在此文中
With Banana Accounting Plus you can use Office Scripts in Excel (the successor of VBA Scripts) to retrieve and display the data of your accounting in Excel.
To read and retrieve data from Banana Accounting with Office Scripts, we use the integrated Banana Web Server.
Prerequisites
To use Office Scripts you need to:
- Download and install Banana Accounting Plus.
- Have the Advanced plan of Banana Accounting Plus.
- Have Excel for Windows (version 2210 or higher) or Excel for Mac.
- Use OneDrive for Business.
Office Scripts files
Office Scripts are written using the TypeScript language. They are stored as .osts files in your Microsoft OneDrive, separately from the Excel file.
For more information visit Office Scripts file storage and ownership.
Configure Banana Accounting Web Server
To read and retrieve data from Banana Accounting with Office Scripts we use the Banana integrated Web Server.
IMPORTANT: To properly configure the Banana Web Server, follow the guide for your operating system:
How to start
- Open Banana Accounting Plus and Configure Banana the Web Server
- Open an accounting file.
- Open an empty Excel file or download the example file from here.
- Select the Automate tab and click on New Script.
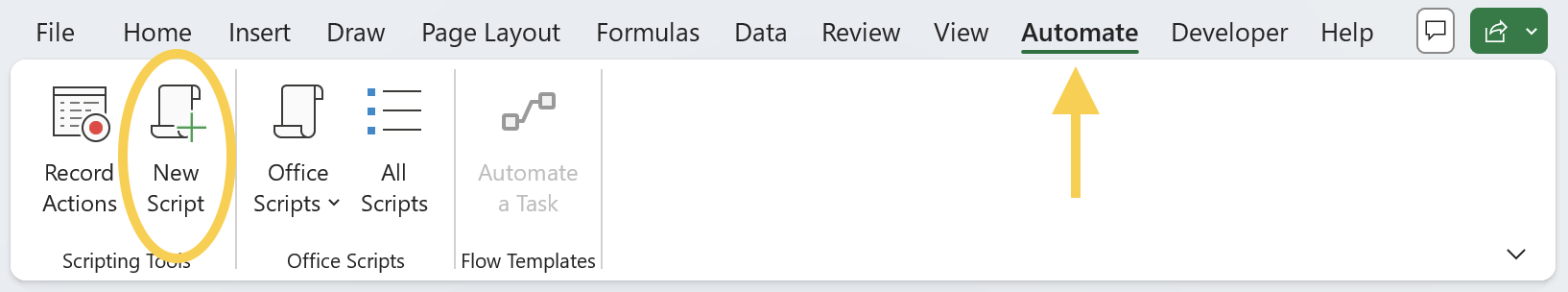
- The Code Editor opens on right side of the Excel window.
- Enter an example code in the Code Editor. If you want to try all the examples, you have to create a new script for each example.
- In the Code Editor delete all the code.
- Copy the code from one of the examples below.
- Paste the copied code in the Code Editor.
- Rename the script as you want.
- Click on Save script .
- Click on Run to run the script.
Note: before running the scripts, set the file name and the server settings.
File Name and Server settings
Define the accounting file name and the server settings (yellow cells). In the Excel file:
- In cell B1, enter the accounting file name (e.g. "company-2024.ac2").
- In cell B2, enter the webserver URL:
- If you are on Windows, enter "http://localhost:8081".
- If you are on macOS, enter "https://127.0.0.1:8089".
- In cell B3, enter the same Access Token key you defined in the httpconfig.ini file during the Configuration Banana Accounting Web Server.
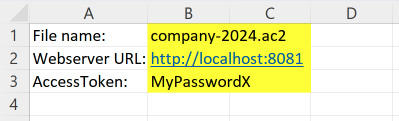
In these examples, we use the B1, B2 and B3 cells to also show how to get a value from a specific cell and use it inside of the Office Script code.
let fileName = sheet.getRange("B1").getValue();
let localhost = sheet.getRange("B2").getValue();
let accessToken = sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
But if you want, you can also enter the file name, the Web Server URL and the Access Token key directly in your Office Script code, without using the B1, B2, and B3 cells.
let fileName = "company-2024.ac2";
let localhost = "http://localhost:8081";
let accessToken = "MyPasswordX";
Example 1: Retrieve data from the table Accounts
This example shows how to retrieve and display the data from the table Accounts.
If the worksheet you are working already contains data, these will be overwritten. Make sure you are in an empty sheet.
To use this script:
- Copy the following script code.
- Paste the script in the Code Editor.
- Save and Run the script.
Note: before running the scripts, set the file name and the server settings.
When you run the script:
- The data of the table Accounts are displayed on the current worksheet.
- If the worksheet you are working already contains data, these will be overwritten.
Script code:
/**
* This example retrieves all the Accounts table.
*
* In order to connect to the Banana Web Server, define some information:
* - Cell B1 the accounting file name
* - Cell B2 the localhost web server url
* - Cell B3 the accessToken security password
*
* You can get these information from cells of the worksheet or you can define them in the script.
* In this example we get the information from the cells B1, B2, B3.
*/
async function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
// Get the current active worksheet
let sheet = workbook.getActiveWorksheet();
// Get the cell values
let fileName = sheet.getRange("B1").getValue();
let localhost = sheet.getRange("B2").getValue();
let accessToken = sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
// Retrieve JSON data of table Accounts from Banana Web Server.
let fetchResult = await fetch(localhost + '/v1/doc/' + fileName + '/table/Accounts?view=Base&format=json&acstkn=' + accessToken);
// Convert the returned data to the expected JSON structure.
let json: JSONData = await fetchResult.json();
// Display the content in a readable format.
console.log(JSON.stringify(json));
// Write columns headers texts on the row 6
let row = 6;
let col = sheet.getRange('A' + row);
col.setValue([['Group']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('B' + row);
col.setValue([['Account']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('C' + row);
col.setValue([['Description']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('D' + row);
col.setValue([['Opening']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('E' + row);
col.setValue([['Balance']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
// Write table Accounts data from the row 7
row = 7;
for (let i in json) {
let col = sheet.getRange('A' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].Group);
col = sheet.getRange('B' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].Account);
col = sheet.getRange('C' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].Description);
col = sheet.getRange('D' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].Opening);
col = sheet.getRange('E' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].Balance);
// increase row
row++;
}
}
// Json structure of table Accounts
interface JSONData {
Section: string;
Group: string;
Account: string;
Description: string;
BClass: number;
Gr: string;
Opening: number;
Balance: number;
}
/* Complete list of columns
SysCod,Links,Section,Group,Account,Description,Notes,Disable,VatCode,GrVat,VatNumber,FiscalNumber,BClass,Gr,Gr1,Gr2,Opening,Debit,Credit,Balance,Budget,BudgetDifference,Prior,PriorDifference,BudgetPrior,PeriodBegin,PeriodDebit,PeriodCredit,PeriodTotal,PeriodEnd,NamePrefix,FirstName,FamilyName,OrganisationName,Street,AddressExtra,POBox,PostalCode,Locality,Region,Country,CountryCode,LanguageCode,PhoneMain,PhoneMobile,Fax,EmailWork,Website,DateOfBirth,PaymentTermInDays,CreditLimit,MemberFee,BankName,BankIban,BankAccount,BankClearing,Code1
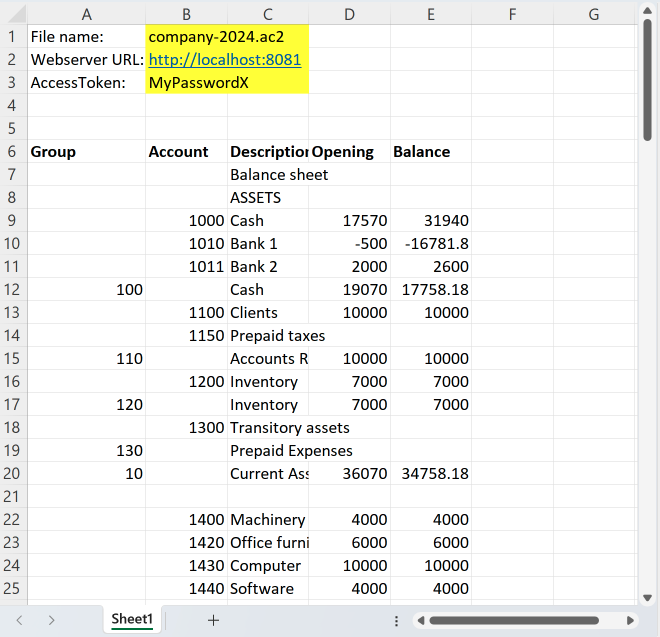
*/After running the script, the result is the following:
Example 2: Retrieve Transactions from the Journal
This example shows how to use the Banana Journal to get all the data, and from that retrieve only the Transactions rows.
The Banana Accounting Journal contains the Transactions Data with one row for each account. It can be useful for creating pivot tables.
If the worksheet you are working already contains data, these will be overwritten. Make sure you are in an empty sheet.
To use this script:
- Copy the following script code.
- Paste the script in the Code Editor.
- Save and Run the script.
Note: before running the scripts, set the file name and the server settings.
When you run the script:
- The transactions rows of the Journal are displayed.
- If the worksheet you are working already contains data, these will be overwritten.
Script code:
/**
* This example retrieves all the Transactions rows from the Journal
*
* In order to connect to the Banana Web Server, define some information:
* - Cell B1 the accounting file name
* - Cell B2 the localhost web server url
* - Cell B3 the accessToken security password
*
* You can get these information from cells of the worksheet or you can define them in the script.
* In this example we get the information from the cells B1, B2, B3.
*/
async function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
// Get the current active worksheet
let sheet = workbook.getActiveWorksheet();
// Get the cell values
let fileName = sheet.getRange("B1").getValue();
let localhost = sheet.getRange("B2").getValue();
let accessToken = sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
// Retrieve JSON data of the journal from Banana Web Server
let fetchResult = await fetch(localhost + '/v1/doc/' + fileName + '/journal?format=json&acstkn=' + accessToken);
// Convert the returned data to the expected JSON structure.
let json: JSONData = await fetchResult.json();
// Display the content in a readable format.
console.log(JSON.stringify(json));
// Write columns headers texts on the row 6
let row = 6;
let col = sheet.getRange('A' + row);
col.setValue([['JDate']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
//col.getFormat().getFont().setColor("black");
//col.getFormat().getFill().setColor("yellow");
col = sheet.getRange('B' + row);
col.setValue([['Doc']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('C' + row);
col.setValue([['JDescription']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('D' + row);
col.setValue([['JAccount']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('E' + row);
col.setValue([['JContraAccount']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('F' + row);
col.setValue([['JOperationType']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('G' + row);
col.setValue([['JDebitAmount']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('H' + row);
col.setValue([['JCreditAmount']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('I' + row);
col.setValue([['JAmount']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('J' + row);
col.setValue([['JVatCodeWithoutSign']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('K' + row);
col.setValue([['VatRate']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('L' + row);
col.setValue([['JVatTaxable']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('M' + row);
col.setValue([['JSegment1']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
col = sheet.getRange('N' + row);
col.setValue([['JSegment2']]);
col.getFormat().getFont().setBold(true);
// Write the transactions rows data from the row 7
row = 7;
for (let i in json) {
if (json[i].JOperationType === "3") { // JOperationType=3 are rows from table Transactions
let col = sheet.getRange('A' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JDate);
col = sheet.getRange('B' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].Doc);
col = sheet.getRange('C' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JDescription);
col = sheet.getRange('D' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JAccount);
col = sheet.getRange('E' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JContraAccount);
col = sheet.getRange('F' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JOperationType);
col = sheet.getRange('G' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JDebitAmount);
col = sheet.getRange('H' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JCreditAmount);
col = sheet.getRange('I' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JAmount);
col = sheet.getRange('J' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JVatCodeWithoutSign);
col = sheet.getRange('K' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].VatRate);
col = sheet.getRange('L' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JVatTaxable);
col = sheet.getRange('M' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JSegment1);
col = sheet.getRange('N' + row);
col.setValue(json[i].JSegment2);
// increase row
row++;
}
}
}
// JSON structure of the Journal
interface JSONData {
JDate: string;
Doc: string;
JDescription: string;
JAccount: string;
JContraAccount: string;
JOperationType: number;
JDebitAmount: number;
JCreditAmount: number;
JAmount: number;
JVatCodeWithoutSign: string;
VatRate: number;
JVatTaxable: number;
JSegment1: string;
JSegment2: string;
}
/* Complete list of journal
SysCod, Section, Date, DateDocument, DateValue, Doc, DocProtocol, DocType, DocOriginal, DocInvoice, InvoicePrinted, DocLink, ExternalReference, Description, Notes, AccountDebit, AccountDebitDes, AccountCredit, AccountCreditDes, Amount, Balance, VatCode, VatAmountType, VatExtraInfo, VatRate, VatRateEffective, VatTaxable, VatAmount, VatAccount, VatAccountDes, VatPercentNonDeductible, VatNonDeductible, VatPosted, VatNumber, Cc1, Cc1Des, Cc2, Cc2Des, Cc3, Cc3Des, Segment, DateExpiration, DateExpected, DatePayment, LockNumber, LockAmount, LockProgressive, LockLine, JDate, JDescription, JTableOrigin, JRowOrigin, JRepeatNumber, JGroup, JGr, JAccount, JAccountComplete, JAccountDescription, JAccountClass, JAccountSection, JAccountType, JOriginType, JOriginFile, JOperationType, JAccountGr, JAccountGrPath, JAccountGrDescription, JAccountCurrency, JAmountAccountCurrency, JAmount, JTransactionCurrency, JAmountTransactionCurrency, JTransactionCurrencyConversionRate, JAmountSection, JVatIsVatOperation, JVatCodeWithoutSign, JVatCodeDescription, JVatCodeWithMinus, JVatNegative, JVatTaxable, JContraAccount, JCContraAccountDes, JContraAccountType, JContraAccountGroup, JCC1, JCC2, JCC3, JSegment1, JSegment2, JSegment3, JSegment4, JSegment5, JSegment6, JSegment7, JSegment8, JSegment9, JSegment10, JDebitAmountAccountCurrency, JCreditAmountAccountCurrency, JBalanceAccountCurrency, JDebitAmount, JCreditAmount, JBalance, JInvoiceDocType, JInvoiceAccountId, JInvoiceCurrency, JInvoiceStatus, JInvoiceDueDate, JInvoiceDaysPastDue, JInvoiceLastReminder, JInvoiceLastReminderDate, JInvoiceIssueDate, JInvoiceExpectedDate, JInvoicePaymentDate, JInvoiceDuePeriod, JInvoiceRowCustomerSupplier, ProbableIndexGroup, VatTwinAccount, DateEnd, Repeat, Variant, ForNewYear, ItemsId, Quantity, ReferenceUnit, UnitPrice, FormulaBegin, Formula, AmountTotal
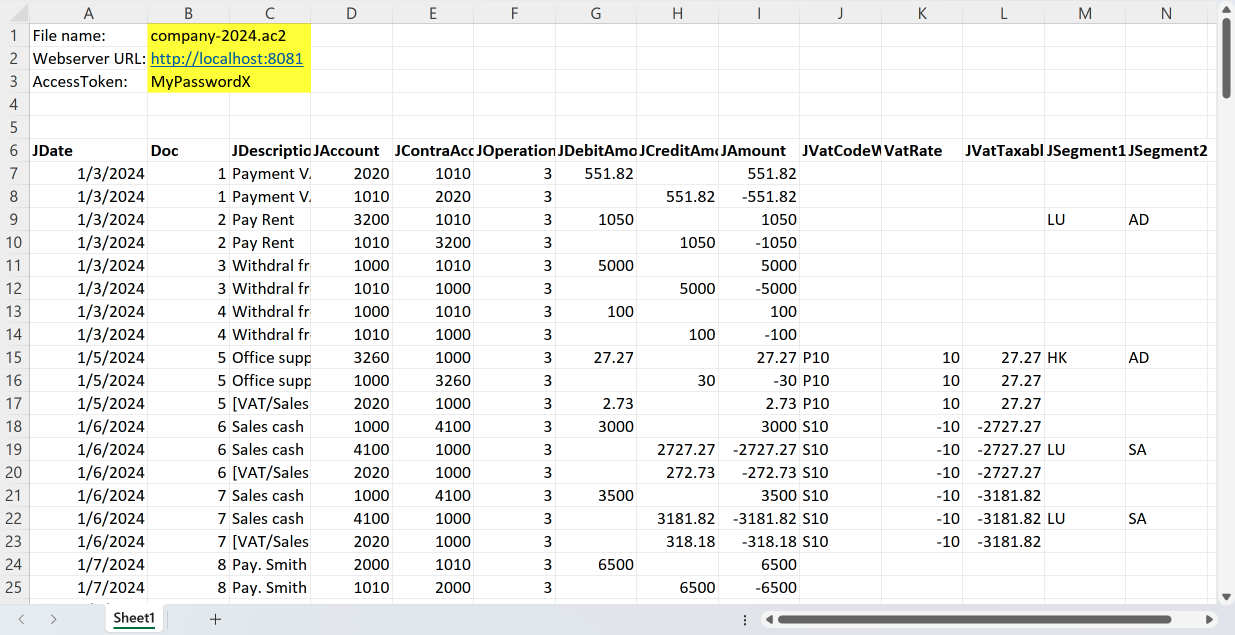
*/After running the script, the result is the following:
Example 3: Create a new accounting file using data from Excel Sheets
For following this example you can download a Excel file that content some data of transactions and accounts.
Download Excel file with transaction and accounts
In this example we want to:
- Create a new Banana Accounting file using the web server Create a new file functionality.
- Take some transactions data from Excel.
For this example, transactions in Excel are entered as shown in the following image: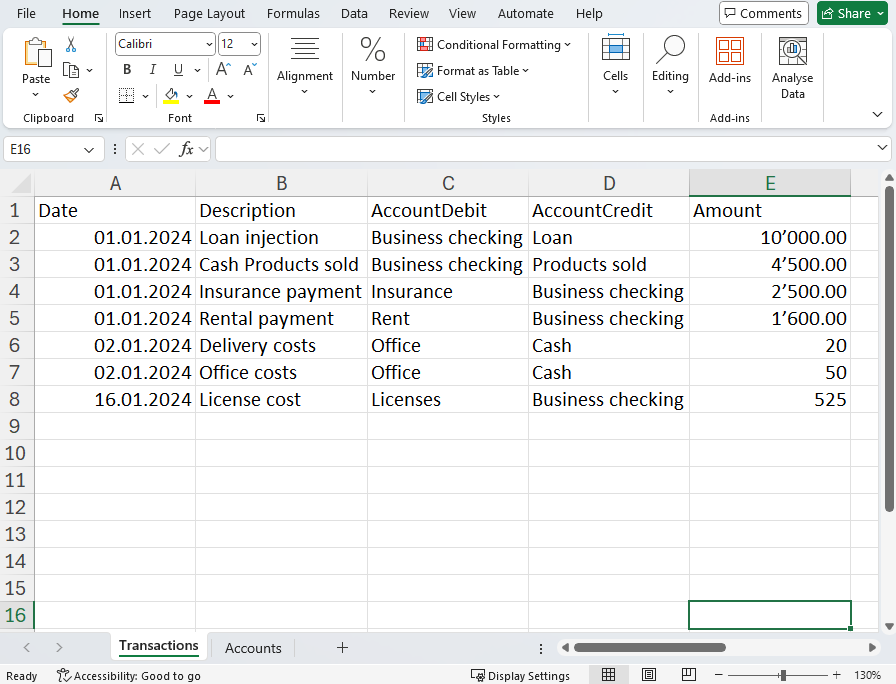
- Take some accounts and descriptions data from Excel.
Accounts can be numbers or texts.
The BClass columns set the type of account (1=assets, 2=liabilities, 3=expenses, 4=revenues).
For this example, accounts in Excel are entered as shown in the following image.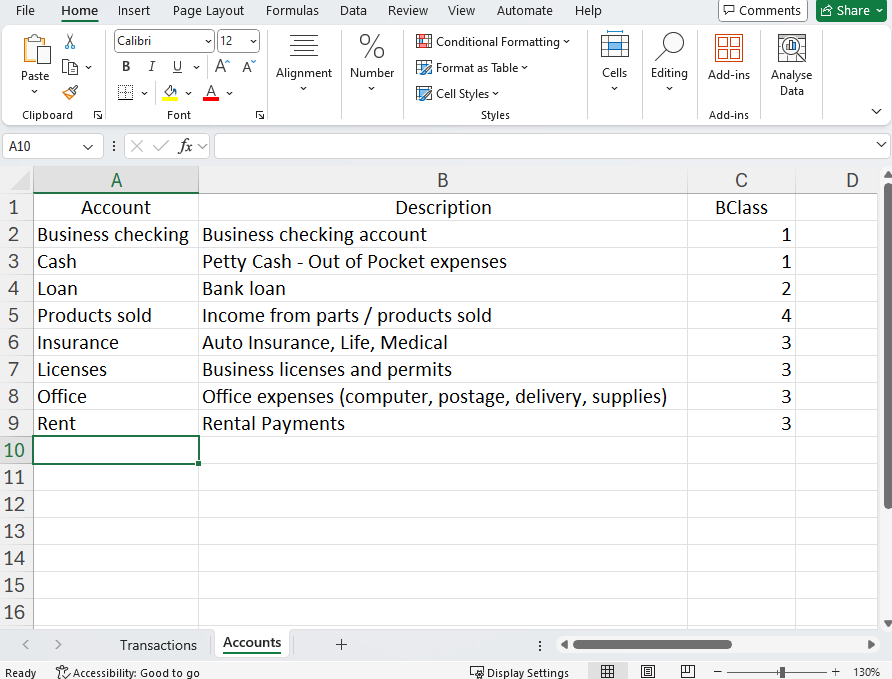
- Create a specific JSON used by the Document change API to add the the data in the accounting file.
We use the add Rows operation to append the transactions to the Transactions table and accounts to the Accounts table.
To use this script:
- Open Banana Accounting Plus and Configure Banana the Web Server.
- Copy the following script code.
- Paste the script in the Code Editor.
- Save and Run the script.
When you run the script:
- The script creates a new Banana Accounting file.
- The Excel transactions rows are added to the Transactions table in the accounting file.
- The Excel accounts rows are added to the Accounts table in the accounting file.
Script code:
async function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
// Get the specific sheet
const sheetTransactions = workbook.getWorksheet("Transactions");
const sheetAccount = workbook.getWorksheet("Accounts");
// Get the range of cells used in the sheet
const usedRangeTransactions = sheetTransactions.getUsedRange();
const usedRangeAccounts = sheetAccount.getUsedRange();
// Get the last used row of the sheet
const lastRowTransactions = usedRangeTransactions.getLastRow().getRowIndex();
const lastRowAccounts = usedRangeAccounts.getLastRow().getRowIndex();
// TRANSACTIONS
const dateRange = sheetTransactions.getRange(`A2:A${lastRowTransactions + 1}`).getValues(); // From line 2 (skip header)
const descriptionRange = sheetTransactions.getRange(`B2:B${lastRowTransactions + 1}`).getValues();
const accountDebitRange = sheetTransactions.getRange(`C2:C${lastRowTransactions + 1}`).getValues();
const accountCreditRange = sheetTransactions.getRange(`D2:D${lastRowTransactions + 1}`).getValues();
const amountRange = sheetTransactions.getRange(`E2:E${lastRowTransactions + 1}`).getValues();
// ACCOUNTS
const accountRange = sheetAccount.getRange(`A2:A${lastRowAccounts + 1}`).getValues();
const descRange = sheetAccount.getRange(`B2:B${lastRowAccounts + 1}`).getValues();
const bclassRange = sheetAccount.getRange(`C2:C${lastRowAccounts + 1}`).getValues();
// Initialize JSON structure.
// The JSON is used by the documentChange to add rows in Transactions table
// https://www.banana.ch/doc/en/node/9841#example_adding_a_row+ var jsonData = {
"format": "documentChange",
"error": "",
"data": [
{
"document": {
"dataUnits": [
{
"data": {
"rowLists": [
{
"rows": []
}
]
},
"nameXml": "Transactions"
},
{
"data": {
"rowLists": [
{
"rows": []
}
]
},
"nameXml": "Accounts"
}
]
}
}
]
};
// TRANSACTIONS: Iteration on each row of the columns.
for (let i = 0; i < dateRange.length; i++) {
let dateValue = dateRange[i][0]; // Value of column A (Date)
let descriptionValue = descriptionRange[i][0]; // Value of column B (Description)
let accountDebitValue = accountDebitRange[i][0]; // Value of column C (AccountDebit)
let accountCreditValue = accountCreditRange[i][0]; // Value of column D (AccountCredit)
let amountValue = amountRange[i][0]; // Value of column E (Amount)
// adds "fields" object to "rows"
jsonData.data[0].document.dataUnits[0].data.rowLists[0].rows.push({
"fields": {
"Date": formatDateToYyyyMmDd(Number(dateValue)),
"Description": descriptionValue,
"AccountDebit": accountDebitValue,
"AccountCredit": accountCreditValue,
"Amount": amountValue.toString()
},
"operation": {
"name": "add"
}
});
}
// ACCOUNTS: Iteration on each row of the columns.
for (let i = 0; i < accountRange.length; i++) {
let accountValue = accountRange[i][0]; // Value of column A (Account)
let descValue = descRange[i][0]; // Value of column B (Description)
let bclassValue = bclassRange[i][0]; // Value of column C (BClass)
// adds "fields" object to "rows"
jsonData.data[0].document.dataUnits[1].data.rowLists[0].rows.push({
"fields": {
"Section": "",
"Group": "",
"Account": accountValue.toString(),
"Description": descValue.toString(),
"BClass": bclassValue.toString(),
"Gr": ""
},
"operation": {
"name": "add"
}
});
}
let jsonString = JSON.stringify(jsonData);
//console.log(jsonString);
createAc2(JSON.parse(jsonString));
}
async function createAc2(jsonData: JSON) {
// Web server url
let _LOCALHOST = "http://localhost:8081"; //for macOS use "https://127.0.0.1:8089";
// Web server password
let _PASSWORD = "MyPasswordX";
// Request to Banana web server
let url = _LOCALHOST + "/v2/doc?show&acstkn=" + _PASSWORD;
// Accounting type parameters
let fileTypeGroup = 100; // Double entry accounting
let fileTypeNumber = 100; // without VAT
let fileDecimals = 2;
try {
// Body of the request
const httpBody = {
fileType: {
accountingType: {
docGroup: fileTypeGroup,
docApp: fileTypeNumber,
decimals: fileDecimals
}
},
data: jsonData,
}
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(httpBody)
});
//const responseData: string = await response.text();
//console.log(responseData);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}
// Convert Date type of Excel in yyyy-mm-dd string format
function formatDateToYyyyMmDd(date: number): string {
let dateString = new Date(Math.round((date - 25569) * 86400 * 1000)).toISOString().split("T")[0];
return dateString;
}Accounting type parameters "_DOC_GROUP" and "_DOC_APP" define the type of accounting to create. For more information please visit the @doctype Attributes page.