Transactions
Explanations of the columns
In the Transactions Table of the multi-currency accounting, other than the columns of the double-entry accounting, there are the following extra columns:
- Currency amount
This is the amount of the currency specified in the column with the currency symbol.
This amount is used by the program to update the balance of the related account in currency. - Currency
This is the currency symbol of the currency to which the amount refers.
The currency symbol has to be the Basic currency, specified in the File and accounting properties, or the currency symbol of an annount indicated in the columns Debit A/C or Credit A/C.You can also use a different currency as long as the indicated Debit A/C and the Credit A/C are Basic currency accounts.In this case the amount in currency is used as a reference, but will not be used for accounting purposes - Exchange rate
Used to convert the foreign currency amount in its Basic currency equivalent. - Amount in Basic currency
The transaction amount, expressed in Basic currency.
This amount is used by the program to update the balance of the related account in Basic currency - Exchange rate multiplier
Normally not visible in the view, this value is multiplied by the exchange rate.
Types of entries in the multicurrency accounting
Please note
All amounts, those in basic currency as well as those in foreign currency, have to always be entered into the Currency Amount column.
For each transaction, there are two accounts (debit account and credit account). In the program, only one foreign curency per transaction row can be used. So there can be the following direct combinations:
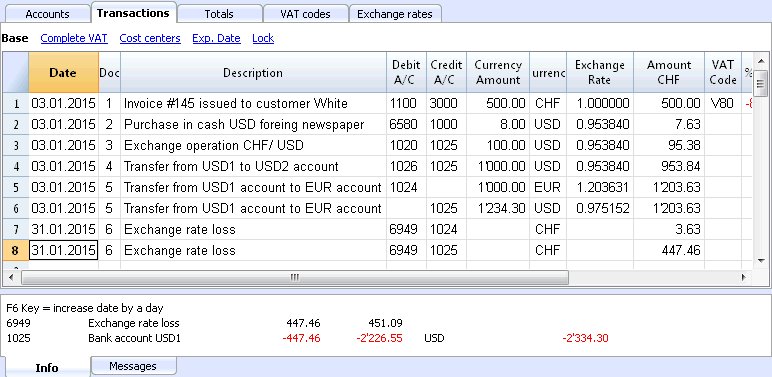
- Entries between two accounts in basic currency with the amount in basic currency. (in the image, transactions n.1 in the Doc column)
The account currency is the basic currency. - Entries between two accounts in basic currency with the amount in foreign currency (Doc 2)
The indicated accounts are in basic currency, but the currency symbol and the amount in currency, indicated in the transaction row, are not in basic currency, but in a different currency.To insert the different currency, the user has to manually change the currency symbol.This is being used when one goes abroad and money is being changed in order to pay in local currency. In this case we do not have a specific account.For the calculation of the balance (both accounts being in basic currency) only the amount of basic currency column is being used. - Entries between an account in foreign currency and one in basic currency (Doc 3)
The currency needs to be the one of the account in foreign currency.
For the calculation of the balance of the account in foreign currency, the program uses the amount in foreign currency and for the balance in basic currency, the program uses the amount in basic currency. - Entries between two accounts with the same foreign currency (Doc 4)
The currency needs to be the same as account currency of both accounts. - Entries with two accounts in different foreign currencies (Doc 5)
For example, the bank makes an exchange operation between two foreign currencies:
In this case, the transaction needs to be recorded on two rows.
The amount in basic currency needs to be the same. It is useful to use an amount close to the current exchange rate to avoid excessive exchange rate differences.
In order for the amounts in basic currency to be equal, the amount in basic currency needs to be indicated manually, and the program will calculate the exchange rate. - Exchange rate differences (Doc 6)
The goal of this transaction is to realign the balance of the Basic currency account with the equivalent of the Foreign currency account at today's exchange rate.
On the Foreign currency account, only the amount in Basic currency related to the exchange rate differences is being recorded.
They are automatically generated with the Create transaction for exchange rate variation command.- For the exchange rate profits, the program automatically indicates the account to be revaluated in debit and the exchange rate profit account in credit. The exchange rate profit account is indicated in the File and Accounting properties (Basic Data), or in the specified account -> Exchange rate differences account column of the "Other" view (intended for one or several specific accounts).
- For the exchange rate losses, the program automatically indicates the account to be revaluated in credit and the exchange rate loss account in debit. The exchange rate loss account is indicated in the File and Accounting properties (Basic Data), or in the specified account -> Exchange rate differences account column of the "Other" view (intended for one or several specific accounts).
- The Currency amount is being left empty
- The Curency symbol is the basic currency
- In the Basic currency amount column, the amount of the revaluation of the account (profit or loss) is being indicated.
Establishing the exchange rate
The accountant is the one who decides which exchange rate to use for each single operation. Generally, the following rusles are being applied:
- For normal operations, the exchange rate of the day is being used
- For buying or selling currency, the values indicated by a money exchange office or a bank are being used.
First the amount in foreign currency is being indicated in the program and then the amount in basic currency. The program calculates the exchange rate. The exchange rate indicated by the bank can be slightly different, because banks specify exchange rates with few figures after the decimal point and often round the amounts. - When several operations with the same exchange rate are being recorded, it is useful to update the exchange rate in the Exchange rate table, so that the program can automatically apply it.
- For operations from abroad that are subject to VAT, the national authority might impose a standard exchange rate. In this case, that exchange rate should be inserted in the Exchange rate column of the transaction
- To purchase real estate or equity investments, an historical exchange rate is being used. In that case, a currency symbol needs to be created in the Exchange rate table (for example USD1) with an historical exchange rate, that is not being subject to the fluctuations of the exchange rate.
One can create as many currency symbols as desired for all historical exchange rates.
Transactions with VAT
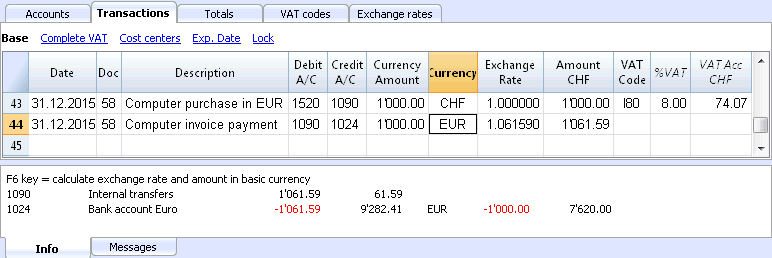
The VAT account and the account from which the VAT is being deducted have to be in basic currency. It is impossible to use a VAT code to deduct the VAT from a foreign currency account. In order to record operations with VAT that have accounts in foreign currency as their counterpart, two transaction rows have to be used:
- First, the amount of the purchase is being recorded on an Internal transfers account in basic currency and the related VAT code is being applied. The amount in basic currency has to be calculated using an exchange rate in accordance with the requirements of the Tax administration.
- In a second row, the balance of the Internal transfers account is being put to zero; as its counterpart, the account in foreign currency should be entered.
The amount used for this transaction, both in basic currency and in foreign currency, has to be excluding VAT. Obviously, the exchange rate that has to be used is the same one as the one being used in the preceding transaction.
In the example, the basic currency is the CHF. We are dealing with a national purchase, but paid from a foreign curency account (EUR).
Automatisms while entering multicurrency transactions
When a new transaction is being entered, the data in the above mentioned columns have to be completed.
When some values of the transaction row are modified, the program completes the transaction with the predefined values. If these values do not satisfy the user's requirements, these have to be modified in the transaction row.
The modification of the values in the Exchange rate table have no effect on already entered transaction rows. Thus, when the exchange rate in the Exchange rate table is modified, this has no influence whatsoever on already inserted transactions.
- When the amount in currency is entered and there is either a Debit A/C or a Credit A/C, and no other values are entered, the program operates as follows:
- the currency symbol is retrieved from the account in use, giving priority to the account that is not in basic currency;
- the exchange rate, defined in the Exchange rate table, is applied with the following logic:
- the historical exchange rate is applied, with a date earlier or equal to the transaction date
- tf there is no historical exchange rate to be found, the exchange rate from the row without date is applied.
- the multiplier, defined in the Exchange rate table, is applied or the number 1 if it is the basic currency;
- the amount in basic currency is calculated.
- When the amount in currency is modified (and there are already other values present), the program operates as follows:
- the amount in basic currency is calculated with the existing exchange rate
- If the currency symbol is modified the program operates as follows:
- the exchange rate with the multiplier is applied and the amount in basic currency is calculated (like above)
- If the exchange rate is modified the program operates as follows:
- the amount in basic currency is calculated using the entered exchange rate
- When the amount in basic currency is modified the program operates as follows:
- the exchange rate is recalculated.
More help
- While being positioned on the Currency Amount column and pressing the F6 key, the program rewrites all values with the earlier explained logic, as if there were no values present. This feature is useful when the Debit A/C or the Credit A/C is modified.
- If there is a registration with a single account in basis currency (in 'Multiple transcations' - see Transaction types) and its value of the column 'Currency' has been changed manualy in a currency symbol of a foreign currency, it is necessary to be positioned on the cell of the column 'Currency' and press the F6 key in order to update the Exchange rate and calculate the amount in basis currency.
- Smart fill for the Exchange rate column
The program suggests several exchange rates, picking them up from the Exchange rates table or from exchange rates previously used in the transactions.
Info window
In the info window, the program indicates:
- Differences, if any, between the Debit and Credit total movements in baskic currency
- Explanation on the different uses of the F6 key
For the accounts related to the transaction row on which one is positioned, the program always indicates in the Info windows:
- the account number
- the account description
- the transaction's amount in basic currency
- the current account balance in basic currency
- the account currency symbol
- the transaction's amount in the account currency (if different from the basic currency)
- the current account balance in currency (if different from the basic currency)
Data transfer from earlier versions
In version 4 or earlier, the absence of a currency symbol in the Transactions table was being interpreted as a transaction in basic currency.
In version 7 and in version 8, each transaction needs to have its own currency symbol. Therefore, when you update from version 4 to version 7 or 8, in the accounting file, the transactions without a currency symbol need to be completed.
Exchange rate differences
At the latest when the accounting period is being closed, the currencies need to revaluated in Basic currency, creating adjustment transactions for exchange rate loss or gain, due to the fluctuations of the exchange rates (for the theoretical aspects, please check Revaluations and exchange rate differences).
The Create transaction for exchange rate variation... command, from the Account2 menu, calculates the revaluations for the foreign currencies accounts.
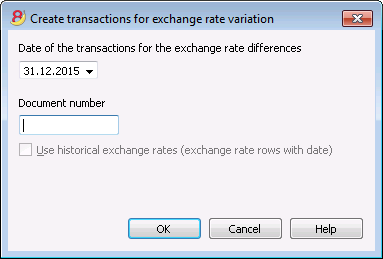
Date of the transactions for the exchange rate differences
Enter the date your exchange rate differences transactions should have.
The program will suggest the final date of the current month, related to the last entered transaction.
If there are transactions for exchange rate differences with the same date, the program asks whether they should be replaced.
The program considers the transactions for the exchange rates differences as existing if they have the same date, doc, description, accounts and currency and when there is no amount in the account currency.
Document number
Enter the document number your exchange rate differences transactions should have.
Use historical exchange rates (exchange rate rows with date)
For the calculation of the exchange rate differences, the program uses the exchange rates of the Exchange rate table without a date (the most recent exchange rates). With the option Use historical Exchange rates, the program instead uses the exchange rates of the Exchange rate table with an equal or earlier date than the one indicated.
Values used to create the transactions
For more information, we refer to our page Multi-currency transactions.
Amount of the transaction
- Transactions for exchange rate differences are being created only for the accounts in foreign currency which, at the specified date, have a different balance in basic currency compared to the calculated one.
- For the amount in basic currency, the difference between the account balance in basic currency and the account balance in foreign currency converted in basic currency is being used.
Account balance
For the calculation of the exchange rate differences, the balances in the account currency and in basic currency are being used, at the specified date.
Exchange rate profit and exchange rate loss accounts
As exchange rate profit and loss accounts are being used, in order of priority:
- The indicated accounts entered in the specific column of the chart of accounts.
- The exchange rate profit & loss accounts indicated in the File and Accounting properties.
Position of inserted rows
If, while imparting the command, you find yourself in the Transactions table, the rows are being inserted at the position of the cursor.
Otherwise, they will be inserted at the end or at the previous position in case they are replacing existing transactions.
Before using the command
- In the File and Accounting properties of the File menu, Foreign Currency section, make sure that the Exchange rate profit and loss accounts are being indicated. It is equally possible to indicate the same account for both the exchange rate profits or losses.
- Make sure that the accounts in foreign currency are being updated and that the balances in foreign currency of these accounts (for exemple bank accounts) correspond with the balance indicated by the bank.
- Update the current exchange rates of the Exchange rate table.
You should indicate the closing exchange rates or those of a period's end in the rows without a date, in the Exchange Rate column (do not modify the opening exchange rate in the Rate Opening column). In order to calculate the Exchange rate differences, the program uses the exchange rates of the rows without a date. If these last ones are absent, the program gives an error message.
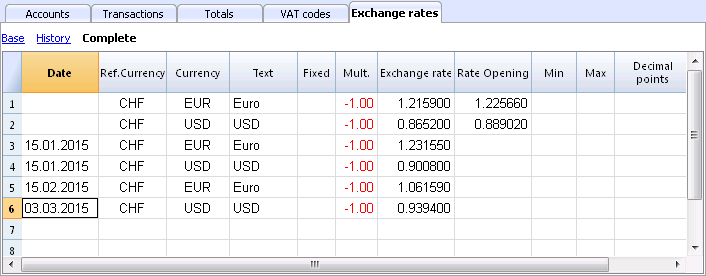
Exchange rates for the New Year
To have the Opening balances of the New Year in Basic currency correspond exactly with the closing balances of the preceding year, the Opening Exchange rates of the New Year, indicated in the Exchange Rate table, have to be the same as those being used for the closing of the accounting, so:
- The closing exchange rates have to be indicated in the Exchange rate column of the rows without a date;
- The opening exchange rates have to be indicated in the Rate Opening columns of the roes without a date.
The procedure of creating a new year or of the updating of the opening balances, copies the closing balances (Exchange rate column, rows without date) of the previous year into the opening exchange rates (Exchange rate table, Rate Opening column, rows without date) of the new year's file.