总金额。 - 数量,单价
指示出根据数量计算价值的组合。 - 公式
允许指定计算金额的公式。
该公式优先计算金额。
一月份的发生业务
这些与发生业务表中输入的完全相同,因为还没有进行重复性发生业务。
这是餐厅开业的第一个月,有所有者权益的登记,购买家具和增加贷款。
下面的屏幕截图中显示的输入,例如,第一个月的租金,被列入非重复性发生的业务,以说明一些简单的业务不具有重复性。

二月份重复性发生业务
在二月份,输入将按月发生的业务。

-
从1月份至6月份的租金为1'000.00每月,并于7月份增加为1'200.00每月。
-
记账凭证号:5
第一笔租金用现金支付。可能还会支付押金。 -
记账凭证号:50
从2月份到6月份租金的预算是1'000.00每月。-
在2月2日,从银行账户支付租金
在接下来的几个月里,租金的支付将在每个月的第2日计算。 -
期末 是6月30日
最后一笔1'000.00每月的租金在6月2日发生。 -
重复 M=每月
-
总金额 5'000.00(5*1'000.00,系统自动计算)是此期间发生业务的总金额。
-
-
记账凭证号:51
从7月份开始的租金预算。-
日期 7月2日
在接下来的几个月中,1'200.00租金的支付在每月的第2 日计算。 -
期末
由于没有指明日期,这笔费用将在接下来的几个月或几年内重复性发生。 -
重复 M=每月
-
总金额 7'200.00(5*1'200.00,系统自动计算)
表示从7月份至12月份六个月的租金。
-
-
- 记账凭证号:52
-
日期 2月10日
-
期末 (租约)2021年1月31日。租约的最后一期到期时间
-
重复 M=每月
该操作每个月重复一次,最后一次是在2021年1月。 -
借方 A/C 管理费用
-
贷方 A/C 银行(用于付款)
-
金额 每月租赁费为200.00
-
总金额 2'200.00(200.00*11个月)
-
- 记账凭证号:53
-
日期 2020年2月10日
-
借方 A/C 管理费用
-
贷方 A/C 银行(用于付款)
-
金额 租赁金额为400.00。
-
总金额 为空,因为本年度没有支出
-
-
租赁退款收银机。
此操作仅在2020年进行,把它列在这里,是因为它与月度租赁有关。 -
记账凭证号:54
月度工资。-
日期 2月25日
-
重复 M=每月
该操作在每个月的25日重复进行。 -
总金额 55'000.00(5'000.00*11个月)
-
-
记账凭证号:55
管理费用(这是一个近似值:为每个单独的费用输入正确的预算是必要的)。-
日期 2月28日
-
重复 ME=月末
该操作在每个月的最后一天重复进行,3月份是3月31日,4月份是4月30日,依此类推。 -
金额 300.00
-
总金额 3'300.00(300.00*11个月)。
-
收入和商品采购的预算
根据业务活动类型,必须选择最适合的收入方式。
考虑到每月可能存在大的波动,收入和商品采购按月度金额逐项列出。
事实证明,对饮料或食品使用单独的营业额数字更为合适。
二月份的重复列为空,因为我们预计明年会有更高的金额,我们会在后期添加。
从三月份开始,营业额被认为是未来数年的表现。

按月计算收入预算和商品成本指标。
- 记账凭证号:101
二月份收入指标-
日期 2月20日
收入发生在一个月的每一天,我们选择一个月的月中日期作为流动性的近似水平。 -
重复 为空(不重复)
预计明年会有更高的数字,并在以后的一年里记录。 -
借方 A/C 存入银行的现金收据
-
贷方 A/C 销售收据
-
金额 10'000.00
-
总金额 10'000.00,下一次的操作在明年,因此总金额代表的是一个单一的金额
-
-
记账凭证号:102
商品预测成本指标,比例按月20%计算。-
日期 2月21日。发生业务后的第二天
-
重复 不重复
该操作于每个月的21日进行重复。因此,每个月的商品成本将按购销账户的发生业务百分比进行计算。 -
借方 A/C 货物成本记在货物账户中
-
贷方 A/C 银行 通过银行账户支付货款
-
-
记账凭证号:103
这两行类似于记账凭证 101和记账凭证 102,但针对的是三月份。-
重复 Y=每年。以后每年三月份的营业额和成本
-
-
记账凭证号:104至记账凭证号:112
在每月的20日预计一年中不同月份的销售额。
以后几年的收益
发生业务可以在接下来的几年中显示。
这些数据将用于确定未来几年的预算。
总金额列保持为空,是因为这些值超出了范围,仅限于当前会计期间。

-
记账凭证号:151
发生业务类似于上一年。-
日期 1月20日
-
重复 Y=每年
这将在今后的几年内重复。 -
总金额 为空(自动计算)
总金额列保持为空,是因为这些值超出了范围,仅限于当前会计期间。
-
季度末
一些典型的发生业务在每个季度末重复。

-
记账凭证号:70
以下是使用数量和单价列的示例。
已知的银行手续费是每月50.00,我们指明的是3个月的费用。-
日期 3月31日
-
重复 3ME=3个月末
-
借方 A/C 管理费用,通常是银行的费用
-
贷方 A/C 银行
-
金额 150.00(自动计算)数量乘以单价
-
总金额 600.00(自动计算)每季度重复一次,直到年底
-
-
记账凭证号:71
需要按季度支付的贷款利息。-
日期 3月31日
-
重复 3ME=3个月末
-
借方 A/C 利息 负债利息费用
-
贷方 A/C 贷款利息被添加到贷款中
-
金额 本季度的利息
-
总金额 本年度的总利息
-
-
记账凭证号:72
贷款的利息是从银行支付的。-
日期 3月31日
-
重复 3ME=3个月末
-
借方 A/C 贷款利息支出账户
-
贷方 A/C 用于支付利息的银行账户
-
金额,使用公式得出的结果,例如,本季度利息
-
总金额 本年度的总利息
-
-
记账凭证号:73
银行存款利息。-
日期 3月31日
-
重复 3ME=3个月末
-
借方 A/C 银行 银行账户
-
贷方 A/C 利息 利息收入
-
金额,本季度的利息收入
-
总金额,本年度的总利息
-
年末
这是一些年终的业务。我们使用重复Y,以便在以后的年份中执行。

-
记账凭证号:200
年末销售额的1%做为佣金。-
日期 12月31日
-
重复 Y=每年重复计算
-
借方 A/C 个人 个人费用
-
贷方 A/C 银行 银行账户
-
金额 付给销售人员的佣金
-
总金额 相同的金额
-
-
记账凭证号:201
偿还10%的未偿还贷款。-
日期 12月31日
-
重复 Y 每年重复计算
-
借方 A/C 贷款 贷款账户(负债)
-
贷方 A/C 银行 用于报销的银行账户
-
金额 6'000.00相当于贷款总金额的10%
-
总金额 相同的金额
-
-
记账凭证号:202
用于摊销的家具。 -
记账凭证号:203
用于调整库存。 -
这是非重复性的,因为评估应基于库存的资产价值。
自定义
使用创建新的自定义命令为打印输出生成新的合成,包括已在预算中设置的按组生成的打印参数。
您可以根据需要预设打印配置。
如果您了解合成的功能,则可以将其与其它命令一起使用,并创建适合自己目的的打印。
账户表中的报告
在账户标签中,查看预算列以浏览更新的预算金额。
第一年的财务和流动性计划
使用命令
- 报表 → 第一年季度预算,可以看到第一年的演变。
自定义已被设置成可视化。
- 按期间细分 → 季度
这两个打印的报表帮助您分析:
- 当前财政年度的经济预测 (费用和收入) 及预算。
- 银行往来账户中流动性的详细演变。
修改或创建一个新的自定义按月细分。

按月

四年的财务和流动性计划
使用命令
- 报表→四年预算
将显示以下内容的预定义组合:
- 从2022年1月1日到2025年12月31日期间
在此报告中,您也可以指定与会计期间不同的时期。程序会在指定期间内自动核算金额。 - 每年细分。

账户明细
打开预算表后,单击银行单元格,将显示账户明细中包含的所有预算发生业务。

Tutorial file for amortisation and interest calculation with budget's formulas
Tutorial file for amortisation and interest calculation with budget's formulasThe possibility to enter formulas is available in Banana Accounting Plus only with the Advanced plan. Update now!
预算及财务计划的完整示例教程 (含公式)
预算及财务计划的完整示例教程 (含公式)此模板中的示例,展示如何使用预算表中的公式选项卡,以及数量和单位价格列。
有关如何使用预算表及其列的说明,请参阅预算及商业计划页面。
请记住,计算是按时间顺序进行的,而不是根据预算登记输入的顺序进行的。
数量和单价列的使用

在公式界面中,您可以看到数量和单位/价格列。
- 记账凭证号 10:在一个月内以价格/单位的价格出售的咖啡数量(数量列)和咖啡销售总收入(总金额列)。
- 数量和价格/单位列的值也可以输入负数,但是金额会自动转化成正数。
JavaScript语言公式
 在公式列,您可以输入JavaScript语言表示的计算。
在公式列,您可以输入JavaScript语言表示的计算。
- 如果公式的结果是数字,它会在相应列中显示为金额。
- 记账凭证号21和22:可以指定数字或数学表达式。
- 记账凭证号40和41:“//”表示已输入注释。
- 记账凭证号42:在 /* e */ 之间输入的文本被视为注释,而不是公式的一部分。
公式错误

当输入数据发生错误时:
- 包含错误的行以红色突出显示。
- 错误消息显示在信息窗口中。
为了避免弹出的错误提示窗口有持续的声音信号,错误已在示例模板中被视为注释(它们以 "//"开头)。
分号分隔符 ";"

JavaScript使用 ";"来终止命令的每一行。您可以将数学表达式连接成一行。返回值将是最后一个表达式的结果。
逗号分隔符 ","

在JavaScript中,逗号用作函数不同表达式之间的分隔符。结果值将是最后一个表达式的结果。
不要把逗号用作小数点的分隔符,因为在公式中它会被视为表达式的分隔符,因此数值将被切断。
句号分隔符 "."

JavaScript使用句号 "." 作为小数点的分隔符。无论操作系统首选项中的小数点设置是什么,都要始终使用句号。
简单数字计算

您可以在公式列中使用简单的数字组合数学计算。
文本和变量

- 文本在引号之间,作为引号。
- 变量是提及的已分配值的元素。
- 变量名称必须以字母或下划线开头。
- 首先,必须通过分配“变量名称=100”来定义变量。
例如:
- 记账凭证号70
引号之间的"Banana" 是一个文本。 - 记账凭证号101
为该变量分配了一个值100。 - 记账凭证号102
将使用金额变量的内容。 - 记账凭证号103
将使用金额变量的内容,增量为10。 - 记账凭证号Doc
金额变量的内容以10的增量分配给金额变量。金额变量等于110。 - 记账凭证号105
该公式将按月重复计算"重复 = M"。- 第一次110+10 = 120
- 第二次120 + 10 = 130,以此类推。
- 记账凭证号106
如果未输入注释,则会显示一条错误信息,表明尚未定义金额1。 - 记账凭证号110
名称 "Banana" 已经分配给文本变量。
控制 if .. then .. else 流
您可以使用JavaScript的所有条件表达式。主题很广泛,建议您参考 有关JavaScript语言文档。
在这里,我们只想指出在JavaScript中:
- 等号 "=" 用于为变量 "a=10" 的分配值
- 相反,为了比较,使用两个连续的等号 "==" 。如果 (10==10) {1};

- 记账凭证号200-203
如果单词 "if" 之后的括号中给出的条件为真 "(10==10)", 则金额列将显示大括号 "{1}" 中的下一个表达式的结果。
如果条件为假,则 "(10==9)" 为零。
属性和功能

可以使用预定义的JavaScript函数,例如,数学模型 .round (请参阅记账凭证号220-222示例)。
要调用一个函数,请在函数名称后面加上括号内的函数参数。
- 记账凭证号220
数学模型中的 .min (10, 30, 2) 将返回逗号之间指定值的最小值。
当前行的"行目标"

行目标是Banana.Document.Row类型,它引用当前行。
通过价值函数指定列名,将返回改特定列的内容。
预定义的借记和贷记功能

公式仅允许使用正值。
- 如果是正数,借记功能将返回作为参数输入的值。
- 如果输入的值是负数,贷记功能函数将返回的值反转。
整个期间的会计功能

在没有指示定义期限的情况下,使用特定的预算功能将返回相对于当前状况的值。
请注意并记住,行中的数据是按顺序处理的,因此该行将没有后续值。
在定义期间使用会计功能

在定义的期间内使用会计功能。
当前期间的budgetBalance函数将始终与整个期间的函数相同,因为budgetBalance函数将返回该期间末的余额,并且处理的最后一行也是当前期间的最后一行。
相反,budgetOpening和budgetTotal函数会将初始日期考虑在内,因此有必要对其进行指示。
利息计算功能

budgetInterest函数以实际天数(365/365)为基础,根据指示的帐户在输入日期计算利息。在计算当月的利息时,必须将月末表示为日期。
- 记账凭证号500
第二个参数代表利率,5表示5%,如果需要支付借方利息,则会在相应的日期进行计算。 - 记账凭证号520
如果有应付利息,会在相应的日期进行计算。这将在银行账户显示为负值。
计算所得税的功能

- 记账凭证号600
对于所得税的金额在损益表的最后一组(在这种情况下,02)中的 "budgetTotal" 期间计算出的移动。
贷记 (budgetTotal("Gr=02","YC"))*0.10- 您可以在当前年度的预算总计中获得组移动
budgetTotal("Gr=02","YC") - 贷记功能 () 函数仅在其值为负为返回该值并将其转换为正。
贷记 (budgetTotal("Gr=02","YC")) - 结果乘以 0.10 (百分比 10%)
- 在借方账户中,必须指出损益表中的税收账户。
- 在贷方账户中,必须指出银行账户或国库贷方账户。
- 您可以在当前年度的预算总计中获得组移动
用户定义功能
在文档表中,添加了一个“ _budget.js”文件,您可以在其中定义公式列中调用的Javascript函数。
以累进税率计算所得税
- 记账凭证号610
利润首先被计算并分配给变量。 - 记账凭证号611
利润被传递到calcTaxes()函数,该函数根据金额应用税率并返回要支付的税额。
其他用户定义的功能
- 记账凭证号620
调用了test()函数,该函数也在budget_js文档中定义,该文档仅返回一个值。
使用变量进行下一步计算

变量对于存储下次计算的值非常有用。
- 记账凭证号700-704
销售指数- 记账凭证号700
索引固定为1(100%)
这里不使用借方账户和贷方帐户,因为该行仅用于定义价格指数。 - 记账凭证号701
成本单价变量用于购置成本的计算(0.2=20%) - 记账凭证号702
销售额是价格指数值的1000倍。 - 记账凭证号704
自3月1日起,该指数将增加
- 记账凭证号700
- 记账凭证号720-722
每月的销售数字分配给月份功能,然后计算销售佣金。
JRepeatNumber列

当行中包含重复时,将会将重复代码作为JrepeatNumber插入公式单元格中。
- 第一个重复值为0
- 第二个重复值是1,依此类推
当重复不允许您覆盖预定义的变量时,请使用JRepeatNumber。
通过使用JrepeatNumber作为对象的参数,可以注册序列并在以后的阶段调用它。
多币种财务计划的完整示例教程 (含公式)
多币种财务计划的完整示例教程 (含公式)该示例说明,如何在复式记账含外币功能中使用公式。
要使用这些功能,需要使用Banana财务会计软件8.0.5以上版本。
在以前的版本中,某些功能不可用,并且会显示错误消息。
请参阅以下页面以获取更多信息:
以基准货币计算的金额
该公式先以帐户的第一货币来计算金额,然后以基准货币计算相对价值。
汇率及历史汇率

-
记账凭证号10和12
如果汇率列中指示了汇率,程序将使用此行中指示的汇率来计算基准货币(在该示例中为EUR)的金额。 -
记账凭证号11和13
如果没有指示汇率,程序则会执行汇率表中汇率进行计算,并在使用重复功能的情况下进行后续操作。 -
如果在汇率表中定义了历史汇率,则可通过添加日期,程序将执行相对于该日期或与上一个日期最近的汇率。
使用基准货币公式

预算表中显示的所有公式都可以在公式列中使用。
以下示例展示了根据公式计算出的基准货币(EUR)的价值。
-
记账凭证号21
销售价值根据公式欧元的价值相乘。相应列中的汇率将被忽略。 -
记账凭证号22
如前面的示例,对于货币金额,是公式计算的结果。 -
记账凭证号23
在 "_budget.js" 文档中,我们定义了一个汇率函数,该函数根据行中的内容计算价值。
利用这些功能,可以创建模拟汇率。
汇率功能示例
美元汇率是按月确定的。
稳定汇率改为使用英镑。
该函数的结果为AmountCurrency的数量乘以汇率。
function cambio() {
var importo = row.value("AmountCurrency");
var cambio = 1;
var moneta = row.value("ExchangeCurrency");
var data = Banana.Converter.toDate(row.value("JDate"));
var mese = data.getMonth() + 1;
if (moneta == "USD") {
cambio = 0.95;
if (mese == 1)
cambio = 0.96;
else if (mese == 2)
cambio = 0.97;
}
if (moneta == "GBP") {
cambio = 1.30;
}
return importo * cambio;
}
汇率差额计算公式
有关计算汇率差额的更多信息,请参考有关多币种发生业务和创建汇率差页面。

-
货币始终是基准货币。
-
不能使用帐户的货币输入金额。
-
汇率留为空白,即使输入值也将被忽略。
-
budgetExchangeDifference函数计算一个帐户的汇率差额,该值表示未实现的汇兑损益。
-
如果该函数是汇兑损失,则函数返回正值;如果是汇兑利润,则返回负数(贷方)。
因此,必须创建两个账户,一个用于汇兑收益,一个用于汇兑损失。 -
返回的金额是基准货币的必要重估,以确保基本货币帐户的余额等于货币帐户的余额,并以用于计算汇兑差额的汇率转换。
-
-
budgetExchangeDifferences函数的第一个“ CUSD”参数是您要为其计算汇兑差额的外币帐户。
-
第二个参数是要被应用的汇率。
- 如果没有显示汇率,则使用与指定日期有关的历史汇率。
- 如果存在“current”,则使用汇率表中没有日期的汇率。
- 您可以指定汇率,小数点分隔符必须是 "."符号。
credit(budgetExchangeDifference("CUSD"))
credit(budgetExchangeDifference("CUSD", "current"))
credit(budgetExchangeDifference("CUSD", "0.95"))
IFRS
Definition and principles of IFRS for SME
Definition of IFRS for SME
They are a set of accounting standards adopted globally for the financial statements of small to medium-sized companies with the goal of ensuring transparency, reliability, and comparability of the companies’ financial information.
They were issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), an independent organization based in London, composed of a group of experts with the function of defining accounting principles, preparing, reviewing, or using financial statements, and in accounting training.
When the IASB releases a new standard, there must be approval from the European Union, in the specific approval process, the responsibility lies with the European Commission with other consumptive entities.
IFRS Purposes
The main purpose is to create a common accounting framework for most companies operating within the European Community, offering the advantage of greater simplicity and transparency in relation to the balance sheets and financial information.
The objectives are characterized in various aspects as follows:
Transparency:
provide stakeholders with clear and detailed information on the company's financial status and performance.
Reliability:
financial reports that correspond to the business reality and are trustworthy.
Uniformity:
to report financial information that is comparable on a global scale.
Relevance:
to ensure that important information is provided to potential investors and other stakeholders.
Fundamental Principles IFRS SME
The characteristics of IFRS standards are based on principles as explained below:
Full Disclosure
All relevant information must be fully disclosed.
Substance over Form Principle
Transactions must be accounted for and presented based on their economic substance and reality, not just their legal form.
Principle of Prudence
Uncertainties and risks must be duly considered.
Fair Value Measurement
Numerous balance sheet items must be measured at their fair value, rather than at their historical cost.
Qualitative characteristics of financial information
Understandability
The presentation of financial statement information should be understandable in terms of the company’s commercial and economic activities. This principle does not allow for the omission of important information as it would become difficult to understand for some users.
Comparability
Information about an entity is useful if it can be compared with similar information from other entities. This characteristic allows stakeholders to identify and understand similarities and differences in business accounting realities.
Verifiability
Verifiability helps ensure a faithful representation of the company’s accounting and financial information. Quantified accounting information does not necessarily have to be an exact estimate to be verifiable.
Timeliness
Timeliness means having information available in time to make decisions. In this sense, the older the information, the less useful it is. There are exceptions, it is emphasized that for some information it can also be less timely since there is an evaluation over a longer period of time to study and identify trends.
References:
Composition of IFRS for SME
Introduction
According to Article 3.17 of the document "Exposure Draft IFRS for SMEs® Accounting Standard - Third edition of the IFRS for SMEs Accounting Standard - September 2022", it must include all of the following documents in order to have a complete set of financial statements:
- Financial statement.
- Income Statement.
- Statement of changes in equity.
- Cash flow.
- Notes.
References
Statement of financial position
It is a document that represents the balance sheet and financial situation of a company. The balance sheet is separated into current and non-current assets, and consists of assets, equity, liabilities.
Current assets comprise resources that are expected to be liquidated or used as part of usual business operations within one year from the date of the balance sheet. The distinction is particularly useful for investors who distinguish between net working capital and capital used for long-term operations in an operating cycle.
There is also another presentation, it is based on the degree of liquidity, but is suitable for banks and financial institutions that do not provide goods or services within an identifiable operating period.
Non-current assets are corporate resources that are expected to remain in use for an extended period beyond twelve months after the balance sheet date.
Short-term (current) liabilities are those due within the usual operating cycle or within twelve months after the balance sheet date. Trade payables must always be classified as short-term liabilities even if their settlement occurs beyond the normal operating cycle or more than twelve months after the balance sheet date.
Long-term (non-current) liabilities are those due beyond the normal operating cycle or more than twelve months after the balance sheet date.
Income statement
The income statement is the representation of the profit and loss account and is classified according to the by nature of expense method.
The classification by nature is one of the options available from the IFRS for SMEs, and since it is the simplest and most flexible for different business realities, it was decided to implement this approach.
The concept is that costs are aggregated according to their nature, such as depreciation, purchases of materials, transportation costs, etc.
There is also the classification by cost destination, where costs are distinguished between cost of goods sold and other costs, which provides more meaningful information but requires a considerable degree of discretion on the part of the financial statement preparer.
Statement of changes in equity
The statement of changes in the equity of a company between two financial years reflects the variations in the net equity due to the increase or decrease of its net assets for the period or the wealth generated, based on the specific valuation criteria implemented and indicated in the financial statements.
Cash flow
The IFRS for SMEs stipulates that entities must categorize their transactions into three distinct activities:
- Operating.
- Investing.
- Financing.
It further permits entities to present their operating cash flows using either the direct or indirect method. Ultimately, the framework’s goal is to furnish decision-useful information to users, aiding them in making informed economic choices.
Notes
The notes to the financial statements represent a fundamental part of financial reporting under IFRS for SMEs. They provide additional and detailed information that integrates and explains the data presented in the main financial statements.
Furthermore, they play a crucial role in ensuring the transparency and completeness of financial reporting, allowing users of the financial statements to fully understand the company's financial position, performance, and cash flows.
In conclusion, the notes to the financial statements are therefore an essential tool for improving the transparency and comparability of financial reporting at an international level.
Reclassification IFRS with Banana
Reclassification IFRS with BananaIntroduction
On this page, there is a brief explanation of the templates created with the Banana accounting software and how to use them to print the income statement and balance sheet report according to IFRS standards for SMEs.
At the bottom of the page are links to download the templates.
Template IFRS SME
The template file is set up with the IFRS SME chart of accounts in which the Statement of financial position, Income statement and Statement of changes in equity are present.
This file refers to the document "Reclassification IFRS SME" to print the report according to the IFRS SME setting, with the use of the financial statements embellished by groups.
For more information on financial statement enhanced balance sheet with groups:
- Video of how-to do enhanced balance sheet with groups.
- Documentation about enhanced balance sheet with groups.
- Documentation about reclassification of financial statement and Income statement.
Reclassification IFRS SME
The document contains the basic settings to print the page layout (document title, company master data), amounts, totals, subtotals of the Statement of Financial Position and Income Statement accounts.
The accounts will be printed even if the amount is zero. If you want to change the setting of this printout or the style you can do so within this file.
Report creation with Statement of financial position and Income statement
To create a report with the Statement of Financial Position and Income Statement documents, follow the next steps:
- Open the template file and record all case-specific accounting transactions.
- Click on Reports -> Enhaced balance sheet with groups
- Enter the important data relating to the reference company (e.g. document name, company master data) in the Page-Header and Footer section.
- You can make other settings by reading the details on Banana's site on the enhanced balance sheet.
- Click OK.
At the end of the process a new file will be opened with the Statement of Financial Position and Income Statement inside.
Download IFRS SME per Banana
We make the models available without any liability, as stipulated in our Terms and Conditions of Use.
Excel file structure
Introduction
On this page, there is a full explanation of how to use the file, what to find in it and its logic.
In addition, there are illustrations and sample figures to help explain how to use the Excel file. The amounts shown in these images are purely for illustrative purposes and do not necessarily reflect actual or significant values.
Documentary reference
For the creation of the accounting structure within the Excel file, the indications of the documentation related to the IFRS standards for SMEs were followed.
Specifically, the documentation is:
- Accounting principles, notes and other: "Exposure Draft IFRS for SMEs Accounting Standard" of September 2022".
- The presentation of the accounts and the explanatory notes: "IFRS Taxonomy Illustrated IFRS Accounting Taxonomy 2023".
Description structure file
The Excel template is divided into ten main parts:
- General information.
- Financial Statement.
- Income Statement.
- Financial Statement detailed.
- Income Statement detailed.
- Statement of changes in equity.
- Cash flow indirect.
- Notes of financial statements.
- Notes of income statement.
- Notes of cash flow statement.
In order to have a complete set of IFRS financial statements for SMEs, it is mandatory to complete the sheets on General information, Financial statement and Notes of financial statements, Income statement and Notes of income statement, Statement of changes in equity and Cash flow indirect and Notes of cash flow statement.
The Financial Statement detailed and Income Statement detailed sheets, are an alternative to the compilation procedure specified above, as they integrate the entire aspect of the Financial Statement and Income Statement, with all accounts detailed by the notes, having a direct view of the composition and structure of an account with the notes.
Organitation of the file
File content
The file contains seven fields:
- Main field.
- Main account.
- Sub-category of the main account.
- Code.
- Formula.
- Note.
- Account amount.
In the main field, you specify the name of the main account, the document reference and generic company information.
The main account is the name of the main account.
The sub-category of the main account can only be displayed if the Statement Financial detailed and Statement Income detailed sheet is used. It is an account taken from the notes and serves to detail the structure of an account, as required in the IFRS notes for SME.
The code is used for Banana's accounting model and serves to identify the account.
The formula is applied for account totals and subtotals.
The note is account-specific and is entered for some accounts as per the IFRS documentation for EMS.
The account amount is a number to two decimal places without currency indication.
Some fields are not editable as they are an essential part of the file structure. The only part to be changed are the amounts to be entered for the various accounts and the descriptions in the note sheet.
The legend below summarises what the fields correspond to and which are and are not editable.
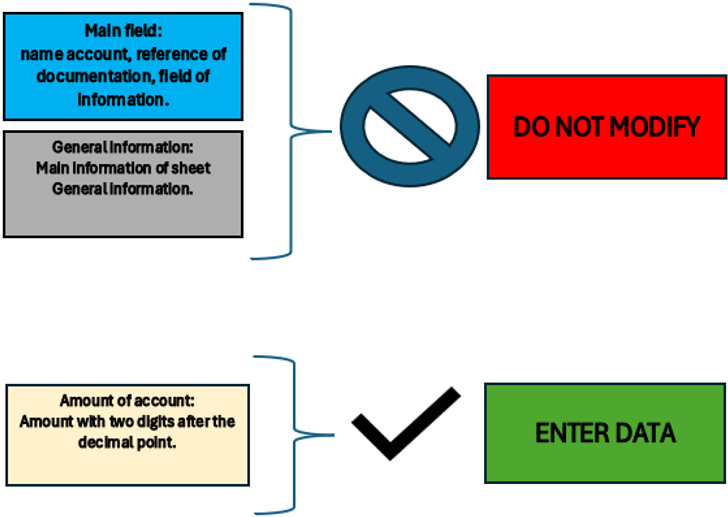
Figure of Excel in the sheet Legend
In the General information sheet, the essential information required by IFRS for SME is entered.
The essential information is useful to understand the biographical data of the company, the relevant accounting period, the currency used, the main activities and the content of this file, which is the complete structure of the financial statement.
Certain information such as company name, company name, domicile and accounting period is reported on all sheets specifically for the Identifying information of company.
General information
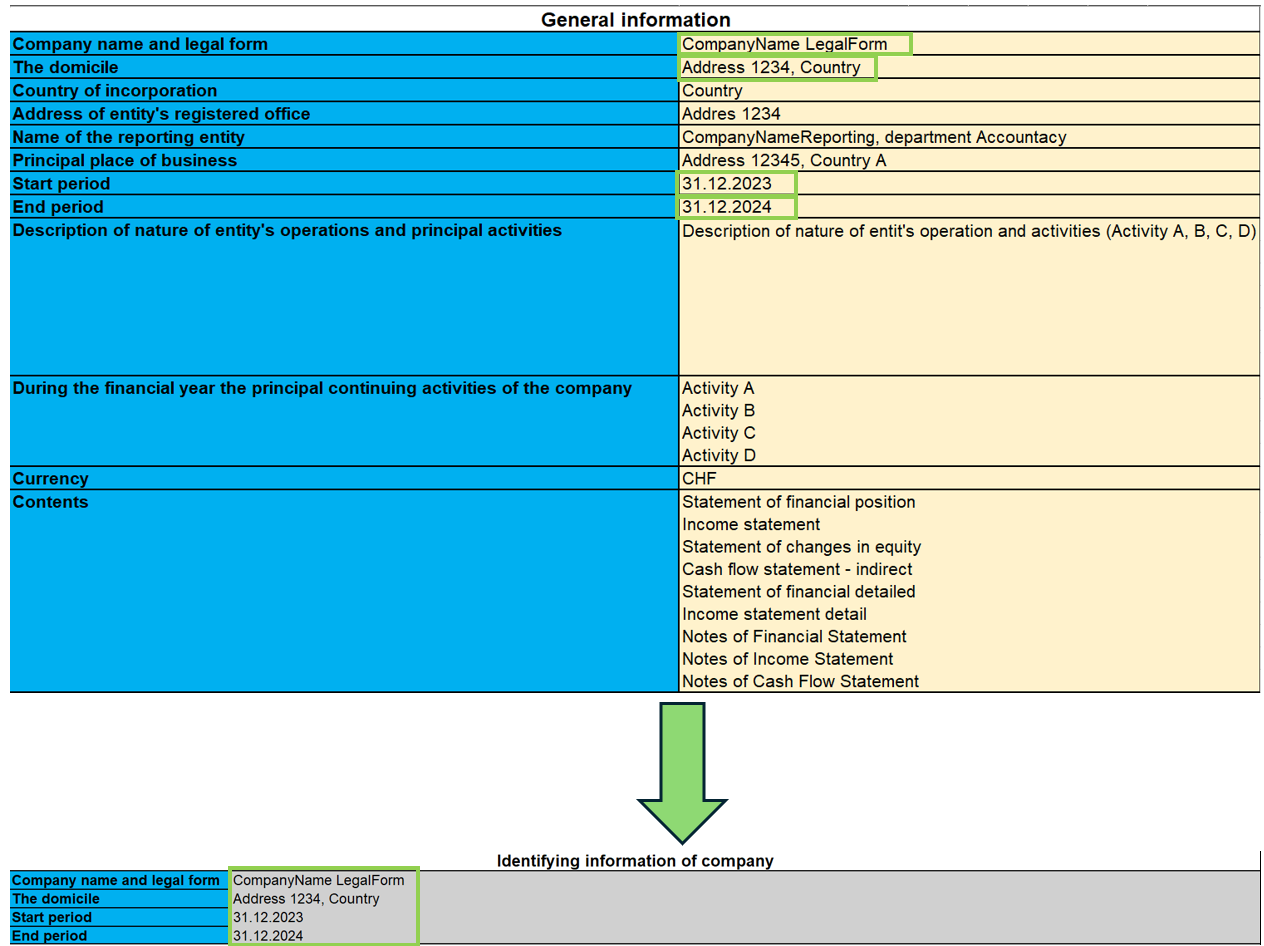
As shown in the image, the information entered on this sheet is carried over to all sheets, so that the company can be identified on each IFRS document, such as: the full name of the company, the address and registered office, and the beginning and end accounting year to be taken into account for accounting purposes.
Statement of financial position
The Financial Statement contains all account items relating to the current and non-current positions of the business for the years 2023 and 2024.
In this part you are required to enter the budget amounts in the specific accounts. Totals and subtotals are calculated automatically by the formulas.
It should also be noted that for some accounts it is mandatory to complete the Notes. This is done by entering the amounts and other descriptive notes in the ‘Notes of Finacial Statement’ sheet.
If an account has notes, its amount for the last year refers to the corresponding cell of the account total put in the notes, so it is necessary to fill in the amounts in the notes first.
For the notes, there is also the possibility of consulting the documentation indicated in the ‘Reference documentation’ field, specifying the page and section where the information on the notes can be found.
Finally, there is a final check part to see if the total assets and liabilities are equal.
Modalities of use
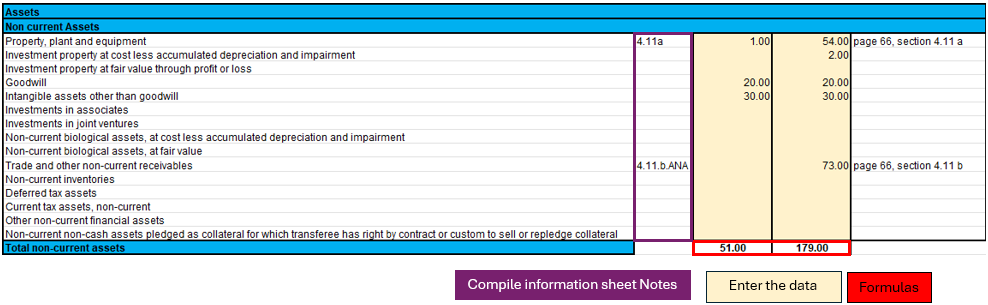
In the picture shown, a part of the Statement of Financial Position is selected as an illustrative example to guide the user. There are three highlighted parts in the image:
- Notes.
- The formulas.
- The data to be filled in.
Each part has its own specific function and in some cases the data are directly linked to each other.
Specifically, if an account has notes, it means that in the ending balance (31.12.xx) there will be the total of the amount calculated in the ‘Notes of financial statement’ sheet. This implies that in order to change that amount, one must fill in the account data on the "Notes of financial statement" sheet.
In this sheet one must therefore:
- Verify that the account is not linked to notes and enter the amount in the account.
- If there are notes, then only the ‘Notes of financial statement’ part of the sheet must be filled in.
The formulas integrated in this sheet will make the totals and subtotals of the accounts in the Statement of financial position.
Income Statement
The income statement is presented according to the classification ‘by nature of expense’.
This classification is an aggregation of costs according to their nature (e.g. depreciation, purchase of materials, transport costs, salaries, advertising costs, etc.) and are not allocated according to their purpose within the company.
The implementation of this classification was decided upon because it is simple and widely applicable for SMEs. The other classification was according to costs by function, where a distinction was made between costs of sales versus other costs (e.g. distribution costs or administrative costs) and this representation requires a considerable degree of discretion on the part of the end user.
As previously done for the Financial Statement, there are the amounts to be entered while the totals are already calculated by means of the formulas applied in the sheets.
In addition, a further breakdown has been made for EBIT (earnings before interest and tax) and EBT (earnings before interest).
Modalities of use
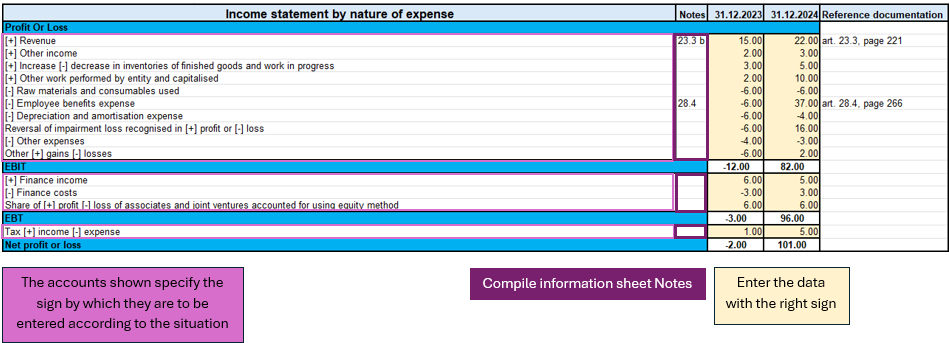
This figure highlights the important parts of the income statement.
Looking at the accounts, there are indications of the signs (+/-) to be used in the various circumstances, which implies that for accounts that have both positive and negative signs, there is an assessment of the positive or negative impact of that amount on the result of the income statement.
As previously seen in the ‘Statement of financial position’, there are also notes to be entered in the relevant sheet ‘Notes of income statement’ in order to be able to correctly define the amount, as the latter depends on the total in the notes.
In summary, what you need to do on this sheet are the following steps:
- Evaluate the circumstances of the account with both positive and negative sign and understand whether you are in a situation where it has a positive or negative impact on the result.
- Verify that the account is not linked to notes and enter the corresponding amount with the correct sign.
- If the account is correspondent with the notes, then only the ‘Notes of income statement’ sheet must be completed.
Statement Financial detailed
This document differs from the Statement of financial position in that there is more detail on the accounts. The official presentation of the accounts can be found in the ‘Statement of financial position’ sheet in terms of how the accounts are summarised; in this sheet, however, we have more detail, with the aim of avoiding filling in the notes directly in the specific sheet. The use of this sheet excludes the use of the ‘Statement of financial position’ sheet because they refer to the same notes.
The main difference is that not only the main accounts required as a presentation by IFRS for EMS are shown, but they are detailed in sub-categories of accounts that are the same as those found in the notes, so that using this document one can avoid filling in the notes, using only the sub-categories of accounts, except in some cases where the account requires descriptive textual type details, without using calculation formulas or amounts. For this reason, not all parts of notes are integrated, as some accounts require a textual type description.
To distinguish the main accounts from the sub-categories of accounts, the main categories are coloured dark, while the light categories are the accounts related to the notes.
If there are no subcategories of accounts (coloured light), then it is sufficient to go to the specific Notes of Statement or financial position sheet.
Modalities of use
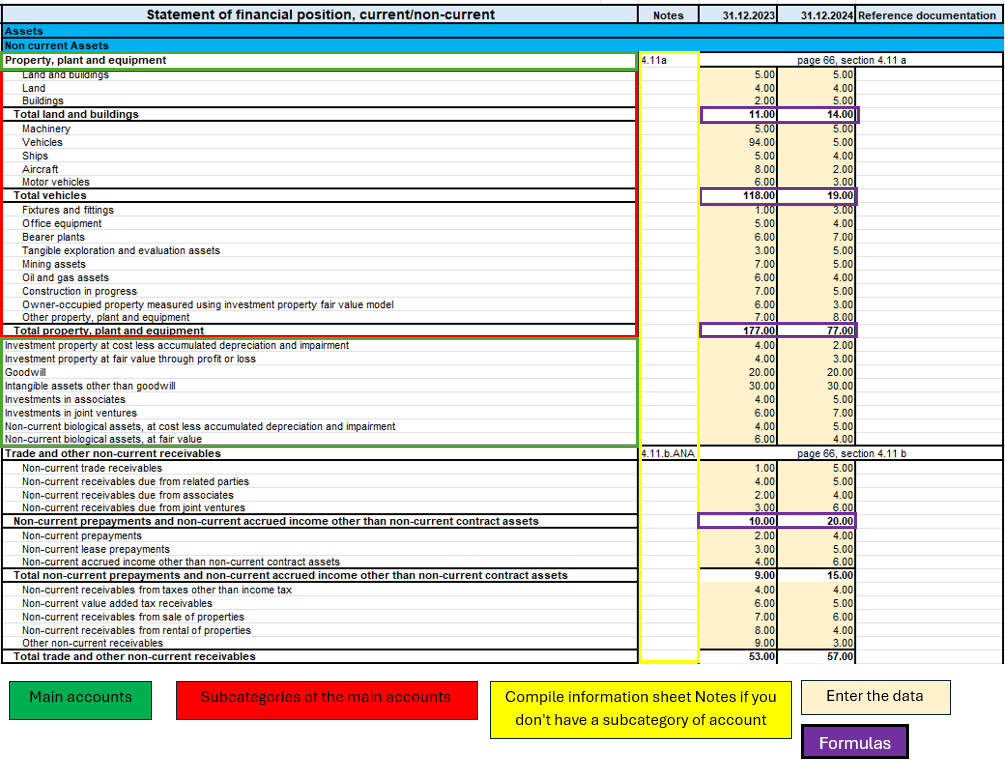
In this image, you can see four essential parts of the document:
- Main accounts.
- Subcategories of the main accounts.
- Notes.
- The amounts to be entered.
- The formulas.
This part, there is more detail only if an account has notes, otherwise it is the same as the Statement of Financial Position. What requires attention is the verification of an account if it is an account with notes and has no sub-categories of accounts, if you find yourself in this situation then it means that the account requires an additional textual description to define some peculiarities in the ‘Notes of financial statement’ sheet.
On the other hand, for accounts that have notes but also account sub-categories, only the amounts of the sub-categories of the specific account need to be filled in. In this way, having filled in all the amounts of the sub-categories of the account, the formulas applied to the sub-categories will calculate the subtotals and the total of the main account.
So to summarise, the procedure for filling in this sheet is:
- I enter the amounts in the main accounts if there are no notes to refer to.
- If the main account has notes, I check that it has sub-accounts, if it does not, then I go to the ‘Notes of financial statement’ sheet and fill in the text description.
- If, on the other hand, the main account has notes and has the subcategories of accounts, then I only fill in the amounts of the subcategories.
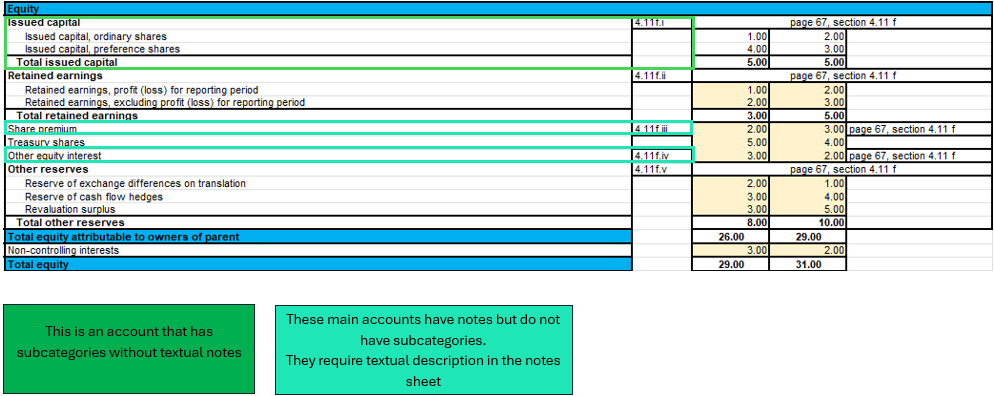
In this example image in the Equity part, a case is illustrated where an account has notes but no account subcategories, which requires a textual description in the ‘Notes of financial statement’ sheet, and a normal case where there are notes with account subcategories.
Income statement detailed
Income statement detail is based on the same logic as the Statement of financial detailed, with the aim of providing a single document for its function, detailed by the accounts of the notes, without having to fill in the Notes of income statement.
There are the main accounts and when there are notes, they are detailed by the sub-categories of accounts that are part of them.
Modalities of use
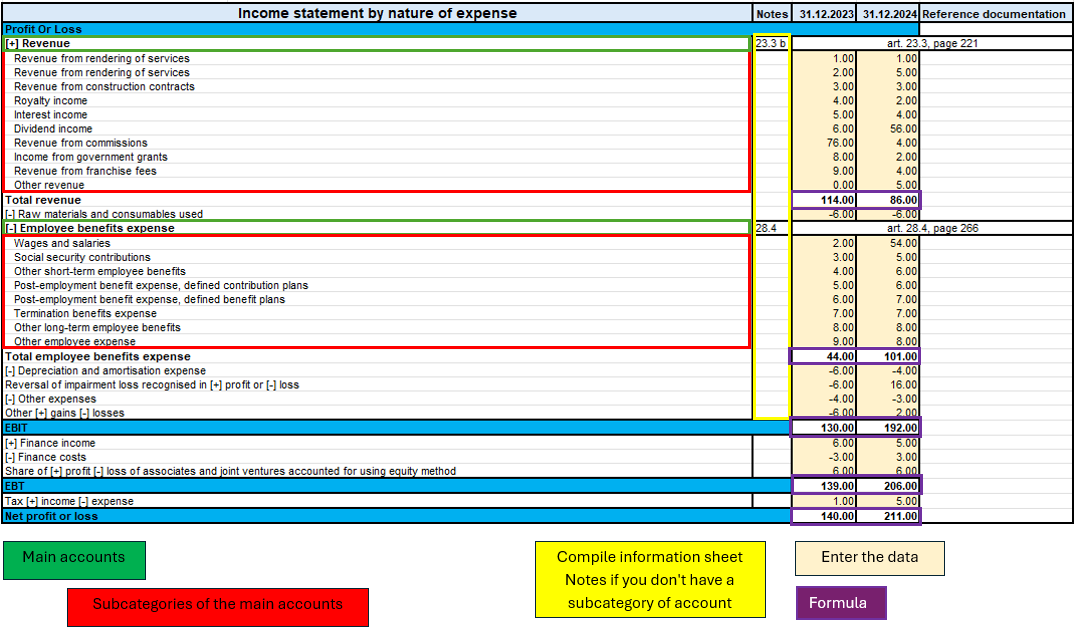
As illustrated in the figure above, there are four equal parts to the ‘Statement of financial detailed’ sheet with the same logic.
The only difference is that there are no descriptive notes, so all accounts with notes are already with their sub-categories without requiring additional compilation on the ‘Notes of income statement’ sheet.
Therefore, to summarise, it is essential to follow these steps:
- Enter the amounts of the main accounts if they have no notes.
- If the main account has notes, enter the amounts only in the subcategories of the account.
The Statement of Changes in Equity
The Statement of Changes in Equity reflects changes in equity.
This part provides insight and transparency into decisions and their effect on the value of equity. It is also a useful tool for investors and other stakeholders to understand how the company has generated and utilised equity capital.
Modalities of use
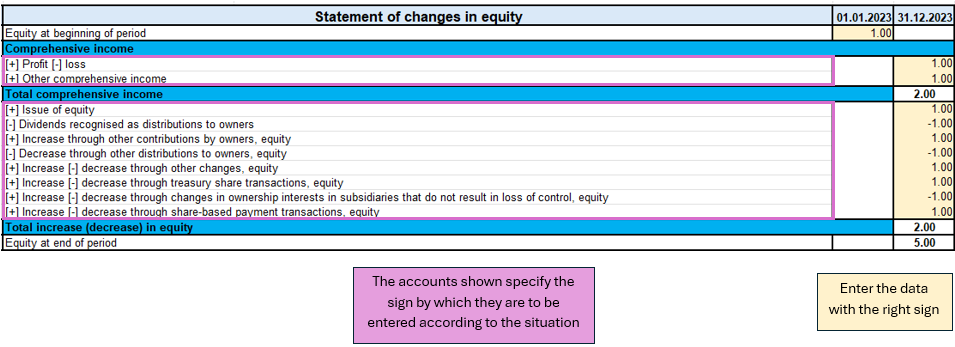
In the sheet ‘Statement of changes equity’ as shown in the image, there is one part to pay attention to.
The first is the evaluation of the change in the account item, whether it increases or decreases, and then according to the sign (+/-) the amount must be written with the correct sign.
Unlike other documents, this one does not require notes.
So the process of completing the document is:
- Evaluate the account change and follow the indications on the sheet on the sign to be taken in the various circumstances (increase or decrease in the account).
- Enter the amount with the correct sign.
Cash flow indirect
This document draws up the entity in four parts:
1. Cash flow from operating activities;
2. Cash flow from investing activities;
3. Cash flow from financing activities;
4. Net cash flow.
The document is independent of the other sheets, so you have to do your own calculations to deduct the various amounts to be included in the cash flow items.
The accounts are taken from the IFRS for SME taxonomy, first there are the profit or loss adjustments and then the operating activities are calculated.
Investing activities are characterised by the purchase or sale of fixed assets such as equipment, real estate, joint venture participations and others.
Cash flows from financing activities are related to the company's sources of financing, such as leasing, share issues, debt repayments or financing income. There is also the payment of dividends to shareholders.
In the last part of cash flow there are some clarifications to be made. The net change in cash is assessed in two steps, the first is calculated before the effect of the exchange rate change and the second after this change. In addition, as a form of control, the change in liquidity is also calculated, showing the changes in the period of activity, by calculating the difference between the initial and final liquidity balance.
Modalities of use
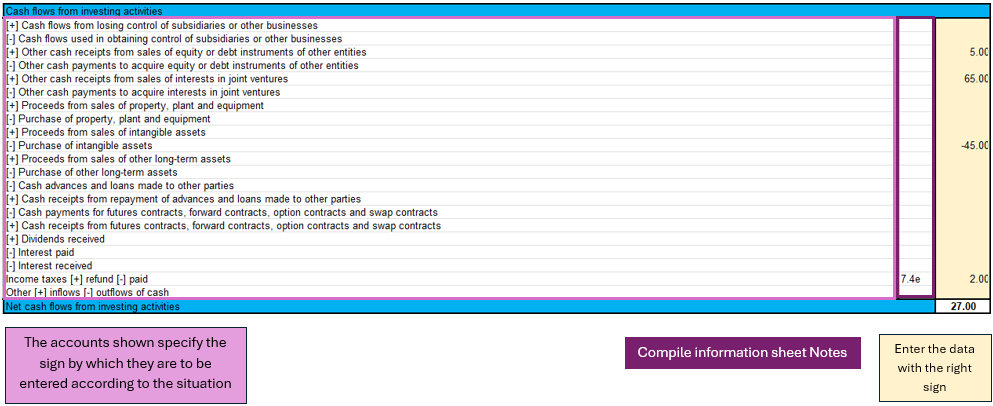
As shown in the figure of the cash flow for investing activities, three main components can be identified:
- The main accounts show the sign depending on the situation.
- For some accounts, the notes of cash flow statement are required.
- Entering the amounts requires attention with respect to the sign.
In the cash flow statement, reasoning on the implications of the balance sheet and profit and loss accounts is required in order to conclude which amount to enter in the specific item of the cash flow statement, so the conclusion depending on which cash flow statement has been analysed, could be an increase or decrease of an asset, a payment for property purchase, payment of dividends to shareholders,...
There is no sheet for this purpose, the user must reason with the amounts available, entered in the balance sheet and profit and loss account, and come to his own conclusions.
Next, having an amount, one must distinguish the situation as indicated in the sheet, in order to enter the amount with the correct sign.
Finally, in the event that it is required, fill in the notes of cash flow statement with the specific amounts in the case.
Notes
The notes are divided by the three IFRS documents:
- Notes to the Financial Statement.
- Notes of the Income Statement.
- Notes to the Cash Flow Statement.
As mentioned in the introductory section, the notes serve to supplement the information taken from the financial documents.
The note sheet contains four essential parts: the note code, reference account, amount and notes (text).
The note code is the reference for each part of the documents that serves to understand in which account the notes are to be completed.
The account represents the account taken from the document (Financial Statement, Income Statement, Cash Flow) to be detailed in the notes.
The amount is singular for the detailed account and is not always required because in some cases only a textual description is needed.
Notes as text are necessary if there are cases where only a description or more detailed customisation is required to explain an account.
Modalities of use
Case for the Financial Statement
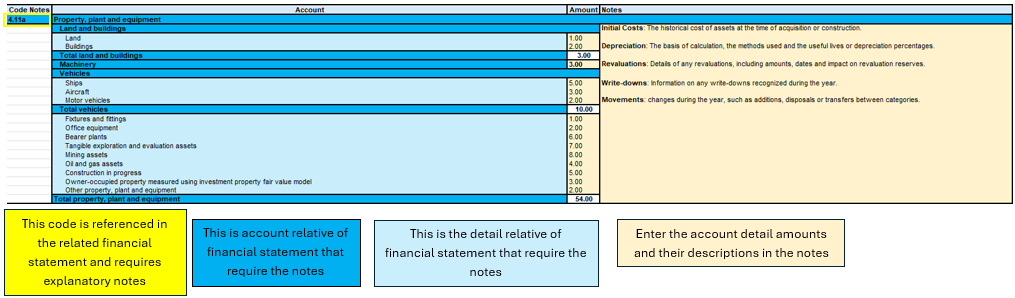
Figure of Excel in the sheet Notes of financial statement
In this image, four main components can be seen, the account reference code, the account, the detail grouping the sub-categories of accounts, the amounts to be entered with any textual notes.
The starting point for completing this sheet is then the financial statement, where we list which accounts need more detail, and then move on to complete the information in the notes sheet.
The data entry part concerns the amount of the detail account and any descriptive text.
The account totals and subtotals are calculated from the formulas, the account total is shown on the main sheet of the financial statement, so it is essential that if an account needs notes, it is only on the notes sheet.
Case for the Income Statement
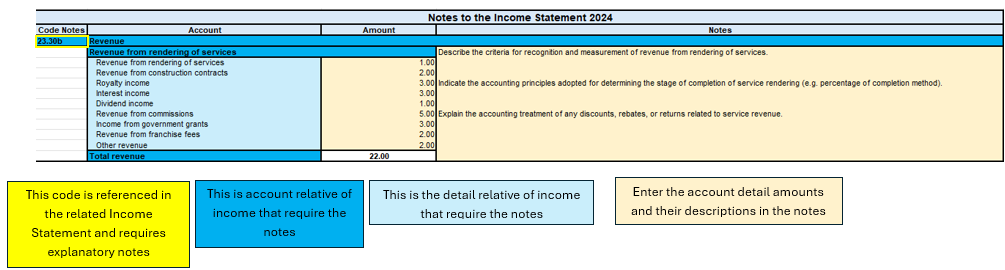
Figure of Excel in the sheet Notes of income statement
As seen above, the structure does not change for the Income statement notes. The main parts are always the same, as also for the cash flow notes.
To summarise therefore in this process one must:
- Depending on which sheet you are compiling, you must check that the analysed account of the financial statement, income statement or cash flow note is there.
- All the necessary data and information must be filled in.
- If there is a sub-account in the notes that is not needed or not used, you can simply leave it blank or enter a zero amount.
Objectives of the file
The process of creating the IFRS structure for SMEs took the official documentation and reconstructed a structure in the Excel template, with the aim of allowing the user to follow the IFRS reporting logic by entering the main information in the parts of the file.
The basic characteristics of such a file is the completeness of the document by having all the main parts required for IFRS, the usefulness of preferring the most widely used models that are more suitable for several companies, and excluding other more specialised models only in certain contexts.
The end result is to have a financial and economic view of the company's situation in the specific period, in compliance with the IFRS standards for SMEs.
In addition, the aim of IFRS for SMEs is to improve the comparability of financial data between different companies, to facilitate the analysis and interpretation of financial results by stakeholders outside the company, and to promote the adoption of IFRS for SMEs by providing a practical and accessible tool.
Free Excel model for the IFRS-SME
We make the model available without liability as per our Terms and Conditions of Use.
Cash Flow Statements and Financial Ratios [BETA]
Cash Flow Statements and Financial Ratios [BETA]Easily add advanced financial reporting and charts to your existing double entry accounting. It works with any accounting plan, the first time you enter your groups/accounts in the settings dialog, and then all calculations and reporting will be done automatically. This extension is available in Banana Accounting Plus only with the Advanced plan. Update now!
How to start
First time setup:
- Open Banana Accounting Plus
- Open your existing Banana double entry accounting file.
- Go to the Extensions menu → Manage Extensions... command and install the Cash Flow Statements and financial Ratios extension.
- Map you accounting plan.
- Extensions menu → Cash Flow and Financial Ratio → Settings.
- Under Grouping enter the groups you have in your accounting plan in the predefined groups.
The extension uses a standard, simplified Balance and Profit and loss structure, that allows to automatically calculate the Financial Ratios. - Click OK to verify your data.
Check the Ignore warnings/errors if you want to save the data and complete the grouping later.
- Add information to some special transactions (dividends, change in reserve, disinvestment, investments) they can be identified for the Cash Flow Statements.
Run the reports (at any time).
- Open your Banana double entry accounting file.
- Menu Extensions → Cash Flow and Financial Ratio
- Financial Charts
- Financial Reports
Available reports and charts
- Reclassification and checks
- Reclassified balance sheet
- Reclassified Profit and Loss Statement
- Control sums
- Cashflow Statement
- Cash Flow statement based on the indirect method.
- Cash Flow ratios.
- Financial ratios and analysis
- Liquidity ratios:
- Financing ratios
- Profitability ratios
- Efficiency ratios
- Dupont Analysis
- Altman index
- Charts
- Evolution of ratios over time
- Evolution of the Reclassified balance sheet
- Evolution of the elements of the Reclassified Profit and Loss Statement.
Prerequisites
In order to be able to use this extension you have to:
- Use Banana Accounting Plus with the Advanced plan. We recommend using the Dev-Channel, some features or functionality present in the insider version may not yet be accessible in the regular version of Banana.
- Open a Double-entry accounting file.
It is important that the various accounting years files included in the analysis have the chart of accounts set up in the same way, at least as far as references to groups are concerned.
For example, if I want to analyze the accounting years: 2018, 2019, 2020, and I set up group 100 in the Liquidity grouping. I need to make sure that for all three years the group is the same.
Try the extension now
You have the opportunity to use a test accounting file with some random entries to get an idea of the extension's functionality. The file already includes the extension, so you don't even have to download it
You can test it by editing the transactions, the chart of accounts or the various settings in the dialog.
The accounting file does not exceed 70 transactions, so you can also try it out with the free or professional version and upgrade to the Advanced plan later.
Compare historical data over more years and forecast data with current year.
Introduction
What is exactly the financial statement analysis?
Financial statement analysis is an accounting tool that provides an assessment of a company's economic, financial and asset condition. It is based on the financial statements and reports the data. It contains the profits and losses of a company and therefore serves to derive the general performance of the company.
Why is this activity very important for your SME ?
Until recently there were few SMEs that often used a financial statement analysis as larger companies could use it.
Today, times have changed. Reading the numbers well can make a difference within the strategy and management of an enterprise. Understanding which products it is worth investing in and which jobs can be neglected determines the difference between the growth or decline of a company.
This activity can be a source of interest for various subjects, external or internal to the company. Entities or external individuals can analyse their solvency profile (current or potential lenders), capacity to provide an adequate return on capital (for those who want to buy shares for example) or even just obtain information on the company's situation with respect to competition in the sector.
Through the comparative balance sheet analysis of the various elements available, it is possible to arrive at the following formulation of a "judgement" on the health of the company in all its dimensions:
- Economic
- Asset
- Financial
How it works
The financial statement analysis is based on two fundamental documents for a company:
- The Balance sheet
- The Profit and loss statement
In order to perform a correct analysis, it is always necessary to start from the reclassification of the accounts, which includes 3 phases in particular.
- Group the account items into groups
- Order such groups
- Bringing out intermediate results
The reclassification allows for a slightly cleaner first view of the company's situation and is already useful information can be obtained from it.
Analysis by Indexes
Once the intermediate results have been obtained, it is possible to proceed with the calculation of the indices useful for the analysis. The financial statements analysis by means of indexes is a very powerful tool that allows you to use indicators capable of providing a very concise assessment of one's own situation.
How should the data be interpreted?
Better results in terms of interpretation and evaluation are therefore achieved by analysing a series of balance sheets and studying the trend over time of the significant balance sheet ratios, so as to understand in which management is moving the company (dynamic financial statements analysis).
How do I evaluate them?
- Temporal evolution
- Comparison with average values of the sector
- Comparison with "normal" values i.e. with the benchmark
- Comparison with objectives
Response to results
This is the last activity of the analysis cycle, where the "relay" passes into the hands of those who deal with the Management of the Company, with data that speak clearly, the Manager will have to plan how to proceed using the right Project Management techniques.
The report contain errors?
If you notice incorrect data within the report or find that for some reason the calculated amounts do not match, please follow the steps below:
- Check that the data in your accounts are correct.
- Check that you have set up the groups correctly in the settings dialog.
If the errors persist, contact us via our feedback form and send us an example accounting file (*.ac2), even with little data, but allowing us to reproduce the possible problem and correct it.
Multi-language
The extension is available in the following languages:
- English
- Italian
- French (translation currently not complete)
- German (translation currently not complete)
And will adapt according to the language in which the application is set up. For all other languages, the standard version in English will be displayed.
Save your analysis
You can save the report in the following formats:
- Html
- Excel
- Latex
Settings Dialog
Dialog is accesible:
- By going to the Extensions menu→Cash Flow Statements and financial Ratios →Financial Reports.
- By going to the Extensions menu→Cash Flow Statements and financial Ratios →Settings.
Set up the groups
The first and most important step is to enter the groups or accounts number you are using in your account table.
Once you enter the groups the report and calculations are all done automatically, except for some specific transactions for the Cash Flow Statement.
- Groups must be entered manually
- Groups must be separated by a semi-colon ';'
- Both groups and accounts can be entered
- It is important to make sure that you include elements that exist in your chart of accounts, if are entered groups or accounts that do not exist in your chart of accounts, a message will be displayed on the row of the grouping concerned, returning those elements for which a match was not found in the chart of accounts. Once corrected, you only need to run the dialogue again and the message will disappear.
- By default, the groups within the dialogue refer to the Swiss SME chart of accounts, and it is possible to return to the base scenario by clicking the Restore Defaults button. Beware, however, that in this way the customisations made will be lost, and will be replaced with the default values.
.png?raw=true)
All the necessary elements must be inserted within the different groupings defined in the dialogue (Liquidity, Fixed Asset,Owned base capital,...).
Assets
They show the total employment of a company, so the investments to which the company has allocated
the means found in carrying out its activity.
- Liquidity: Must include groups or accounts that define liquidity in the company, such as cash or bank
- Credits: Must include groups or accounts within which are recorded all the operations
concerning money due to buyers who didn’t paid yet for their purchases - Stocks: Must include groups or accounts with all goods for resale in the ordinary course of business.
- Fixed assets: Must include groups or accounts containing fixed assets elements, as:
- Buildings
- Computer equipment
- Computer software
- Furniture and fixtures
- Intangible assets
- Land
- Leasehold improvements
- Machinery
- Vehicles
Liabilities and Equity
Shows where company's resources come from. In general, the funds at the company's disposal are
classified in a way to distinguish between own funds (which flow into equity) and those from third parties.
- Short-term debt capital: Must include groups or accounts representing the company commitments that must be fulfilled, without any particular cancellation, in the current year.
- Long term debt capital: Must include groups or accounts containing that kind of capital that the company can have at its disposal for several years, on a fixed basis, and that can usually only be withdrawn within a set time limit.
- Own Base capital: Must include groups or accounts those group referring to the company's own capital.
- Reserves and Profits: Must include groups or accounts within which are recorded the amounts to be paid to reserves or designated as profits.
Revenues
Indicates what is produced by the company during a financial year. Whether it is an increase in the value of products or semi-finished products in the course of production or services in progress, revenue from the sale of products or services or the increase in the value of fixed assets thanks to own resources, all these heterogeneous factors add up.
- Sales turnover: Must include groups or accounts within which is recorded what is produced by the company during a financial year. Whether it is an increase in the value of products or semi-finished products in the course of production or services in progress.
Costs
- Costs of Merchandise and services: Must include those groups or accounts in which all costs relating to goods and services consumed during the annual financial year are recorded.
- Personnel Costs: Must include all those accounts referring to a cost due to personnel, such as:
- Salaries
- Social charges
- Severance Pay
- Pension and similar treatment
- Other costs
- Different Costs: Must include all other groups or accounts relating to costs during the operating period.
- Interests: Must include groups or accounts containing the costs of financing sources, such as bank interest payable or interest on loans.
- Depreciation and Adjustments: Must include groups or accounts where are registered possible revaluations and write-downs of equity investments, as well as of financial fixed assets and securities included in current assets that are not equity investments.
- Final Result: The group containing the difference between the costs and the revenues at the end of the year.
Average Number of employees
This information is useful for calculating efficiency ratios, enter the average number of employees in the company and find out information such as the average company revenue per employee.
Printing Preferences
To make the Analysis as close as possible to your needs you can set some preferences, and choose about the details of printing and analysis
.png?raw=true)
Printing Details
- Page header: Include the header in the report, the header is composed with the information retrieved from the properties of the file.
- Logo: Choose whether to include your company logo in the report. for information on how to set up a logo visit this Logo set up page.
- Background color of headers: Choose the colors for the table headings
- Text color of headers: Choose the color for the texts in the table headings
- Report Without colors: Check the box for no colours in the report.
Analysis Details
- Number of previous years: Set the number of previous accounts (years) to be included in the analysis, which will be added to the current year and the Budget (if present and included).If you don't know how to set the previous year to a file, go to “File→File and Accounting Properties→Options Tab.
- Number of decimals: Choose how many numbers after the decimal point you want for the digits in the report, if you don't want to have decimals you only need to insert a zero 0.
- Include Budget: If you are using the Budget table for your financial planning, you have the possibility to include it in the analysis.
- Include Budget to date column: Include the columns showing the values of the budget up to that day, compare the values with those of the year-to-date.
- Include Current year projection column: You can include the projection for the current year. The programme uses the values in the budget table to return what could be the values at the end of the year.
- Current Date: Insert the current date. If no date is entered, the date of the day is taken automatically
- Include DuPont Analysis: Choose whether to include the Dupont Analysis
- Include Control Sums: Choose whether to include the table with the control sums, useful to inform in case of errors on the totals (assets/liabilities, operating result).
- Show the formulas column: Choose whether to show the column with the calculation formulas.
- Show the acronym column: Decide whether or not to show the acronym column, which is useful for identifying the elements used for formulas.
The columns of acronyms and formulas are complementary, that's beacuse the acronym column is useful to uderstand how the formulas are composed. if you dont need these columns, just uncheck the checkbox.
Set the benchmarks
Benchmarking is a method of assessing an organisation's competences based on comparison with the "best
in class", whatever sector it belongs to. So the Benchmark is a key performance indicator on the basis of
which a company assesses its performance with regarding to products, services and business processes.
You can customise these values depending on your company:
- Sector
- Size
- Targets
These values are only representative, which means that the figures you enter are not used in the analysis but are shown as they are. In the report, they are displayed in the Benchmark column, in the indexes tables, so that you can quickly assess the situation.
.png?raw=true)
It's also possible to call the dialog from the opened report and change the parameters. The values of the
analysis will be updated automatically.
Cash Flow Statement
Cash Flow is an analytical tool that helps to visualise the positive and negative changes in liquidity as a result of management, with reference to a given period of time: it is in fact the reconstruction of monetary flows, then the difference between all the monetary income and expenditure of a company.
Cash Flow analysis is not subject to accounting rules and many investors use the data to assess the strength of the company.
Essentially, if the Cash Flow is positive, it shows the financial availability for the company within the reporting period, whereas if the cash flow is negative, it means that more resources have been absorbed than have been received.
Special Cash Flow transactions
The first step to obtain the Cash flow Statement i its to setup the account groups in the settings dialog, Most value needed for preparing the Cash Flow Statement can be calculated based on the changes of the standard account classification. Identifying Disinvestments, Revaluations, transactions and other specific movements effecting the cash flow, would require a restructuring of the account plan. We have therefore opted to identify these values, by adding a special code to the description of a transaction.
It is important that these transactions are made using the recommended account type or group, because the program searches for cashflow amounts in certain groups, so if an entry is made using another account type, there could be an error as the amount may not be found.
If we talk about entering a fixed asset account, the account must belong to one of the groups entered in the fixed assets section of the dialogue. For example, if I disinvest by selling a vehicle and I use the standard chart of accounts for SMEs, I can use the account Vehicles '1530', which is part of the group 150, which in the dialogue is entered under the section 'Tangible Assets' in the fixed assets.
- Disinvestments (#disinvest)
- A disinvestment simply represents the sale of a fixed asset such as a vehicle or machinery. When recording a disinvestment.
- Debit Column: Insert the account where you will collect the money from the sale, such as the post or the bank.
- Credit Column: Insert a fixed asset account that relates to the item sold.
- Knowing the amount of disinvestments, the program is able to calculate in detail the real amount of investments that have been made during the year. For an SME, the number of disinvestments during the accounting period usually remains quite small, whereas investment activities are much more frequent operations, which is why it is very important to find the real amount net of all other movements.
- A disinvestment simply represents the sale of a fixed asset such as a vehicle or machinery. When recording a disinvestment.
- Revaluations of fixed assets (#revaluations)
- Revaluation of a fixed asset is the accounting process of increasing the carrying value of a company's fixed asset or group of fixed assets to account for any major changes in their fair market value.
- Debit Column: Enter the account of the fixed asset item you are revaluing to increase its value.
- Credit Colum: Enter an income account, if you don't have a particular one you can enter it as extraordinary income.
- Revaluation of a fixed asset is the accounting process of increasing the carrying value of a company's fixed asset or group of fixed assets to account for any major changes in their fair market value.
- Devaluations of fixed assets (#devaluations)
- It works in the same way as a revaluation, but instead of increasing the value of the fixed asset it decreases it, which means that the accounting entry is also reversed, i.e. the income becomes a cost.
- Debit Column: Enter a cost account, if you don't have a particular one you can enter it as extraordinary cost.
- Credit Colum: Enter the account of the fixed asset item you are revaluing to increase its value.
- It works in the same way as a revaluation, but instead of increasing the value of the fixed asset it decreases it, which means that the accounting entry is also reversed, i.e. the income becomes a cost.
- Dividends (#dividends)
- Dividends are fees paid to shareholders and usually depend on the profit made. The payment of a dividend must be recorded in a specific liability account, and should appear under short-term liabilities.
- Debit Column: Enter the reported balance sheet Profit / Loss carried forward account.
- Credit Colum: Enter the specific account for dividends.
- Dividends are fees paid to shareholders and usually depend on the profit made. The payment of a dividend must be recorded in a specific liability account, and should appear under short-term liabilities.
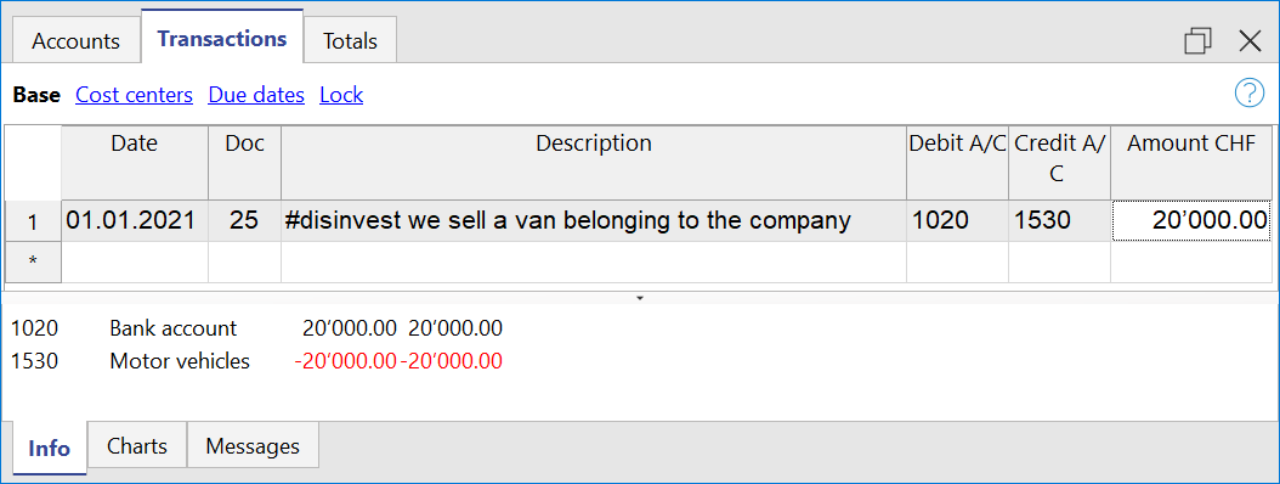
Cashflow Statement
Cash flow is divided into three main components:
- Operating cash flow which originates from the core business operations of a company.
- Cash flow for the company, which is the cash flow available to all investors in the company.
- Cash flow available to shareholders, which only considers the cash flows that are due to the shareholders, resulting from the net of all payments made and received, including from debt holders.
Adding up all the totals you find the amount that corresponds to the change in liquidity for the period, which in turn when added to the value of the liquidity at the opening of the period should give you the current liquidity balance.
If the results do not match, an error message is displayed.
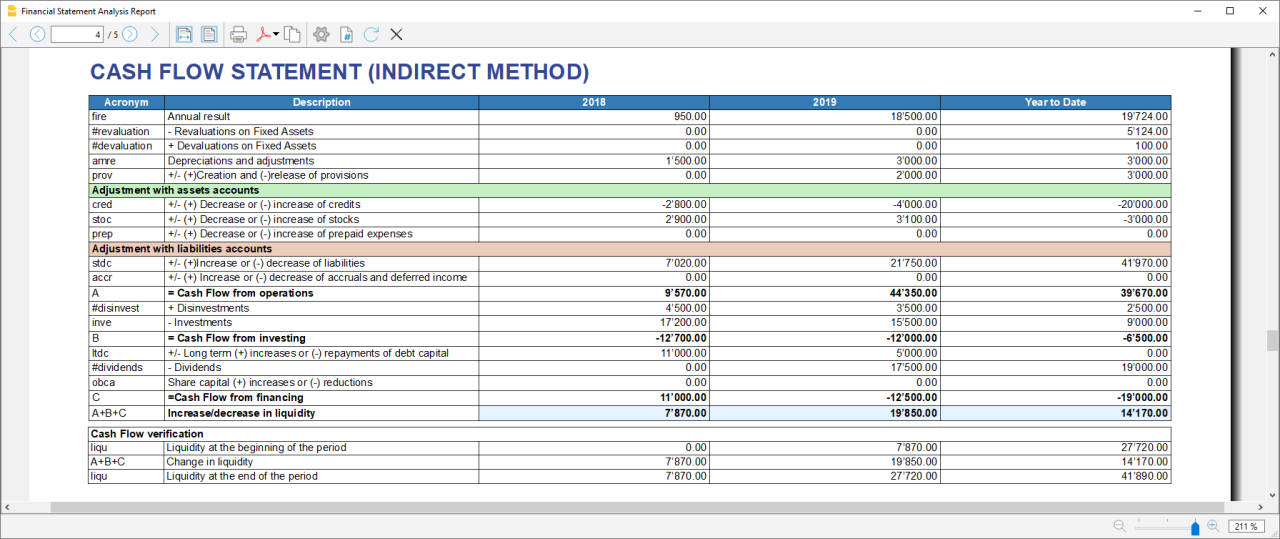
Acronym column
In the acronym column of the cashflow, the reference to the account taken into account in the calculation is entered, or in the case of special entries, the prefix of the entry, so that it is easy to see which item of the balance sheet or income statement a certain movement relates to.
Cash Flow verification
This table shows any differences between the change in cash flow calculated in the cashflow and the actual cash flow in the accounts, which in an optimal situation should match. If there is a difference in one of the years of analysis the amount in question is printed in red on a line below.
Usually, when an error occurs, the first thing to do is to check whether the amounts in the balance sheet and profit and loss statement are correct or whether there are differences between the assets and liabilities, for checking them, control sums are very useful because they immediately show whether there is a difference.
if you realise there is some error but you dont know exactly where, you can check the amounts by comparing the ones in the report with those in the chart of accounts.
The differences are generally due to an error when entering groups in the settings dialog, which can occur in two ways:
- One or more groups were not included
- One or more groups were entered under the wrong heading
In case the balance and profit and loss amounts are correct but the cashflow displays an error, is probably due to the fact that a group has been inserted in the wrong place.
Retained Earnings Statement
This table shows the movements made with the annual profit achieved. Starting from the reported annual profit it adds the profit for the period and adjusts the value by taking into account the payment of dividends and the creation or dissolution of reserves. The last two rows show the total undistributed profit, and the undistributed profit realised in the current year.

This information is somewhat supportive of Cash Flow but since earnings management does not directly affect cash, it is presented in a separate statement.
Record Transactions
It is useful to first record the transfer of the profit for the year from the profit and loss account to the profit shown in the balance sheet as shown in the example image.
In order to record the payment/discharge of reserves and the payment of dividends, it is sufficient to use the specific account of one of the above items and to decrease or increase the profit account shown in the balance sheet. The remaining amount (not allocated to reserves or dividends) then increases the retained earnings.

Cash Flow Ratios
In addition to the ratios already present, those ratios are added just below the Cashflow table and in the Charts
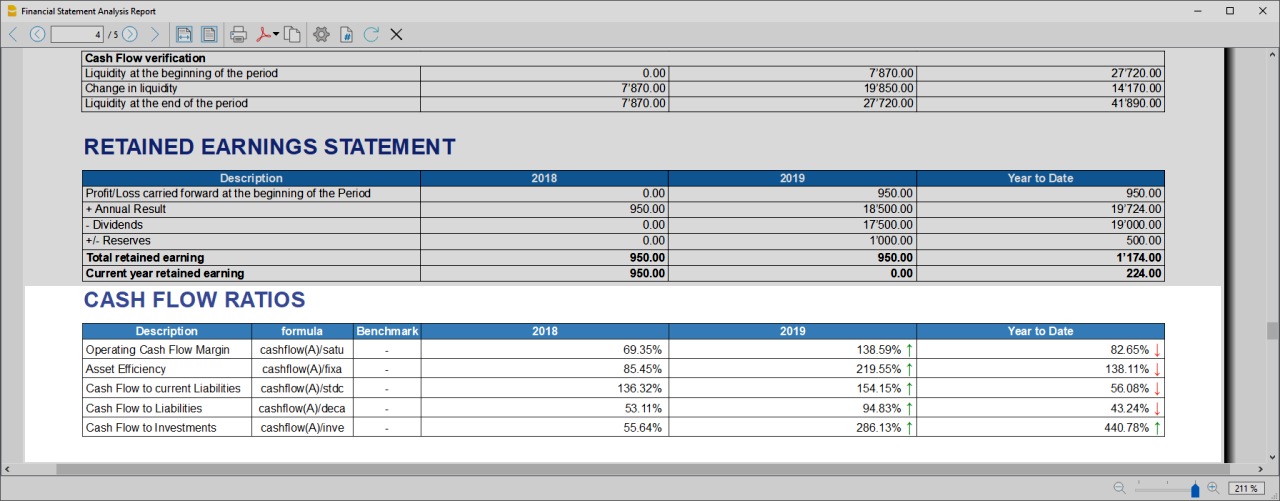
- Cashflow margin: Measures the amount of revenue a firm can convert into operating cash flow. When a firm is thriving, operating cash flow should grow alongside revenue. While profit margins measure a firm's pricing power; a declining cash flow margin also measures the health of customer and supplier relationships.
- Asset Efficiency Ratio: This is a basic ratio to show you how well the company uses its assets to generate cash flow. It’s best used to view the historical trend as well as to compare with competitors.
- Cashflow to current Liabilties: This ratio gives you an idea about the company’s debt management practices.It’s also a better indicator of the company’s ability to pay current liabilities than the current ratio or quick ratio
- Cashflow to Liabilities: Measures the amount of operating cash flow a firm generates on each dollar of total liabilities. Businesses that can't produce operating cash flow to pay off all their liabilities cannot continue to operate indefinitely, making this ratio an important indicator of liquidity as well as solvency
- Cashflow to Investments: Measures the amount a company outlays for capital assets for each dollar of cash dollar it generates from those investments.
Why Is Cash Flow Analysis Important?
Performing cash flow calculations in combination with constant monitoring of the company's cash flows is the winning formula for effective treasury management, and is useful for making the best use of available cash.
Thanks to the ability to generate cash flow and the financial solvency of the company, you gain confidence from banks and suppliers, as it symbolises a certain control over your business: the calculation of cash flow is in fact a way to detect the actual availability of the company, giving the possibility to face unexpected events or to plan consistently the future of projects.
For more information on Cashflow Analysis, please refer to the following page.
Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Reclassification
Generate the Report by going to the Extensions menu→Cash Flow Statements and financial Ratios →Financial Reports.
The Report contains all the analysis data processed by the extension:
- Reclassified balance sheet
- Reclassified Profit and Loss Statement
- Control Sums table
Reclassified Balance Sheet
The reclassification of accounts allows for the display of a series of values, results and intermediate margins that contain more information than the traditional structure.
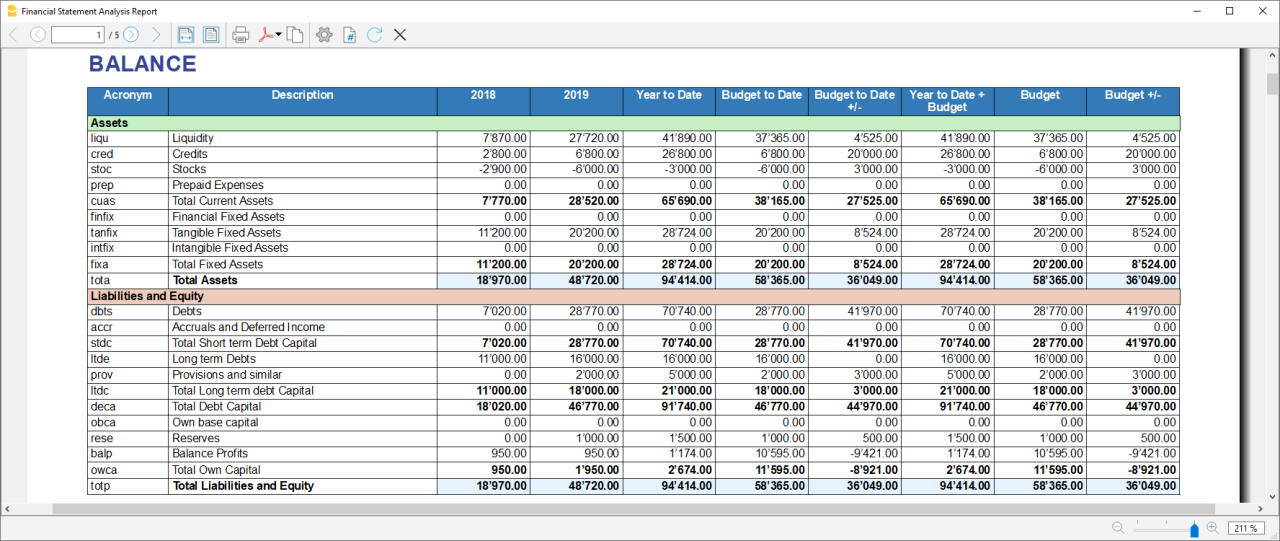
- Current Assets: All the assets of a company that are expected to be sold or used as a result of standard business operations over the next year.
- Fixed Assets: Items, such as property or equipment, a company plans to use over the long-term to help generate income.
- Total Assets: The sum of current assets and fixed assets.
- Debt Capital: Is the capital that a business raises by taking out a loan. It is a loan made to a company, typically as growth capital, and is normally repaid at some future date.
- Own Capital: It is the capital owned by the company.
- Total Liabilites and equity: The sum of Debt Capital and Own Capital.
Reclassified Profit and Loss Statement
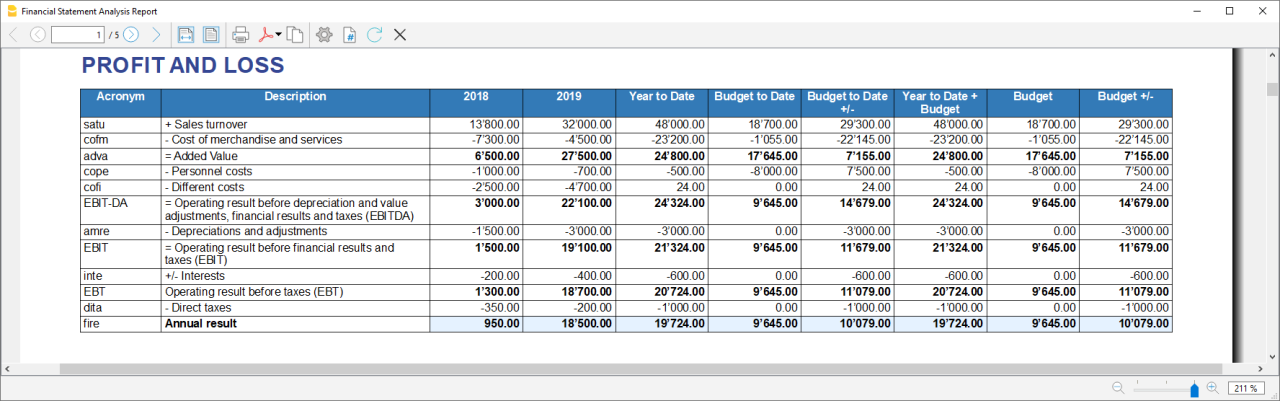
- Added value: The difference between operating costs and operating revenues incurred for resources outside the company, expresses the company's ability to create wealth and then remunerate the various production factors and stakeholders.
- MOL /EBITDA: "Earning Before Interests, Taxes, Depreciation and amortization" is obtained by subtracting from production revenues the costs of production (including internal costs such as personnel costs), without considering provisions and depreciation. As it does not contain economic items without monetary movement, its value assumes very important information for financial investors.
- EBIT :"Earning Before interests and Taxes", helps to understand whether the company is also able to cover the financial charges arising from its financial commitments.
Control Sums
Resumes the totals of the reclassified accounts (Assets, Liabilities and Equity , Annual Result). Checks that the sums calculated in the analysis match the totals in the accounting sheets and that Assets and Labilities and equity match.
- Accounting Total column: Represents the actual total in the accounts.
- Calculated Total column: Represents the total calculated by the program based on the groups entered.
- Difference column: Represents the difference found between the total in the accounts and the calculated total for each year. The value equal to 0, otherwise will be displayed an error message, which means that there may have been an error in entering the accounts/groups .In this case it is useful to check in the dialogue that you have entered the groups correctly.
Financial Ratios
Generate the Report by going to the Extensions menu→Cash Flow Statements and financial Ratios →Financial Reports.
The balance sheet ratios are formulas calculated on financial, economic and asset values. These ratios are derived from the income statement and balance sheet data. Balance sheet indices are important analysis tools that provide essential indications for the entrepreneur's activity.
It is widely used by all professionals who are interested in assessing the soundness of a company for their work.
In fact, banks use the balance sheet indexes to evaluate company loan applications.
the indexes are divided into four main types
- Liquidity ratios:
- Financing ratios
- Profitability ratios
- Efficiency ratios
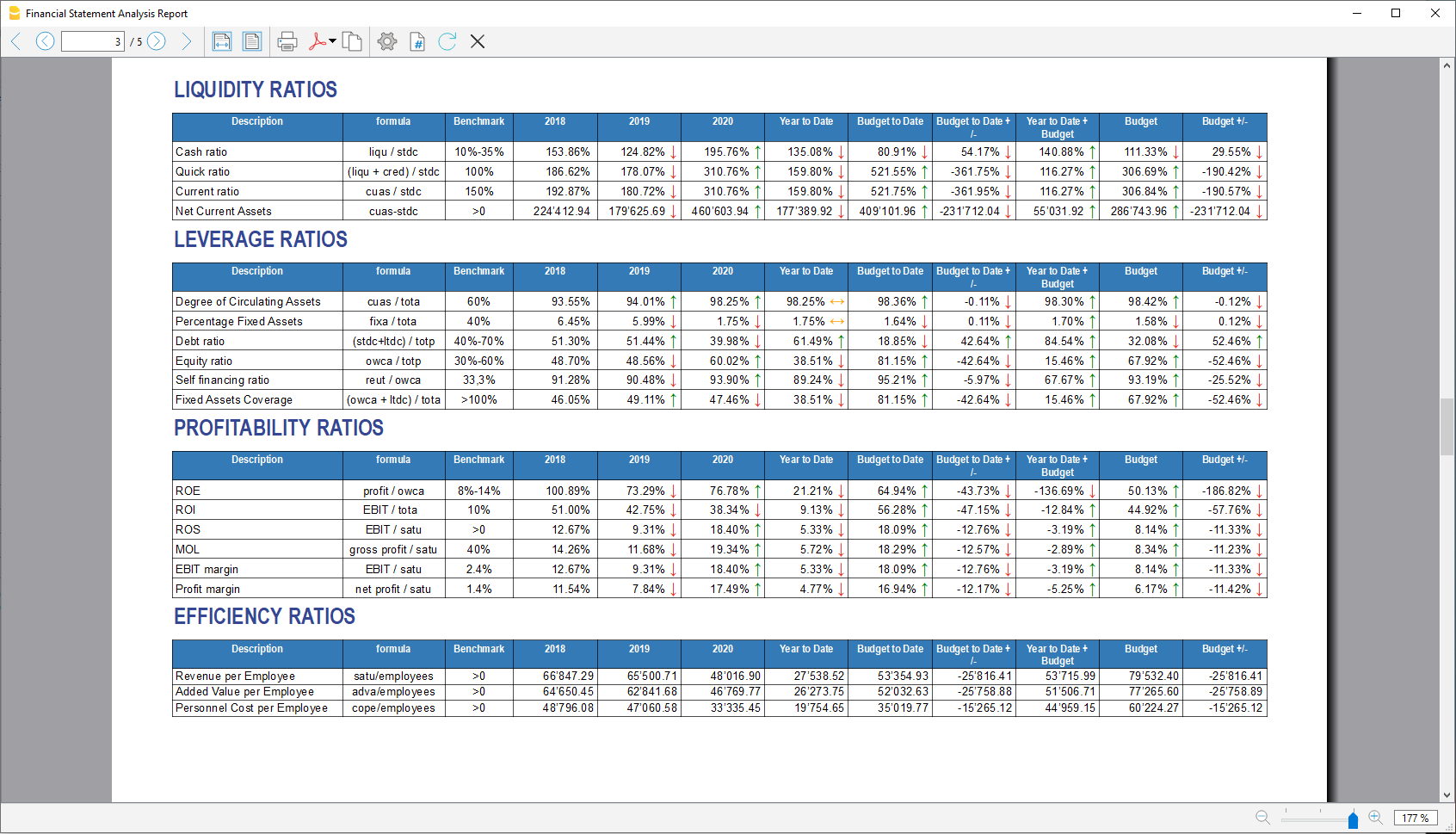
Liquidity ratios
An important class of financial metrics used to determine a debtor's ability to pay off current debt obligations without raising external capital. Liquidity ratios measure a company's ability to pay debt obligations and its margin of safety through the calculation of metrics.
- Cash ratio: Indicates the extent to which the company is able to repay its debts at the end of the term.
- Quick ratio: Indicates the extent to which the company is able to pay its debts when due.
- Current ratio: Indicates the extent to which the company is able to pay its short-term debts without touching fixed assets.
- Net Current Asset: Indicates the part of the current assets free of short-term commitments, which can therefore be used in the activity.
Financing ratios
They look at how much capital comes in the form of debt (loans) or assesses the ability of a company to meet its financial obligations.
- Degree of Circulating Assets: It allows us to understand whether there is a balance within the company's assets, a judgement can only be made if we have the average data for the same line of business.
- Percentage Fixed Assets: It is complementary to the previous one.
- Debt ratio: Indicates the extent to which the company has had to resort to external financing, the judgement depends very much on the branch of activity.
- Equity ratio: Is complementary to the previous one, equity ratio has the advantage of being less expensive.
- Self-Financing ratio: Indicates the extent to which the company has been able to accumulate undistributed profits.
- Fixed Asset coverage: The fixed assets must absolutely be financed from equity or possibly from long term capital, otherwise major repayment problems could occur.
Profitability ratios
Are useful to assess a business's ability to generate earnings relative to its revenue, operating costs, balance sheet assets, or shareholders' equity over time, using data from a specific point in time.
- Return on equity (ROE): By comparing the percentage obtained with the rates commonly applied for other investments, it is possible to understand whether the equity invested by the company gives a sufficient return or not.
- Return on investment (ROI): Identifies the return on invested capital. Basically it serves to understand how much the invested capital returns in terms of income.
- Gross Operating Margin (MOL) :Is a value that measures the profitability of a company. In other words, it measures the ability to make profit margins: Indicates the company's return on sales made.
- EBIT margin: Is the ratio of EBIT to turnover of a company. This ratio provides information on its profitability and helps to compare different companies and sectors.
- Profit margin: It represents what percentage of sales has turned into profits.
Efficiency ratios
Express the degree of efficiency of the company's factors of production, those chosen by us give us an indication of the relationship between the number of employees and the various margins of the profit and loss account. Efficiency indicators are related to profitability indicators, as higher productivity generates an improvement in profitability indicators.
- Revenue per Employee: An increase indicates greater efficiency of the company and a lowering of the break even point. Its increase is certainly an indicator of the good health of the company itself.
- Added Value per Employee: Gives evidence of efficiency in terms of cost reduction (e.g. economies of scale). If the revenue per capita index remains stable and the value added per capita index increases, this is evidence of cost efficiency.
- Personnel Cost per Employee: Highlights the trend in average personnel costs.
Within the tables and also visible the calculation formula of each index.
Dupont Analysis and Altman index Z-Score
Dupont Analysis
The Dupont model is a technique that can be used to analyse the profitability of a company using
traditional performance management tools. To enable this, the model integrates the elements of the Profit
and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
Altman index Z-Score
The Z-Score is an index of the discriminating analysis used to determine the probability of bankruptcy of a
company within 2 years using statistical techniques.
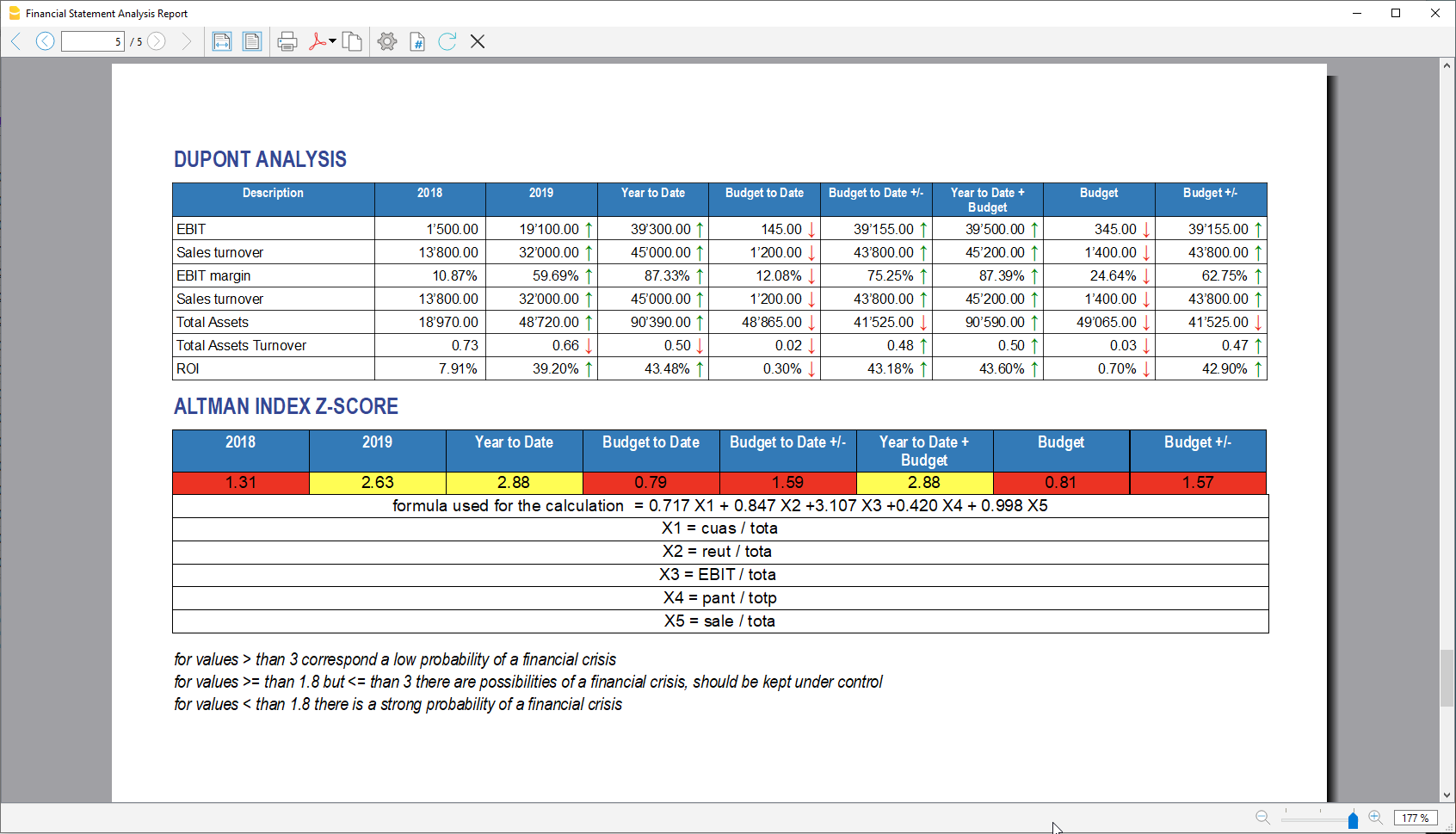
Financial Charts
It’s possible to access to the charts by going to the Extensions menu→Cash Flow Statements and financial Ratios →Financial Charts.
Charts allow you to read the same information as you can find in the report but in a clearer and more
intuitive way. Once the dialogue is open, you can move between the various elements thanks to a drop-down menu.
Ratios charts
- Financing ratios evolution
- Liquidity ratios evolution
- Profitability ratios evolution
- Efficiency ratios evolution
- Cashflow ratios evolution
These charts represent the evolution of the indexes over time. For each type of index there is a bar chart,
within which there is a section that represents the evolution over time of each index for each year included
in the analysis.
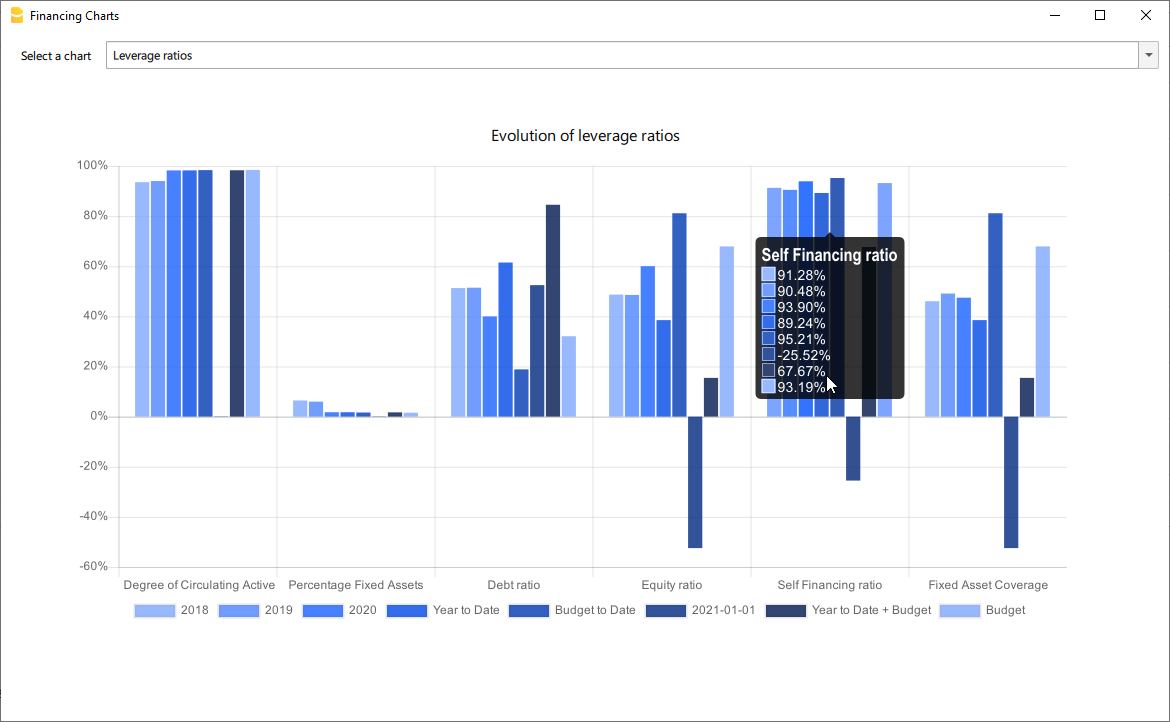
Reclassified Elements charts
- Reclassified asset variation
- Reclassified liabilities and equity variation
These charts show the time evolution of the reclassified assets, and reclassified liabilities, using stacked
chart. It is possible to see how and in what quantity the groups make up the total of assets and liabilities (in
percentage %)
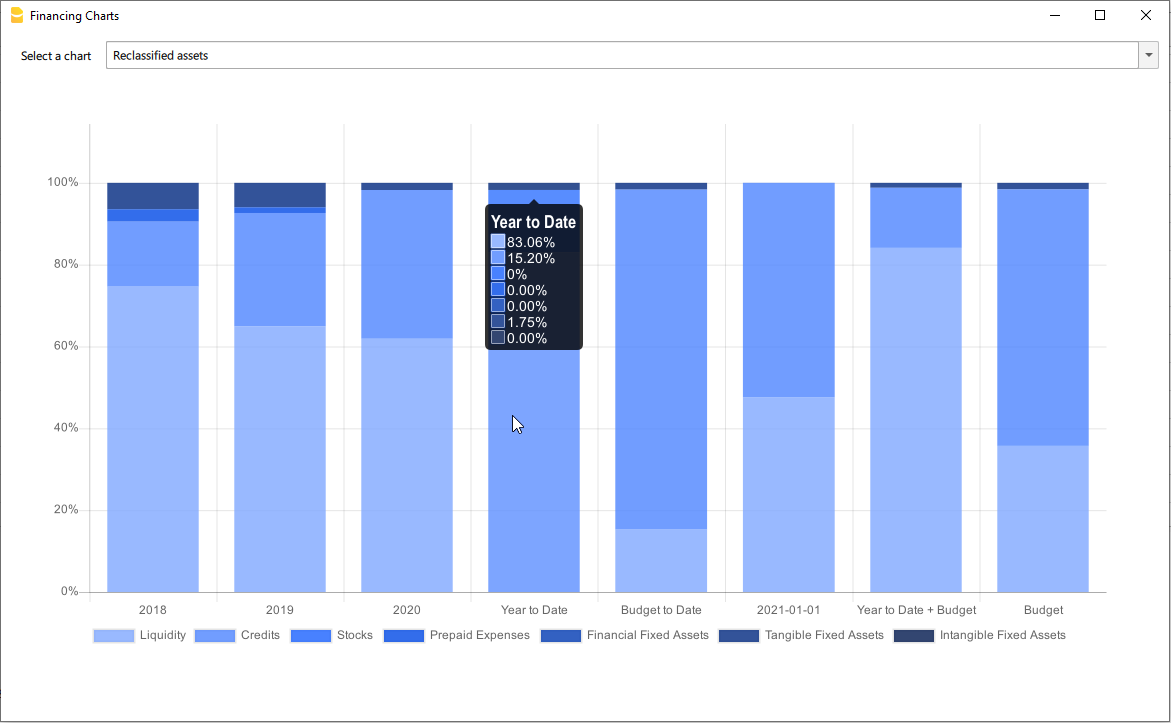
Reclassified profit and loss variation
Shows by using histogram the value of the intermediate totals (EBIT,EBIT-DA,..) of the reclassified profit and loss account ,and their evolution over the time.
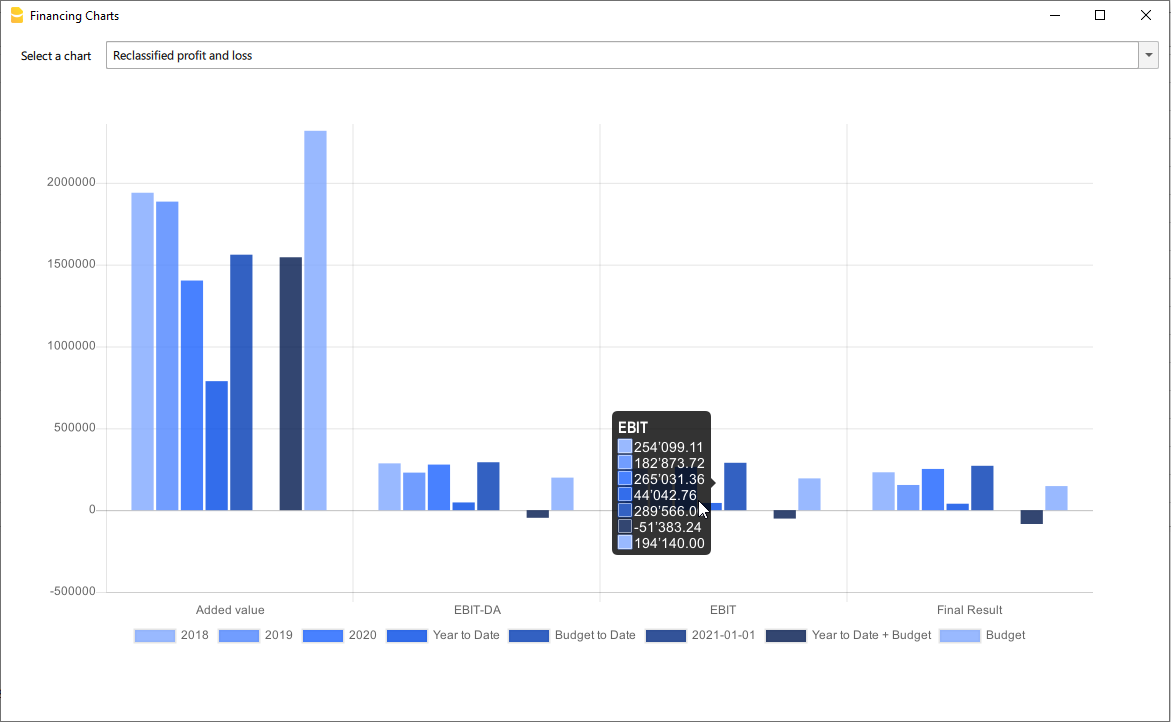
Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo and similiar hosting platform templates
Those who have an Airbnb rental business and are looking for a simple and efficient way to manage their finances will find the ideal solution in Banana Accounting Plus templates for several reasons.
With the templates, you can manage and track all expenses and income for all the rooms, apartments or houses you rent without any limits.
Moreover, you can manage the budget for your business in a flexible and personalized way. Whether you have multiple rooms, apartments or houses, you can keep track of specific income and expenses either collectively or divided for each individual rental unit. Additionally, you can set the budget according to irregular or regular deadlines such as monthly, quarterly, semi-annually or annually. This way, you can adapt the budget to your financial and business planning needs.
Through the budget feature in the templates, you can also make financial forecasts for your short-term rental business. You can gain a clear and detailed overview of your future income and plan ahead for all your activities.
Inventory management is another useful and powerful functionality offered by Banana Accounting Plus. You can keep track of all the items relevant to your business, categorizing them by room, apartment or rented house. This way, you will always be aware of what you own and easily manage the purchase or replacement of any necessary assets. With Banana Accounting Plus, you can create all the accounting files you need without limitations.
Regarding the management of income from hosting platforms such as Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo and others, the templates provide you with the option to record both the actual income deposited into your bank account and all other rental-related income, especially the commissions paid to the platforms. This information is crucial for tax purposes as it allows you to comply with the rules of the country where you operate your business.
For those who have an Airbnb business and are looking for a simple and efficient way to manage their finances, Banana Accounting Plus templates provide the ideal solution for other several reasons too.
Available templates
There are two templates available for short-term rental hosts on Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo or similar platforms.
The completely free template is suitable for those without accounting knowledge who want to manage the finances of their business. The second template is designed for those with double-entry accounting knowledge and who manage a business using multiple assets and possibly different currencies:
- Free template based on Banana Accounting Plus Cash Manager.
- Double-entry and multi-currency template.
All the functionalities and features described in the free template are also included in the double-entry multi-currency template.
In each template, you can easily view some sample accounting entries.
Manage Airbnb reservations
With Banana Accounting Plus templates, you have complete control over your reservations even before they are paid. This allows you to keep track of all bookings in your file, ensuring you are always up to date on availability and key dates. You can input reservations into the system and monitor them, making planning and management of your rental properties easier.
In addition to managing reservations, the templates also allow you to record payment receipts and income. This is particularly useful for monitoring and ensuring compliance with maximum nights allowed regulations in your country. You will have an accurate record of guest stays and corresponding income, providing clear and transparent documentation for regulatory compliance purposes.
Manage Airbnb Experiences
Banana Accounting Plus templates also enables you to manage and track Airbnb experience reservations. If you offer unique experiences such as sailing trips, mountain bike tours, tastings or others, you can record these specific bookings and efficiently monitor them. You will have a comprehensive overview of your Airbnb experience activities, including booking details and corresponding income.
With Banana Accounting Plus templates you simplify the financial management of your Airbnb rental business. You can take advantage of all the features offered and gain a clear and organized view of your finances.
Manage Airbnb business budget and financial forecasts
The Budget table in all Banana Accounting Plus files provides a comprehensive tool for creating your business budget and forecasting future financials.
This feature, always accessible through the Tools > Add/Remove functionalities menu, allows you to generate cash flow statements, liquidity plans and investment plans.
For more advanced needs, you can create budgets using formulas and automatic calculations. Additionally, you can obtain monthly, quarterly and annual financial forecasts as well as projections for multiple years.
Explore the full documentation on budget management and financial forecasting with Banana Accounting Plus.
Manage inventory along with their corresponding receipts
On all files, Banana Accounting Plus allows the display of the Link column in the Transactions table, enabling you to attach supporting documents to each accounting entry.
If needed, there are other predefined columns that you can easily show in your accounting file.
Additionally, with Banana, you can add your custom columns, additional tables, and link them to existing ones. Refer to the documentation on enabling the display of predefined columns and adding columns and new tables to your file.
The ability to add new tables and create custom columns also allows you to integrate the inventory of items in the rooms and apartments you rent into your file and attach relevant documentation, which can be useful, for example, for warranty or insurance purposes.
If you prefer you can create a dedicated new file to create and manage the inventory of your rooms and rented apartments. With all Banana Accounting Plus subscription plans, there are no limits on the number of files you can create and manage.
Handle the accounting recording of the fees you pay to platforms
Using a spreadsheet like Excel or Google Sheets doesn't always allow for proper management of income received from platforms such as Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo or similar ones. Often, the income received in your bank account does not include the commissions you need to pay to the platforms.
These platforms deduct the commissions before making payments, but there are countries where you are required to declare the gross income for tax purposes, including the deducted commissions.
With Banana Accounting Plus you can record the gross income you receive, ensuring that everything is accurately accounted for and that your bank balance always matches the actual balance in your account.
Check the example entries in the provided templates pages to see how this accounting record is done.
Free Airbnb template for income and expenses management: ideal also for Booking.com and Vrbo
Free Airbnb template for income and expenses management: ideal also for Booking.com and VrboManage your accommodation on Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo or the platforms you use with this free template and keep track of your finances easily and efficiently.
The Banana Accounting Plus template is superior to an Excel spreadsheet or a Google Sheet but avoids potential errors and time loss due to formula management. This way, you have a completely free accounting management template specifically designed for hosts.
With Banana Accounting Plus, unlike Excel or Google spreadsheets, there are no limits on the number of rooms, apartments or houses you can manage, and it allows you to easily track income and expenses for each individual rental property and your entire short-term rental business.
With this template, you can record and monitor all your income and expenses quickly and easily, providing you with a clear and detailed snapshot of your finances and how to optimize expenses. The accounting management template on Banana Accounting Plus offers a simple and effective way to organize and analyze all the financial data that is important for hosts.
Here are some of the key features and benefits of the free accounting management template:
- Easy to use: the template is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, even for those who are not accounting experts. No technical skills or in-depth knowledge of Excel spreadsheets are required to use it. Banana Accounting also has extensive online documentation in multiple languages readily available.
- Startup budget: create, manage and update the budget of your startup to generate detailed and useful reports and forecasts for the success of the business.
- Income tracking: record all income generated from bookings, including payments from platforms, booking fees and reimbursement of cleaning expenses for rooms, apartments or houses, with all the necessary tracking details.
- Expense management: keep track of all expenses associated with your properties, such as utilities, cleaning, maintenance and supplies. Choose the level of detail you prefer for each expense associated with your rental properties. Add, edit, group and customize expenses you want to monitor without limitations.
- Track rental property information: easily track guest names, rented room, apartment or house, check-in and check-out dates, total nights stayed, number of guests per booking, the source of guests' bookings and payment dates from platforms.
- Automatic calculations: the template performs calculations automatically for you, without the potential errors of Excel or Google Sheet formulas, providing a clear overview of your cash flow, profits and expenses for your entire business or for a single room, apartment or house you manage.
- Detailed reports: generate comprehensive and professional financial reports, including profit and expense statements, balance sheets and more. These reports will help you make informed decisions and have detailed control over your finances.
- Manage hosting platform Experiences: easily and quickly manage the Experiences you offer on Airbnb, Vrbo or other similar platform.
- Customizable: the template can be easily customized to fit your specific needs. You can add custom categories, modify, group and personalize all the details you want to monitor according to your preferences.
- Privacy: it's important to note that the data entered into Banana Accounting is not used for commercial purposes. Your information remains confidential, offline and is not repurposed in any way.
This free template for income and expense accounting management for hosts managing their short-term rental properties simplifies the management of your finances, saves you valuable time, and provides you with a clear and comprehensive overview of your income and expenses professionally.
Banana Accounting is a highly versatile and customizable accounting software that can be used for broader accounting purposes beyond managing hosts on Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo and other hosting platforms.
Totally free
This template is based on the Cash Manager feature of Banana Accounting Plus, which can be used for free and without limitations with the free subscription plan.
Create and save the file
You can open and save your new file to start either through Banana Accounting Plus Web or by downloading and installing the software on your computer:
- Download and install Banana Accounting Plus.
- Click on File > New.
- Select Cash Manager.
- Search for the Category Business.
- Select the template "Income and expenses management template for Airbnb or similar platforms".
- Click on Create.
If you click on the text "More info...", you will be directed to this specific documentation page for the template. On this page, you can always find the tutorial file including sample records.
Using the command File > File Properties, set your references, the accounting period with opening, closing dates and the base currency. In the Address section, fill in the fields for the entity managing the rental properties. If necessary, change the base currency of the accounting file in the Accounting section.
With the command File > Save As, save the file. It is useful to include the name of your business and the year in the file name. For example, "BusinessName-2023.ac2".
Also, refer to the article on organizing accounting files locally, on a network, and in the cloud.
Banana Accounting Plus Web Access
When you have downloaded and saved your new accounting file to open and use it from the web, you can bookmark the following link to access Banana Accounting Plus Web. However, it is recommended to download and install Banana Accounting Plus on the computers where it is needed, because Banana Accounting Plus Web does not yet have all the features available.
Create the budget
With Banana Accounting Plus, you can easily create a startup budget for your new short-term rental business on Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo and other platforms, and forecast all the costs you'll need to deal with. Consult all the relevant documentation on how to create a budget with Banana Accounting for detailed information.
Customize and categorize expenses
If you prefer, you can group similar costs into categories and maintain the detail for each type of expense:
- Properties costs: mortgage payments, repairs and insurance coverage.
- Initial setup expenses: spending on furniture and household utensils.
- Bills: electricity, gas and water expenses.
- Supplies: expenses for items like linens, toiletries and cleaning products.
- Business expenses: costs related to accounting, software and taxes.
- Other costs: payments for cleaners, laundry services and ads.
See how you can easily create accounts groups.
Recording transactions
In the Transactions table, record all transactions in chronological order, including debtor payments and invoice payments, as well as other types of transactions. The recordings can always be sorted and viewed instantly. You can highlight rows, correct any mistakes and copy and paste previously entered transactions.
To expedite data entry, we suggest using the various features of Banana:
- The auto-completion data entry feature automatically retrieves previously entered data.
- The recurring transactions feature (in the Actions menu) allows you to store frequently recurring transactions in a dedicated table.
- You can import data from bank statements, automatically capturing all bank transactions.
- You can link each recording to its corresponding digital document, and with a simple click, you can view the document. Refer to accounting files and digital documents for better document organization.
- Use the sort recordings command to arrange rows in chronological order.
- Use the print/preview command to print or export the journal in PDF format.
Bank transactions import
You can import bank statements, eliminating the need for manual entry.
Additionally, with the Advanced plan, it also allows for easy management of rules to automate accounting according to your specified criteria. This significantly reduces the effort required for accounting management, resulting in unmatched time savings.
Print financial statements or accounting reports
To view and print the financial statements at any time, click on the Report menu > Enhanced financial statements with groups. You can customize them or have an accounting report for a specific period.
Obtain detailed and customizable reports on all expenses and revenues of your business with Airbnb. You can compare them with the budget to always keep track of the performance of your startup.
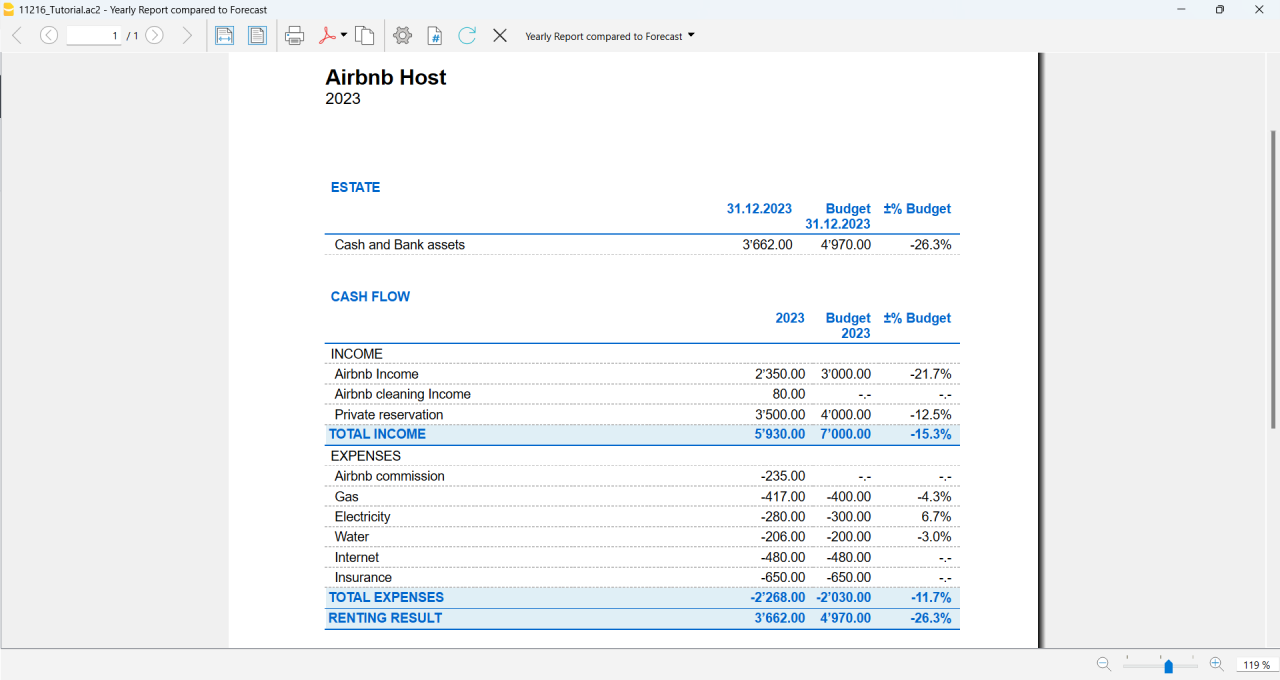
If you manage multiple rooms, apartments or rental properties, you can keep track of expenses and revenues allocated to each individual property you rent. You can also create room-specific budgets and compare the results with the actual expenses and earnings whenever you want.
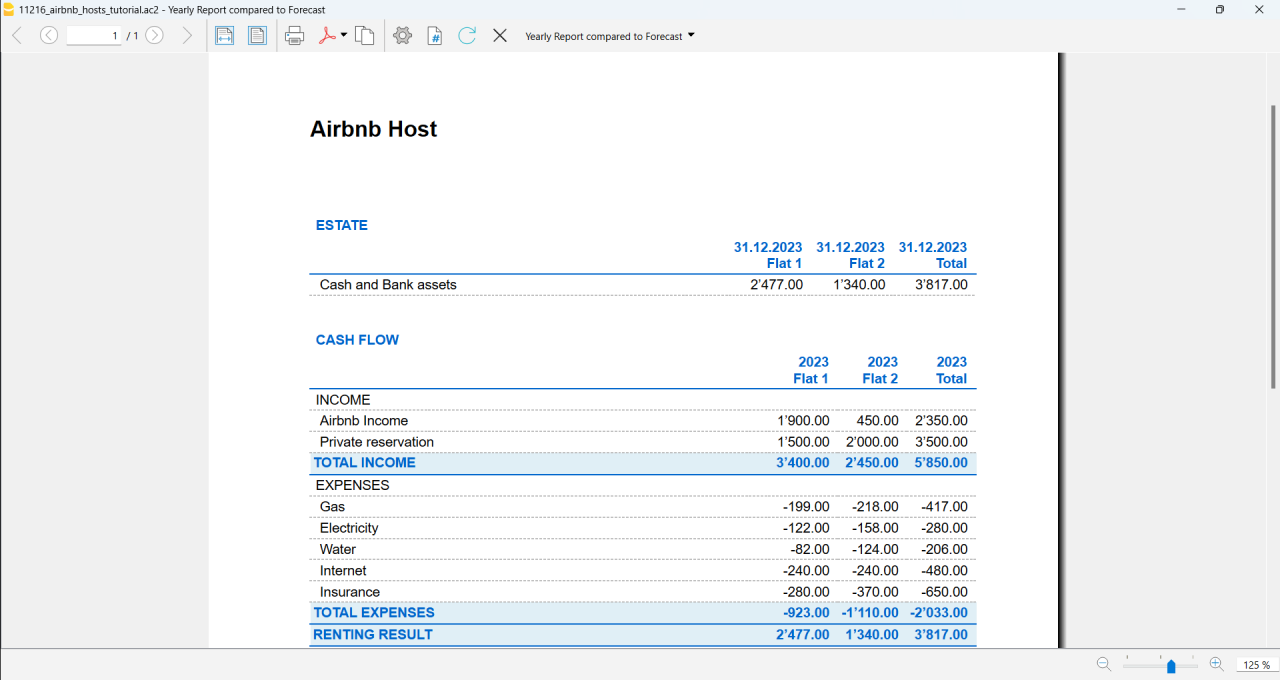
Advanced management
If you want, you can manage your Airbnb business in an advanced and optimized way through the rental management view called Manage Rentals. This allows you to keep track of all the necessary information about the reservations you receive. For those who offer Airbnb Experiences, there is the experiences management view, called Manage Experiences, available to track guest bookings related to experiences.
Navigate between the various available views to keep all the relevant data under control.
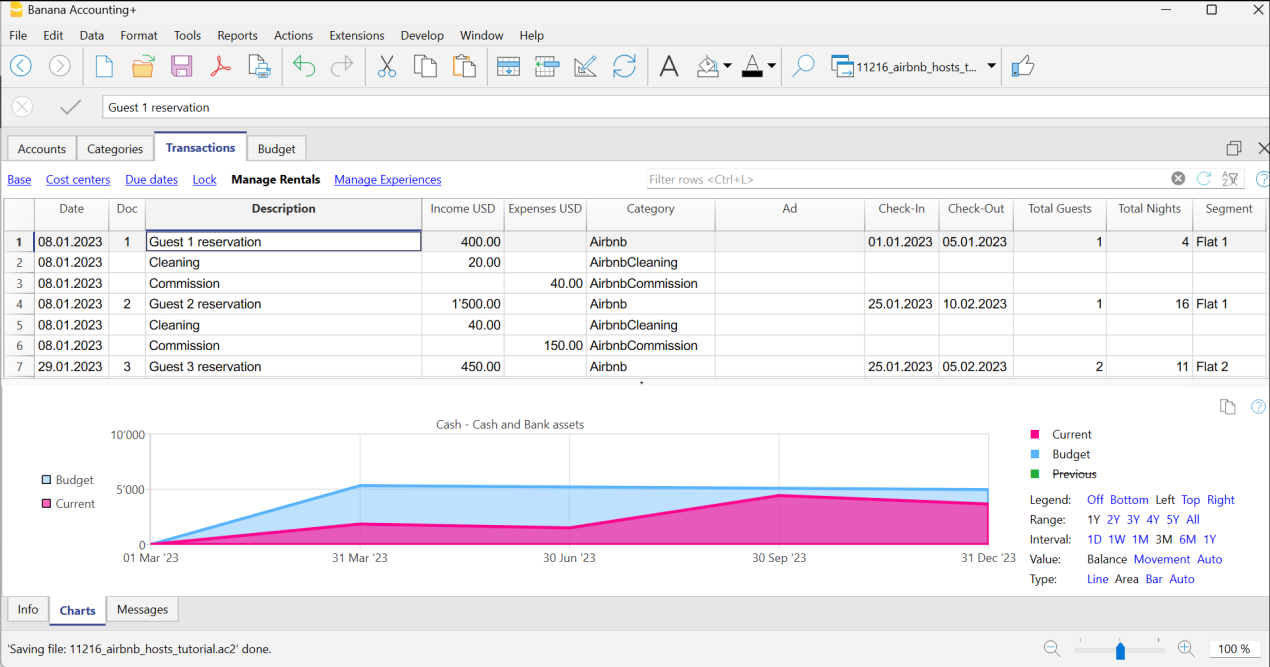
Questions or specific requests
Do you have any questions or specific requests regarding this template for Airbnb hosts or other short-term rental platforms? Please e-mail us.
Sample records for managing income and expenses for Airbnb hosts or other hosting platforms
Here are the sample accounting records for this template.
Recording an Airbnb or other platform revenue transaction
Record revenue from online platforms such as Airbnb, where you receive booking fees, with the preferred breakdown of the collected amounts and platform commissions. If you want, keep track of the ad from which the guest made the reservation, the check-in and check-out dates, the number of guests for the booking, the booked nights, the room or flat rented and the date of payment from the online platform.
To print the receipt to be given to the guest upon arrival, enter the receipt number in the Doc column and use the designated printer extension. You can also attach the receipt to the corresponding revenue record using the Link column.

Recording an expense for your short-term rental business
Record the expenses you incur for your Airbnb business by indicating the date of the expense, a description of the purchase, the amount incurred, the expense category, and the room or flat associated with your monetary outflow. You can always attach your receipts using the Link column.
Airbnb template for multi-currency accounting management
Airbnb template for multi-currency accounting managementThis template is useful for comprehensive and efficient accounting management for Airbnb hosts who need a system that supports double-entry bookkeeping and handles multiple currencies. Banana Accounting Plus provides a wide range of features to track the income and expenses of your short-term rental business.
Banana Accounting Plus is an advanced accounting software that is superior to Excel, yet it is simpler and more cutting-edge, catering to the common needs of Airbnb hosts. The accounting template has been specifically designed to offer a comprehensive and customizable solution for the financial management of your Airbnb properties. It allows you to track expenses, record income, monitor cash flow and much more.
The key features of this accounting template for Airbnb include:
- Asset Management: this template encompasses all the features of the free template for Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo and similar hosting platforms and provides an advanced solution for those with greater needs. It allows you to manage unlimited assets compared to the free template.
- Double-Entry Bookkeeping: the template adheres to the fundamental accounting principle of double-entry bookkeeping, ensuring the accuracy and correctness of your financial records.
- Multi-Currency Management: if you manage Airbnb properties using different currencies, Banana Accounting enables you to record and track income and expenses in different currencies, simplifying international financial management.
- Advanced Reporting: the software offers the ability to generate detailed reports on your finances, including profit and loss statements, account statements, balance sheets and detailed budgets. These reports provide you with a comprehensive overview of the performance of your Airbnb properties.
- User-Friendly: the software is designed to be user-friendly, even for those new to double-entry bookkeeping or without extensive accounting experience. The accounting template is intuitive, and the extensive available online documentation guides you step-by-step in managing your finances.
Banana Accounting Plus is intuitive, easy to use and simplifies your accounting management for Airbnb.
Example of a multi-currency income transaction for hosts
Here's how to use the multi-currency feature of Banana Accounting Plus:
- Set the desired currency exchange rate through the Exchange Rates table.
- Perform the accounting entry by entering date, description, bank of the currency received, income account, amount in the currency received and specify the currency received. Banana Accounting Plus will automatically calculate the amount in the main currency used for managing your Airbnb accounting.

Image of the Exchange Rates table
Image of the Transactions table where to record the income received from Airbnb or similar platform.
Accounting templates with crypto currencies
Accounting with crypto currencies Bitcoin (cash)
Accounting with crypto currencies Bitcoin (cash) tizianaIncome & Expense Accounting with crypto currencies Bitcoin
Income & Expense Accounting with crypto currencies Bitcoin tizianaDouble-Entry Accounting with crypto currencies Bitcoin
Double-Entry Accounting with crypto currencies Bitcoin tizianaDouble-Entry Accounting for digital currencies Bitcoin and Ethereum (Base Currency ETH)
Double-Entry Accounting for digital currencies Bitcoin and Ethereum (Base Currency ETH) tizianaDouble-Entry Accounting for digital currencies Bitcoin and Ethereum (Base currency USD)
Double-Entry Accounting for digital currencies Bitcoin and Ethereum (Base currency USD) tizianaEssential Expense Manager PDF report with embedded receipts
Essential Expense Manager PDF report with embedded receiptsImproving how employee expenses are managed is crucial for all businesses.
Whether employees are traveling for work or working from home, keeping track of their expenses and making sure they get reimbursed correctly has become a complex task.
Banana Accounting expense manager functionality to create a PDF dossier is essential and cost-effective for the majority of small and medium-sized businesses. It helps track expenses, improves transparency and makes it smoother for employees to interact with the company's accounting department.
All in one PDF report with embedded receipts
Banana Accounting create a PDF report with embedded receipts. The PDF file includes everything is necessary for reporting, approval and reimbursement.
- The list of expenses with all information necessary and the link to receipt.
- The report of the categorized expenses, for accounting purposes.
- The scanned receipt's files.
PDF file can embed other files. If you don't know just open this example PDF file and click on the link (look the link icons on the left in the image below), so that the receipt document will directly open (some browser don't show the files, better use Adobe Acrobat Reader that is free to use).
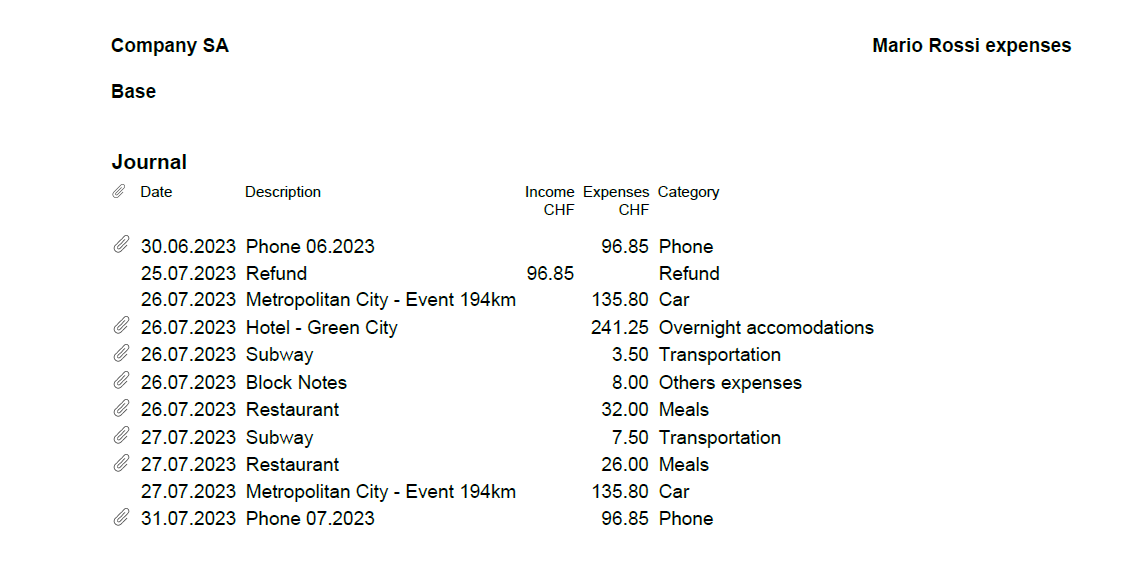
Totally free for up to 70 expense entries
The Banana Accounting template is designed to benefit companies of all sizes. The expense manager template is a software entirely free for up to 70 expense entries, making it a very accessible solution.
How to start
Using this Banana Accounting functionality allows you to obtain your PDF dossier with expenses categorized and embedded in a simple and immediate way:
- Install Banana Accounting
- Open the template file and save to a directory, where you also scan your documents.
- Scan your receipts or invoices (Banana Accounting does not perform the scanning).
- Enter the incurred expenses in the Transaction table and add a Link to the scanned receipt file.
- With File menu > Create Pdf Dossier create the PDF report (check the Include attachments).
- Transmit the file for reimbursement.
Now you'll be ready to send your PDF dossier by email to the accounting department, for approval and reimbursement.
This workflow is essential and cost-effective for the majority of small and medium-sized businesses.
Add the payment methods used by employees
If you wish, you can manage the payment methods used for expenses through the CC3 column.
To enable it, double-click on the column headers in the Transactions table. In the window that opens, on the left, enable the display of the Cc3 column and confirm with the Ok button.
Manage the different payment methods from the Categories table by adding the accounting accounts with a semicolon in front. You can add as many payment methods as you prefer.
Add the quantity columns to manage travel kilometers
To manage travel expenses based on the distance traveled, it could be useful to enable the display of columns related to quantities.
To enable them, double-click on the column headers in the Transactions table. In the window that opens, on the left, enable the display of the columns Quantity, ReferenceUnit, UnitPrice, and confirm with the Ok button.
Remember to enter Unit Price in the Transactions table with a negative sign.
Additional features of the Essential Expense Manager
Easy Expense Logging: the core of this tool is a user-friendly interface. Employees can quickly record their expenses by entering the date, category, amount and payment method. This reduces mistakes and ensures accurate data entry.
Digital Receipts: instead of using paper receipts, the software lets employees attach digital copies of receipts. This prevents losing receipts and keeps expense records secure.
Detailed PDF Reports: the software is great at creating comprehensive expense reports. These reports include all embedded receipts in a single PDF file, which can be easily shared with accountants through email. The reports break down expenses, categories and receipts, promoting transparency.
Customizable Categories: the software lets administrators customize expense categories to fit the company's needs. This ensures that expenses are organized in a way that matches the company's reporting and analysis requirements.
Easy Access: the expense manager can be shared through email, which is helpful for remote employees or those who often travel for work.
Data Privacy: it's important to note that the data entered into Banana Accounting is not used for commercial purposes. Your information remains confidential, offline and is not repurposed in any way.
WooCommerce Products Export-Import [BETA]
WooCommerce Products Export-Import [BETA]WooCommerce extension description
This extension for importing and exporting products sold on WooCommerce online shop simplifies and optimizes the integration between your online store and Banana Accounting software.
The extension either allows the export of products already listed in your inventory from Banana Accounting to your WooCommerce online store, or may become an intuitive and efficient solution to easily allow you to import products directly from your online store into Banana Accounting.
Banana Accounting is superior to Excel, allowing you to swiftly edit product details at any time and it guarantees that the information remains aligned to your online store on WooCommerce.
The Banana Accounting extension offers you the opportunity to export product data already present in your Banana Accounting inventory in a format already prepared for import into WooCommerce. This streamlines the input and/or management of products in your online store, enabling you to maintain coherence and consistency between the two platforms and to begin selling online more seamlessly.
As it is crucial to manage product information accurately and effortlessly in your online store and inventory, this extension allows you to do so in a simple and secure manner. With the export file obtained from the WooCommerce platform, you can easily create your inventory in Banana Accounting or update existing products directly in Banana Accounting to align them with those present on your online store.
Both functions eliminate the need for lengthy and complex manual procedures and reduce the risk of transcription errors, ensuring data accuracy and efficiency.
This solution is suitable for those who want to manage the inventory in a simple way, exporting or importing to WooCommerce whenever they desire. It is not suitable for those looking for a cloud solution that automatically synchronizes warehouse management with WooCommerce.
Banana Accounting key features
Easy: the Banana Accounting software is easy to use and every file can be shared through email, which is helpful for a easy support too.
Privacy: it's important to note that the data entered into Banana Accounting is not used for commercial purposes. Your information remains confidential, offline and is not repurposed in any way.
Beta version
This extension is published in BETA version. We recommend creating a backup copy of the inventory file. Having regular file backups is always useful in any context. This WooCommerce extension require a subscription to Banana Accounting Plus Advanced version.
Primary Key Used
The Id column from Banana's Items table will be exported and used as the primary key for import and it must contain the product's SKU reference of WooCommerce online shop.
Those who already have a warehouse in Banana Accounting can replace the codes in the Id column using the Rename function from Banana's Data menu. This function will automatically replace the Id value even in the Transactions table.
Create/Update products from WooCommerce
The Create/Update products from WooCommerce function will create the products exported from WooCommerce (CSV file format) in the Items table of the inventory in Banana Accounting if they do not exist. If products with the same Id value already exist, it will update the values in the Description, Quantity begin and Unit Price columns in the Items table with the information present in the exported file from WooCommerce.
Export products for WooCommerce
The Export products for WooCommerce function will export data from the Id, Description, Quantity balance and Unit Price columns in the Items table into a CSV file format, ready to be imported into WooCommerce.